Difference between revisions of "2020 AIME II Problems/Problem 4"
(→Solution 7) |
m (→Solution) |
||
| (8 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
==Solution== | ==Solution== | ||
| − | After sketching, it is clear a <math>90^{\circ}</math> rotation is done about <math>(x,y)</math>. Looking between <math>A</math> and <math>A'</math>, <math>x+y=18 | + | After sketching, it is clear a <math>90^{\circ}</math> rotation is done about <math>(x,y)</math>. Looking between <math>A</math> and <math>A'</math>, <math>x+y=18</math>. Thus <math>90+18=\boxed{108}</math>. |
~mn28407 | ~mn28407 | ||
| Line 81: | Line 81: | ||
==Solution 6== | ==Solution 6== | ||
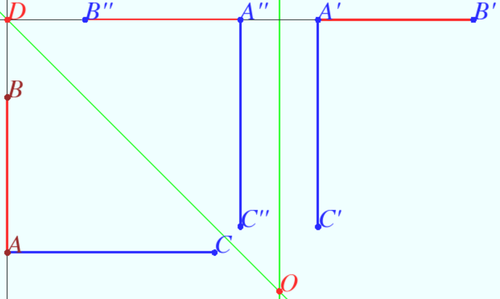
| − | [[File:2020 AIME II 4.png| | + | [[File:2020 AIME II 4.png|500px|right]] |
We make transformation of line <math>AB</math> into line <math>A'B'</math> using axes symmetry. Point <math>D(0,18)</math> is the crosspoint of this lines. Equation of line <math>DO</math> is | We make transformation of line <math>AB</math> into line <math>A'B'</math> using axes symmetry. Point <math>D(0,18)</math> is the crosspoint of this lines. Equation of line <math>DO</math> is | ||
<cmath>x + y = 18.</cmath> | <cmath>x + y = 18.</cmath> | ||
| − | <math>\triangle ABC</math> maps into <math>\triangle A''B''C''</math> where < | + | <math>\triangle ABC</math> maps into <math>\triangle A''B''C''</math> where <cmath>A''(18,18), B''(6,18), C''(18,2).</cmath> |
| − | We make transform of the line <math>A''C''</math> into line <math>A'C'</math> using axes symmetry with respect to line <cmath>x = \frac {A'' + A'}{2} = \frac {24 + 18}{2} = 21.</cmath> | + | We make transform of the line <math>A''C''</math> into line <math>A'C'</math> using axes symmetry with respect to line |
| + | <cmath>x = \frac {A'' + A'}{2} = \frac {24 + 18}{2} = 21.</cmath> | ||
The composition of two axial symmetries is a rotation through an angle twice as large as the angle between the axes <math>(45^o)</math> around the point of their intersection <math>O(21, – 3).</math> | The composition of two axial symmetries is a rotation through an angle twice as large as the angle between the axes <math>(45^o)</math> around the point of their intersection <math>O(21, – 3).</math> | ||
<cmath>m + x + y = 90 + 21 – 3 = \boxed {108}</cmath>. | <cmath>m + x + y = 90 + 21 – 3 = \boxed {108}</cmath>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Solution 7 (Matrix and Transformations)== | ||
| + | For a matrix to rotate a figure on a coordinate plane by <math>m</math> degrees, it is written as: | ||
| + | <math>\left[ {\begin{array}{cc} | ||
| + | cos(m^{\circ}) & sin(m^{\circ}) \ | ||
| + | -sin(m^{\circ}) & cos(m^{\circ}) \ | ||
| + | \end{array} } \right]</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | We can translate the whole figure so that the centre of rotation is at <math>(0,0)</math>, which is equivalent to subtracting <math>x</math> and <math>y</math> from all <math>x</math>-coordinates and the <math>y</math>-coordinates respectively of the given points. | ||
| + | |||
| + | We then record all the points <math>A</math>, <math>B</math>, <math>C</math> in a matrix as follows: | ||
| + | <math>\left[ {\begin{array}{ccc} | ||
| + | 0-x & 0-x & 16-x \ | ||
| + | 0-y & 12-y & 0-y \ | ||
| + | \end{array} } \right]</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | and all the points <math>A'</math>, <math>B'</math>, <math>C'</math> in a matrix as follows: | ||
| + | <math>\left[ {\begin{array}{ccc} | ||
| + | 24-x & 36-x & 24-x \ | ||
| + | 18-y & 18-y & 2-y \ | ||
| + | \end{array} } \right]</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Since <math>\triangle A'B'C'</math> is a rotation around <math>(x,y)</math> of <math>\triangle ABC</math> by <math>m^{\circ}</math>, by the left multiplication rule, we can equate that: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\left[ {\begin{array}{cc} | ||
| + | cos(m^{\circ}) & sin(m^{\circ}) \ | ||
| + | -sin(m^{\circ}) & cos(m^{\circ}) \ | ||
| + | \end{array} } \right]</math> | ||
| + | <math>\left[ {\begin{array}{ccc} | ||
| + | 0-x & 0-x & 16-x \ | ||
| + | 0-y & 12-y & 0-y \ | ||
| + | \end{array} } \right]</math> | ||
| + | <math>=</math> | ||
| + | <math>\left[ {\begin{array}{ccc} | ||
| + | 24-x & 36-x & 24-x \ | ||
| + | 18-y & 18-y & 2-y \ | ||
| + | \end{array} } \right]</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | We can obtain the follow equations: | ||
| + | <math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | From the first 2 equations, we get <math>m=90</math>, substituting into the 3rd equation, we get <math>x+y=18</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Therefore, <math>m+x+y=90+18=\boxed{108}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ~VitalsBat | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Solution 8== | ||
| + | |||
| + | It is clear that <math>\bigtriangleup CPC'</math> is a <math>45-45-90</math> right triangle so <math>m=90</math>. We use the <math>\tan</math> angle formula, <math>\tan{(a-b)}=\frac{\tan(a)-\tan(b)}{1+\tan(a)\tan(b)}</math> to find the slope of line <math>CP</math>. We know that line <math>CC'</math> has slope <math>\frac{1}{4}</math> and let <math>b=-45^{\circ}</math>, then plugging both values into the formula, we find that the slope of <math>CP</math> is <math>\frac{-3}{5}</math>. Also, <math>CC'</math> has length <math>\sqrt{34}</math>. Create a right triangle <math>KCP</math> where <math>KP</math> is parallel to the <math>x</math> axis and <math>CP</math> is the hypotenuse. Then <math>CK=3x</math> and <math>KP=5x</math> and doing Pythagorean on <math>\bigtriangleup KCP</math> gives <math>x=1</math>. Therefore, we know that <math>P</math> is a translation 3 units down and 5 units right from <math>C(16,0)</math>, from which we obtain <math>P(21,-3)</math>. Adding the three variables, we obtain <math>90+21-3=\boxed{108}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ~[https://artofproblemsolving.com/wiki/index.php/User:Magnetoninja Magnetoninja] | ||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
Latest revision as of 12:29, 19 January 2024
Contents
[hide]Problem
Triangles ![]() and
and ![]() lie in the coordinate plane with vertices
lie in the coordinate plane with vertices ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() . A rotation of
. A rotation of ![]() degrees clockwise around the point
degrees clockwise around the point ![]() where
where ![]() , will transform
, will transform ![]() to
to ![]() . Find
. Find ![]() .
.
Solution
After sketching, it is clear a ![]() rotation is done about
rotation is done about ![]() . Looking between
. Looking between ![]() and
and ![]() ,
, ![]() . Thus
. Thus ![]() .
~mn28407
.
~mn28407
Solution 2 (Official MAA)
Because the rotation sends the vertical segment ![]() to the horizontal segment
to the horizontal segment ![]() , the angle of rotation is
, the angle of rotation is ![]() degrees clockwise. For any point
degrees clockwise. For any point ![]() not at the origin, the line segments from
not at the origin, the line segments from ![]() to
to ![]() and from
and from ![]() to
to ![]() are perpendicular and are the same length. Thus a
are perpendicular and are the same length. Thus a ![]() clockwise rotation around the point
clockwise rotation around the point ![]() sends the point
sends the point ![]() to the point
to the point ![]() . This has the solution
. This has the solution ![]() . The requested sum is
. The requested sum is ![]() .
.
Solution 3
![[asy] /* Geogebra to Asymptote conversion by samrocksnature, documentation at artofproblemsolving.com/Wiki go to User:Azjps/geogebra */ real labelscalefactor = 0.5; /* changes label-to-point distance */ pen dps = linewidth(0.7) + fontsize(10); defaultpen(dps); /* default pen style */ pen dotstyle = black; /* point style */ real xmin = -8.0451801958033, xmax = 47.246151591238494, ymin = -10.271454747548662, ymax = 21.426040258770957; /* image dimensions */ pen zzttqq = rgb(0.6,0.2,0); pen qqwuqq = rgb(0,0.39215686274509803,0); pen qqffff = rgb(0,1,1); draw((16,0)--(0,0)--(0,12)--cycle, linewidth(2) + zzttqq); draw((24,2)--(24,18)--(36,18)--cycle, linewidth(2) + blue); draw((16,0)--(21,-3)--(24,2)--cycle, linewidth(2) + qqwuqq); draw((21.39134584768662,-2.3477569205223032)--(20.73910276820892,-1.9564110728356852)--(20.347756920522304,-2.608654152313382)--(21,-3)--cycle, linewidth(2) + qqffff); /* draw figures */ draw((16,0)--(0,0), linewidth(2) + zzttqq); draw((0,0)--(0,12), linewidth(2) + zzttqq); draw((0,12)--(16,0), linewidth(2) + zzttqq); draw((24,2)--(24,18), linewidth(2) + blue); draw((24,18)--(36,18), linewidth(2) + blue); draw((36,18)--(24,2), linewidth(2) + blue); draw((16,0)--(24,2), linewidth(2)); draw((16,0)--(21,-3), linewidth(2) + qqwuqq); draw((21,-3)--(24,2), linewidth(2) + qqwuqq); draw((24,2)--(16,0), linewidth(2) + qqwuqq); draw((21,-3)--(20,1), linewidth(2.8) + qqffff); /* dots and labels */ dot((0,0),linewidth(4pt) + dotstyle); label("$A$", (-0.6228029714727868,0.12704474547474198), NE * labelscalefactor); dot((0,12),dotstyle); label("$B$", (0.1301918194013232,12.354245873478124), NE * labelscalefactor); dot((16,0),dotstyle); label("$C$", (16.15822379657881,0.34218611429591583), NE * labelscalefactor); dot((24,18),dotstyle); label("$A'$", (24.154311337765787,18.342347305667463), NE * labelscalefactor); dot((24,2),dotstyle); label("$C'$", (23.186175178070503,1.95574638045472), NE * labelscalefactor); dot((36,18),dotstyle); label("$B'$", (36.13051420214449,18.342347305667463), NE * labelscalefactor); dot((21,-3),dotstyle); label("$P$", (21.35747354309052,-3.458644734878156), NE * labelscalefactor); dot((20,1),linewidth(4pt) + dotstyle); label("$D$", (20.13833911977053,1.2744653791876692), NE * labelscalefactor); clip((xmin,ymin)--(xmin,ymax)--(xmax,ymax)--(xmax,ymin)--cycle); /* end of picture */ [/asy]](http://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/e/6/d/e6d780ebded36fac9b18532fa74b8e4400d8b87c.png)
We first draw a diagram with the correct Cartesian coordinates and a center of rotation ![]() . Note that
. Note that ![]() because
because ![]() lies on the perpendicular bisector of
lies on the perpendicular bisector of ![]() (it must be equidistant from
(it must be equidistant from ![]() and
and ![]() by properties of a rotation).
by properties of a rotation).
Since ![]() is vertical while
is vertical while ![]() is horizontal, we have that the angle of rotation must be
is horizontal, we have that the angle of rotation must be ![]() , and therefore
, and therefore ![]() . Therefore,
. Therefore, ![]() is a 45-45-90 right triangle, and
is a 45-45-90 right triangle, and ![]() .
.
We calculate ![]() to be
to be ![]() . Since we translate
. Since we translate ![]() right and
right and ![]() up to get from point
up to get from point ![]() to point
to point ![]() , we must translate
, we must translate ![]() right and
right and ![]() down to get to point
down to get to point ![]() . This gives us
. This gives us ![]() . Our answer is then
. Our answer is then ![]() . ~Lopkiloinm & samrocksnature
. ~Lopkiloinm & samrocksnature
Solution 4
For the above reasons, the transformation is simply a ![]() rotation. Proceed with complex numbers on the points
rotation. Proceed with complex numbers on the points ![]() and
and ![]() . Let
. Let ![]() be the origin. Thus,
be the origin. Thus, ![]() and
and ![]() . The transformation from
. The transformation from ![]() to
to ![]() is a multiplication of
is a multiplication of ![]() , which yields
, which yields ![]() . Equating the real and complex terms results in the equations
. Equating the real and complex terms results in the equations ![]() and
and ![]() . Solving,
. Solving, ![]()
~beastgert
Solution 5
We know that the rotation point ![]() has to be equidistant from both
has to be equidistant from both ![]() and
and ![]() so it has to lie on the line that is on the midpoint of the segment
so it has to lie on the line that is on the midpoint of the segment ![]() and also the line has to be perpendicular to
and also the line has to be perpendicular to ![]() . Solving, we get the line is
. Solving, we get the line is ![]() . Doing the same for
. Doing the same for ![]() and
and ![]() , we get that
, we get that ![]() . Since the point
. Since the point ![]() of rotation must lie on both of these lines, we set them equal, solve and get:
of rotation must lie on both of these lines, we set them equal, solve and get: ![]() ,
,![]() . We can also easily see that the degree of rotation is
. We can also easily see that the degree of rotation is ![]() since
since ![]() is initially vertical, and now it is horizontal. Also, we can just sketch this on a coordinate plane and easily realize the same. Hence, the answer is
is initially vertical, and now it is horizontal. Also, we can just sketch this on a coordinate plane and easily realize the same. Hence, the answer is ![]()
Video Solution
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=iJkNkSAmqhg
~North America Math Contest Go Go Go
Video Solution
~IceMatrix
Solution 6
We make transformation of line ![]() into line
into line ![]() using axes symmetry. Point
using axes symmetry. Point ![]() is the crosspoint of this lines. Equation of line
is the crosspoint of this lines. Equation of line ![]() is
is
![]()
![]() maps into
maps into ![]() where
where ![]()
We make transform of the line ![]() into line
into line ![]() using axes symmetry with respect to line
using axes symmetry with respect to line
![]() The composition of two axial symmetries is a rotation through an angle twice as large as the angle between the axes
The composition of two axial symmetries is a rotation through an angle twice as large as the angle between the axes ![]() around the point of their intersection
around the point of their intersection ![]()
![]() .
.
vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss
Solution 7 (Matrix and Transformations)
For a matrix to rotate a figure on a coordinate plane by ![]() degrees, it is written as:
degrees, it is written as:
![]()
We can translate the whole figure so that the centre of rotation is at ![]() , which is equivalent to subtracting
, which is equivalent to subtracting ![]() and
and ![]() from all
from all ![]() -coordinates and the
-coordinates and the ![]() -coordinates respectively of the given points.
-coordinates respectively of the given points.
We then record all the points ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() in a matrix as follows:
in a matrix as follows:
![]()
and all the points ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() in a matrix as follows:
in a matrix as follows:
![]()
Since ![]() is a rotation around
is a rotation around ![]() of
of ![]() by
by ![]() , by the left multiplication rule, we can equate that:
, by the left multiplication rule, we can equate that:
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
We can obtain the follow equations:

From the first 2 equations, we get ![]() , substituting into the 3rd equation, we get
, substituting into the 3rd equation, we get ![]() .
.
Therefore, ![]()
~VitalsBat
Solution 8
It is clear that ![]() is a
is a ![]() right triangle so
right triangle so ![]() . We use the
. We use the ![]() angle formula,
angle formula, ![]() to find the slope of line
to find the slope of line ![]() . We know that line
. We know that line ![]() has slope
has slope ![]() and let
and let ![]() , then plugging both values into the formula, we find that the slope of
, then plugging both values into the formula, we find that the slope of ![]() is
is ![]() . Also,
. Also, ![]() has length
has length ![]() . Create a right triangle
. Create a right triangle ![]() where
where ![]() is parallel to the
is parallel to the ![]() axis and
axis and ![]() is the hypotenuse. Then
is the hypotenuse. Then ![]() and
and ![]() and doing Pythagorean on
and doing Pythagorean on ![]() gives
gives ![]() . Therefore, we know that
. Therefore, we know that ![]() is a translation 3 units down and 5 units right from
is a translation 3 units down and 5 units right from ![]() , from which we obtain
, from which we obtain ![]() . Adding the three variables, we obtain
. Adding the three variables, we obtain ![]()
See Also
| 2020 AIME II (Problems • Answer Key • Resources) | ||
| Preceded by Problem 3 |
Followed by Problem 5 | |
| 1 • 2 • 3 • 4 • 5 • 6 • 7 • 8 • 9 • 10 • 11 • 12 • 13 • 14 • 15 | ||
| All AIME Problems and Solutions | ||
The problems on this page are copyrighted by the Mathematical Association of America's American Mathematics Competitions.