Difference between revisions of "Asymptote: Macros and Packages"
(→Packages) |
|||
| (21 intermediate revisions by 10 users not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
==Definitions== | ==Definitions== | ||
| − | You can define your own functions in Asymptote | + | You can define your own functions in Asymptote. As an example, let's say you wanted to make a function called <tt>newfunction</tt> that takes a pair <math>(a,b)</math> and a real value <math>r</math> as input, and returns the pair <math>(a+r,b+r)</math>. In addition, you want it to simply return the pair <math>(a,b)</math> if no value of <math>r</math> is specified, so you want <math>r</math> to default to <math>0</math>. The code would be as follows: |
pair newfunction(pair z, real r=0) | pair newfunction(pair z, real r=0) | ||
{ | { | ||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
See if it works! | See if it works! | ||
| − | Notice that the function must be declared a pair since it returns a pair, and each of the variables must be declared some data type too. The default value of <math>r</math> was set to <math>0</math> by <math>r=0</math>, and the actual function procedure goes in between <tt>{}</tt>. | + | Notice that the function must be declared a pair since it returns a pair, and each of the variables must be declared some data type too. The default value of <math>r</math> was set to <math>0</math> by <math>r=0</math>, and the actual function procedure goes in between <tt>{}</tt>. To define a function with no output simply put <tt>void</tt> before the function name. This is the general format for a function definition. |
==Packages== | ==Packages== | ||
| − | + | Asymptote comes with several packages that contain useful functions for various purposes. For example, the package <tt>graph.asy</tt> contains the function | |
Circle(pair p, real r, int n=400); | Circle(pair p, real r, int n=400); | ||
which is a more accurate circle (having 400 nodes by default) than the built-in <tt>circle</tt> command. To use this function and others in graph.asy, simply put the command | which is a more accurate circle (having 400 nodes by default) than the built-in <tt>circle</tt> command. To use this function and others in graph.asy, simply put the command | ||
| − | + | import graph; | |
| − | at the top of your Asymptote document. | + | at the top of your Asymptote document. Graph also has more advanced functions such as the ability to [http://artofproblemsolving.com/wiki/index.php?title=Asymptote:_Graphing Graph a function] |
| − | You can create your own package by simply creating a new .asy file (say <tt>MyMacros.asy</tt>) with your own definitions in it, and saving it in the directory in which Asymptote is installed (<tt>C:\Program Files\Asymptote</tt> by default). Then < | + | You can create your own package by simply creating a new .asy file (say <tt>MyMacros.asy</tt>) with your own definitions in it, and saving it in the directory in which Asymptote is installed in Windows (<tt>C:\Program Files\Asymptote</tt> by default) and <tt>~/.asy</tt> on Mac where <tt>~</tt> is <tt>/Users/YOUR_USERNAME</tt>. Then <tt>import MyMacros;</tt> in your document, and you'll be set! |
===The Olympiad Package=== | ===The Olympiad Package=== | ||
| − | We have created an Olympiad package for Asymptote which includes macros for all the constructions that come up most often in Olympiad geometry problems! You can obtain the package olympiad.asy by clicking | + | We have created an Olympiad package for Asymptote which includes macros for all the constructions that come up most often in Olympiad geometry problems! You can obtain the package olympiad.asy by clicking [http://math.berkeley.edu/~monks/images/olympiad.asy here] or [http://www.artofproblemsolving.com/Forum/viewtopic.php?f=519&t=165767 here] (the latter link has a few usage examples). |
This package includes the following definitions: | This package includes the following definitions: | ||
| Line 43: | Line 43: | ||
'''Note:''' A sequence of variables without type declarations indicates that they are the same type as the variable preceding it. For example, the notation <tt>concurrent(pair A, B, C, D, E, F)</tt> indicates that all of the variables should have type pair. | '''Note:''' A sequence of variables without type declarations indicates that they are the same type as the variable preceding it. For example, the notation <tt>concurrent(pair A, B, C, D, E, F)</tt> indicates that all of the variables should have type pair. | ||
| − | These boolean functions test for equality within <math>10^{-5}</math> ps points in order to avoid approximation errors. | + | <tt>*</tt> These boolean functions test for equality within <math>10^{-5}</math> ps points in order to avoid approximation errors. |
| + | |||
| + | [[Asymptote: Advanced|Next: Advanced]] | ||
Latest revision as of 09:48, 4 October 2024
Definitions
You can define your own functions in Asymptote. As an example, let's say you wanted to make a function called newfunction that takes a pair ![]() and a real value
and a real value ![]() as input, and returns the pair
as input, and returns the pair ![]() . In addition, you want it to simply return the pair
. In addition, you want it to simply return the pair ![]() if no value of
if no value of ![]() is specified, so you want
is specified, so you want ![]() to default to
to default to ![]() . The code would be as follows:
. The code would be as follows:
pair newfunction(pair z, real r=0)
{
real a,b;
a=z.x;
b=z.y;
return (a+r,b+r);
}
Put this definition in an asymptote document and then test it using some command like
draw(newfunction((20,30))--newfunction((20,30),30)--(0,0)--cycle);
See if it works!
Notice that the function must be declared a pair since it returns a pair, and each of the variables must be declared some data type too. The default value of ![]() was set to
was set to ![]() by
by ![]() , and the actual function procedure goes in between {}. To define a function with no output simply put void before the function name. This is the general format for a function definition.
, and the actual function procedure goes in between {}. To define a function with no output simply put void before the function name. This is the general format for a function definition.
Packages
Asymptote comes with several packages that contain useful functions for various purposes. For example, the package graph.asy contains the function
Circle(pair p, real r, int n=400);
which is a more accurate circle (having 400 nodes by default) than the built-in circle command. To use this function and others in graph.asy, simply put the command
import graph;
at the top of your Asymptote document. Graph also has more advanced functions such as the ability to Graph a function
You can create your own package by simply creating a new .asy file (say MyMacros.asy) with your own definitions in it, and saving it in the directory in which Asymptote is installed in Windows (C:\Program Files\Asymptote by default) and ~/.asy on Mac where ~ is /Users/YOUR_USERNAME. Then import MyMacros; in your document, and you'll be set!
The Olympiad Package
We have created an Olympiad package for Asymptote which includes macros for all the constructions that come up most often in Olympiad geometry problems! You can obtain the package olympiad.asy by clicking here or here (the latter link has a few usage examples).
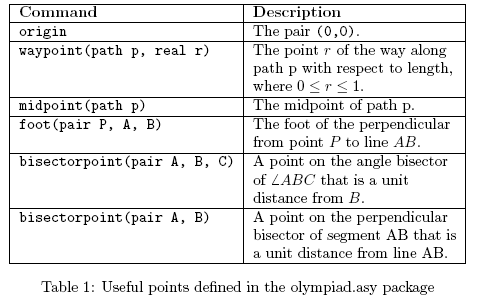
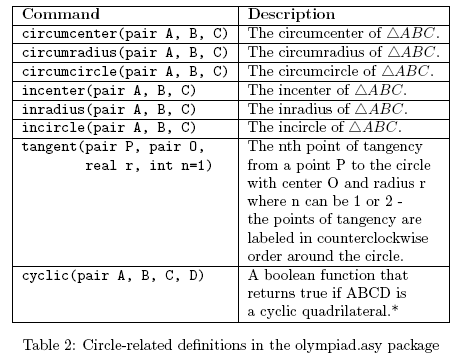
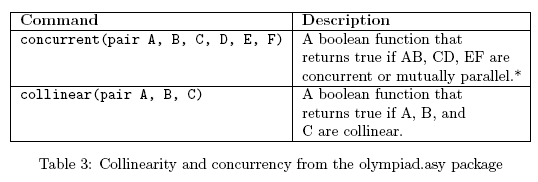
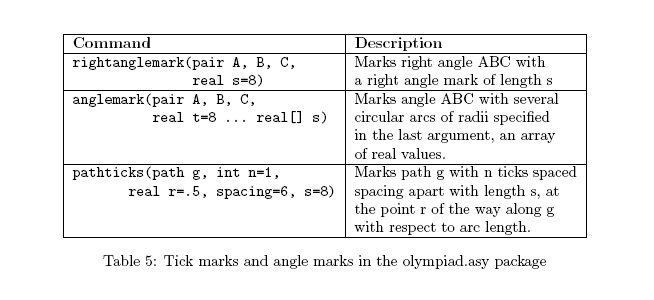
This package includes the following definitions:
Note: A sequence of variables without type declarations indicates that they are the same type as the variable preceding it. For example, the notation concurrent(pair A, B, C, D, E, F) indicates that all of the variables should have type pair.
* These boolean functions test for equality within ![]() ps points in order to avoid approximation errors.
ps points in order to avoid approximation errors.