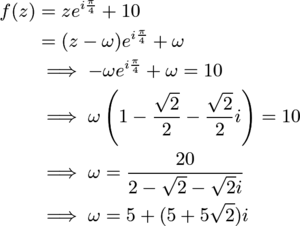Difference between revisions of "2008 AIME II Problems/Problem 9"
I like pie (talk | contribs) m (→Solution 2: Style, formatting) |
Martin2001 (talk | contribs) (→Solution 2) |
||
| (31 intermediate revisions by 16 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | __TOC__ | ||
| + | |||
== Problem == | == Problem == | ||
A particle is located on the coordinate plane at <math>(5,0)</math>. Define a ''move'' for the particle as a counterclockwise rotation of <math>\pi/4</math> radians about the origin followed by a translation of <math>10</math> units in the positive <math>x</math>-direction. Given that the particle's position after <math>150</math> moves is <math>(p,q)</math>, find the greatest integer less than or equal to <math>|p| + |q|</math>. | A particle is located on the coordinate plane at <math>(5,0)</math>. Define a ''move'' for the particle as a counterclockwise rotation of <math>\pi/4</math> radians about the origin followed by a translation of <math>10</math> units in the positive <math>x</math>-direction. Given that the particle's position after <math>150</math> moves is <math>(p,q)</math>, find the greatest integer less than or equal to <math>|p| + |q|</math>. | ||
| − | + | == Solutions == | |
| − | == | ||
=== Solution 1 === | === Solution 1 === | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | Let <math>P(x, y)</math> be the position of the particle on the <math>xy</math>-plane, <math>r</math> be the length <math>OP</math> where <math>O</math> is the origin, and <math>\theta</math> be the inclination of OP to the x-axis. If <math>(x', y')</math> is the position of the particle after a move from <math>P</math>, then we have two equations for <math>x'</math> and <math>y'</math>: | ||
| + | <cmath>x'=r\cos(\pi/4+\theta)+10 = \frac{\sqrt{2}(x - y)}{2} + 10</cmath> | ||
| + | <cmath>y' = r\sin(\pi/4+\theta) = \frac{\sqrt{2}(x + y)}{2}.</cmath> | ||
| + | Let <math>(x_n, y_n)</math> be the position of the particle after the nth move, where <math>x_0 = 5</math> and <math>y_0 = 0</math>. Then <math>x_{n+1} + y_{n+1} = \sqrt{2}x_n+10</math>, <math>x_{n+1} - y_{n+1} = -\sqrt{2}y_n+10</math>. This implies | ||
| + | <math>x_{n+2} = -y_n + 5\sqrt{2}+ 10</math>, <math>y_{n+2}=x_n + 5\sqrt{2}</math>. | ||
| + | Substituting <math>x_0 = 5</math> and <math>y_0 = 0</math>, we have <math>x_8 = 5</math> and <math>y_8 = 0</math> again for the first time. Thus, <math>p = x_{150} = x_6 = -5\sqrt{2}</math> and <math>q = y_{150} = y_6 = 5 + 5\sqrt{2}</math>. Hence, the final answer is | ||
| + | <center><math>5\sqrt {2} + 5(\sqrt {2} + 1) \approx 19.1 \Longrightarrow \boxed{019}</math></center> | ||
| + | |||
| + | If you're curious, the points do eventually form an octagon and repeat. Seems counterintuitive, but believe it or not, it happens. | ||
| + | |||
| + | https://www.desmos.com/calculator/febtiheosz | ||
=== Solution 2 === | === Solution 2 === | ||
| − | Let the particle's position be represented by a complex number. | + | Let the particle's position be represented by a complex number. Recall that multiplying a number by cis<math>\left( \theta \right)</math> rotates the object in the complex plane by <math>\theta</math> counterclockwise. In this case, we use <math>a = cis(\frac{\pi}{4})</math>. Therefore, applying the rotation and shifting the coordinates by 10 in the positive x direction in the complex plane results to |
| + | <center><math>a_{150} = (((5a + 10)a + 10)a + 10 \ldots) = 5a^{150} + 10 a^{149} + 10a^{148}+ \ldots + 10</math></center> | ||
| + | where a is cis<math>\left( \theta \right)</math>. By De-Moivre's theorem, <math>\left(cis( \theta \right)^n )</math>=cis<math>\left(n \theta \right)</math>. | ||
| + | Therefore, | ||
| + | <center><math>10(a^{150} + \ldots + 1)= 10(1 + a + \ldots + a^6) = - 10(a^7) = - 10(\frac{ \sqrt {2} }{2} - \frac{i\sqrt {2}} {2})</math></center> | ||
| + | Furthermore, <math>5a^{150} = - 5i</math>. Thus, the final answer is | ||
| + | <center><math>5\sqrt {2} + 5(\sqrt {2} + 1) \approx 19.1 \Longrightarrow \boxed{019}</math></center> | ||
| − | + | ==== Solution 3 ==== | |
| − | <center><math> | + | As before, consider <math>z</math> as a complex number. Consider the transformation <math>z \to (z-\omega)e^{i\theta} + \omega</math>. This is a clockwise rotation of <math>z</math> by <math>\theta</math> radians about the points <math>\omega</math>. Let <math>f(z)</math> denote one move of <math>z</math>. Then |
| − | + | ||
| − | <center><math> | + | [[File:2008AIMEII9Sol3.png|center|300px]] |
| − | + | Therefore, <math>z</math> rotates along a circle with center <math>\omega = 5+(5+5\sqrt2)i</math>. Since <math>8 \cdot \frac{\pi}{4} = 2\pi</math>, <math>f^9(z) = f(z) \implies f^{150}(z) = f^6(z) \implies p+q = \boxed{019}</math>, as desired (the final algebra bash isn't bad). | |
| − | < | + | |
| + | === Solution 4 === | ||
| + | Let <math>T:\begin{pmatrix}x\\y\end{pmatrix}\rightarrow R(\frac{\pi}{4})\begin{pmatrix}x\\y\end{pmatrix}+\begin{pmatrix}10\\0\end{pmatrix}</math>. We assume that the rotation matrix <math>R(\frac{\pi}{4}) = R</math> here. Then we have | ||
| + | <center><math>T^{150}\begin{pmatrix}5\\0\end{pmatrix}=R(R(...R(R\begin{pmatrix}5\\0\end{pmatrix}+\begin{pmatrix}10\\0\end{pmatrix})+\begin{pmatrix}10\\0\end{pmatrix}...)+\begin{pmatrix}10\\0\end{pmatrix})+\begin{pmatrix}10\\0\end{pmatrix}</math></center> | ||
| + | This simplifies to | ||
| + | <center><math>R^{150}\begin{pmatrix}5\\0\end{pmatrix}+(I+R^2+R^3+...+R^{149})\begin{pmatrix}10\\0\end{pmatrix}</math></center> | ||
| + | Since <math>R+R^{7}=O, R^2+R^6=O, R^3+R^5=O, I+R^4=O</math>, so we have <math>R^6\begin{pmatrix}5\\0\end{pmatrix}+(-R^6-R^7)\begin{pmatrix}10\\0\end{pmatrix}</math>, giving <math>p=-5\sqrt{2}, q=5\sqrt{2}+5</math>. The answer is yet <math>\lfloor10\sqrt{2}+5\rfloor=\boxed{019}</math>. | ||
== See also == | == See also == | ||
| Line 21: | Line 45: | ||
[[Category:Intermediate Algebra Problems]] | [[Category:Intermediate Algebra Problems]] | ||
| + | {{MAA Notice}} | ||
Latest revision as of 21:37, 28 January 2024
Contents
Problem
A particle is located on the coordinate plane at ![]() . Define a move for the particle as a counterclockwise rotation of
. Define a move for the particle as a counterclockwise rotation of ![]() radians about the origin followed by a translation of
radians about the origin followed by a translation of ![]() units in the positive
units in the positive ![]() -direction. Given that the particle's position after
-direction. Given that the particle's position after ![]() moves is
moves is ![]() , find the greatest integer less than or equal to
, find the greatest integer less than or equal to ![]() .
.
Solutions
Solution 1
Let ![]() be the position of the particle on the
be the position of the particle on the ![]() -plane,
-plane, ![]() be the length
be the length ![]() where
where ![]() is the origin, and
is the origin, and ![]() be the inclination of OP to the x-axis. If
be the inclination of OP to the x-axis. If ![]() is the position of the particle after a move from
is the position of the particle after a move from ![]() , then we have two equations for
, then we have two equations for ![]() and
and ![]() :
:
![]()
![]() Let
Let ![]() be the position of the particle after the nth move, where
be the position of the particle after the nth move, where ![]() and
and ![]() . Then
. Then ![]() ,
, ![]() . This implies
. This implies
![]() ,
, ![]() .
Substituting
.
Substituting ![]() and
and ![]() , we have
, we have ![]() and
and ![]() again for the first time. Thus,
again for the first time. Thus, ![]() and
and ![]() . Hence, the final answer is
. Hence, the final answer is
If you're curious, the points do eventually form an octagon and repeat. Seems counterintuitive, but believe it or not, it happens.
https://www.desmos.com/calculator/febtiheosz
Solution 2
Let the particle's position be represented by a complex number. Recall that multiplying a number by cis![]() rotates the object in the complex plane by
rotates the object in the complex plane by ![]() counterclockwise. In this case, we use
counterclockwise. In this case, we use ![]() . Therefore, applying the rotation and shifting the coordinates by 10 in the positive x direction in the complex plane results to
. Therefore, applying the rotation and shifting the coordinates by 10 in the positive x direction in the complex plane results to
where a is cis![]() . By De-Moivre's theorem,
. By De-Moivre's theorem, ![]() =cis
=cis![]() .
Therefore,
.
Therefore,
Furthermore, ![]() . Thus, the final answer is
. Thus, the final answer is
Solution 3
As before, consider ![]() as a complex number. Consider the transformation
as a complex number. Consider the transformation ![]() . This is a clockwise rotation of
. This is a clockwise rotation of ![]() by
by ![]() radians about the points
radians about the points ![]() . Let
. Let ![]() denote one move of
denote one move of ![]() . Then
. Then
Therefore, ![]() rotates along a circle with center
rotates along a circle with center ![]() . Since
. Since ![]() ,
, ![]() , as desired (the final algebra bash isn't bad).
, as desired (the final algebra bash isn't bad).
Solution 4
Let ![]() . We assume that the rotation matrix
. We assume that the rotation matrix ![]() here. Then we have
here. Then we have
This simplifies to
Since ![]() , so we have
, so we have ![]() , giving
, giving ![]() . The answer is yet
. The answer is yet ![]() .
.
See also
| 2008 AIME II (Problems • Answer Key • Resources) | ||
| Preceded by Problem 8 |
Followed by Problem 10 | |
| 1 • 2 • 3 • 4 • 5 • 6 • 7 • 8 • 9 • 10 • 11 • 12 • 13 • 14 • 15 | ||
| All AIME Problems and Solutions | ||
The problems on this page are copyrighted by the Mathematical Association of America's American Mathematics Competitions.