Difference between revisions of "1987 AIME Problems/Problem 15"
m (→Solution: diagram looks bad large) |
(→Solution) |
||
| (11 intermediate revisions by 6 users not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
[[Image:AIME_1987_Problem_15.png]] | [[Image:AIME_1987_Problem_15.png]] | ||
| + | |||
== Solution == | == Solution == | ||
[[Image:1987 AIME-15a.png|360px]] | [[Image:1987 AIME-15a.png|360px]] | ||
| Line 8: | Line 9: | ||
Because all the [[triangle]]s in the figure are [[similar]] to triangle <math>ABC</math>, it's a good idea to use [[area ratios]]. In the diagram above, <math>\frac {T_1}{T_3} = \frac {T_2}{T_4} = \frac {441}{440}.</math> Hence, <math>T_3 = \frac {440}{441}T_1</math> and <math>T_4 = \frac {440}{441}T_2</math>. Additionally, the area of triangle <math>ABC</math> is equal to both <math>T_1 + T_2 + 441</math> and <math>T_3 + T_4 + T_5 + 440.</math> | Because all the [[triangle]]s in the figure are [[similar]] to triangle <math>ABC</math>, it's a good idea to use [[area ratios]]. In the diagram above, <math>\frac {T_1}{T_3} = \frac {T_2}{T_4} = \frac {441}{440}.</math> Hence, <math>T_3 = \frac {440}{441}T_1</math> and <math>T_4 = \frac {440}{441}T_2</math>. Additionally, the area of triangle <math>ABC</math> is equal to both <math>T_1 + T_2 + 441</math> and <math>T_3 + T_4 + T_5 + 440.</math> | ||
| − | Setting the equations equal and solving for <math>T_5</math>, <math>T_5 = 1 + T_1 - T_3 + T_2 - T_4 = 1 + \frac {T_1}{441} + \frac {T_2}{441}</math>. Therefore, <math>441T_5 = 441 + T_1 + T_2</math>. However, <math>441 + T_1 + T_2</math> is equal to the area of triangle <math>ABC</math>! This means that the ratio between the areas <math>T_5</math> and <math>ABC</math> is <math>441</math>, and the ratio between the sides is <math>\sqrt {441} = 21</math>. As a result, <math>AB = 21\sqrt {440} = \sqrt {AC^2 + BC^2}</math>. We now need <math>(AC)(BC)</math> to find the value of <math>AC + BC</math>, because <math>AB^2 + 2(AC)(BC) = (AC + BC)^2</math>. | + | Setting the equations equal and solving for <math>T_5</math>, <math>T_5 = 1 + T_1 - T_3 + T_2 - T_4 = 1 + \frac {T_1}{441} + \frac {T_2}{441}</math>. Therefore, <math>441T_5 = 441 + T_1 + T_2</math>. However, <math>441 + T_1 + T_2</math> is equal to the area of triangle <math>ABC</math>! This means that the ratio between the areas <math>T_5</math> and <math>ABC</math> is <math>441</math>, and the ratio between the sides is <math>\sqrt {441} = 21</math>. As a result, <math>AB = 21\sqrt {440} = \sqrt {AC^2 + BC^2}</math>. We now need <math>(AC)(BC)</math> to find the value of <math>AC + BC</math>, because <math>AB^2 + BC^2 + 2(AC)(BC) = (AC + BC)^2</math>. |
| + | |||
| + | Let <math>h</math> denote the height to the [[hypotenuse]] of triangle <math>ABC</math>. Notice that <math>h - \frac {1}{21}h = \sqrt {440}</math>. (The height of <math>ABC</math> decreased by the corresponding height of <math>T_5</math>) Thus, <math>(AB)(h) = (AC)(BC) = 22\cdot 21^2</math>. Because <math>AC^2 + BC^2 + 2(AC)(BC) = (AC + BC)^2 = 21^2\cdot22^2</math>, <math>AC + BC = (21)(22) = \boxed{462}</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Easy Trig Solution == | ||
| + | |||
| + | Let <math>\tan\angle ABC = x</math>. Now using the 1st square, <math>AC=21(1+x)</math> and <math>CB=21(1+x^{-1})</math>. Using the second square, <math>AB=\sqrt{440}(1+x+x^{-1})</math>. We have <math>AC^2+CB^2=AB^2</math>, or <cmath>441(x^2+x^{-2}+2x+2x^{-1}+2)=440(x^2+x^{-2}+2x+2x^{-1}+3).</cmath> Rearranging and letting <math>u=x+x^{-1} \Rightarrow u^2 - 2 = x^2 + x^{-2}</math> gives us <math>u^2+2u-440=0.</math> We take the positive root, so <math>u=20</math>, which means <math>AC+CB=21(2+x+x^{-1})=21(2+u)=\boxed{462}</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Messy Trig Solution == | ||
| − | Let <math> | + | Let <math>\theta</math> be the smaller angle in the triangle. Then the sum of shorter and longer leg is <math>\sqrt{441}(2+\tan{\theta}+\cot{\theta})</math>. We observe that the short leg has length <math>\sqrt{441}(1+\tan{\theta}) = \sqrt{440}(\sec{\theta}+\sin{\theta})</math>. Grouping and squaring, we get <math>\sqrt{\frac{440}{441}} = \frac{\sin{\theta}+\cos{\theta}}{1+\sin{\theta}\cos{\theta}}</math>. Squaring and using the double angle identity for sine, we get, <math>110(\sin{2\theta})^2 + \sin{2\theta} - 1 = 0</math>. Solving, we get <math>\sin{2\theta} = \frac{1}{10}</math>. Now to find <math>\tan{\theta}</math>, we find <math>\cos{2\theta}</math> using the Pythagorean |
| + | Identity, and then use the tangent double angle identity. Thus, <math>\tan{\theta} = 10-3\sqrt{11}</math>. Substituting into the original sum, | ||
| + | we get <math>\boxed{462}</math>. | ||
== See also == | == See also == | ||
| Line 16: | Line 27: | ||
[[Category:Intermediate Geometry Problems]] | [[Category:Intermediate Geometry Problems]] | ||
| + | {{MAA Notice}} | ||
Revision as of 17:49, 2 September 2020
Problem
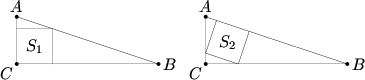
Squares ![]() and
and ![]() are inscribed in right triangle
are inscribed in right triangle ![]() , as shown in the figures below. Find
, as shown in the figures below. Find ![]() if area
if area ![]() and area
and area ![]() .
.
Solution
Because all the triangles in the figure are similar to triangle ![]() , it's a good idea to use area ratios. In the diagram above,
, it's a good idea to use area ratios. In the diagram above, ![]() Hence,
Hence, ![]() and
and ![]() . Additionally, the area of triangle
. Additionally, the area of triangle ![]() is equal to both
is equal to both ![]() and
and ![]()
Setting the equations equal and solving for ![]() ,
, ![]() . Therefore,
. Therefore, ![]() . However,
. However, ![]() is equal to the area of triangle
is equal to the area of triangle ![]() ! This means that the ratio between the areas
! This means that the ratio between the areas ![]() and
and ![]() is
is ![]() , and the ratio between the sides is
, and the ratio between the sides is ![]() . As a result,
. As a result, ![]() . We now need
. We now need ![]() to find the value of
to find the value of ![]() , because
, because ![]() .
.
Let ![]() denote the height to the hypotenuse of triangle
denote the height to the hypotenuse of triangle ![]() . Notice that
. Notice that ![]() . (The height of
. (The height of ![]() decreased by the corresponding height of
decreased by the corresponding height of ![]() ) Thus,
) Thus, ![]() . Because
. Because ![]() ,
, ![]() .
.
Easy Trig Solution
Let ![]() . Now using the 1st square,
. Now using the 1st square, ![]() and
and ![]() . Using the second square,
. Using the second square, ![]() . We have
. We have ![]() , or
, or ![]() Rearranging and letting
Rearranging and letting ![]() gives us
gives us ![]() We take the positive root, so
We take the positive root, so ![]() , which means
, which means ![]() .
.
Messy Trig Solution
Let ![]() be the smaller angle in the triangle. Then the sum of shorter and longer leg is
be the smaller angle in the triangle. Then the sum of shorter and longer leg is ![]() . We observe that the short leg has length
. We observe that the short leg has length ![]() . Grouping and squaring, we get
. Grouping and squaring, we get ![]() . Squaring and using the double angle identity for sine, we get,
. Squaring and using the double angle identity for sine, we get, ![]() . Solving, we get
. Solving, we get ![]() . Now to find
. Now to find ![]() , we find
, we find ![]() using the Pythagorean
Identity, and then use the tangent double angle identity. Thus,
using the Pythagorean
Identity, and then use the tangent double angle identity. Thus, ![]() . Substituting into the original sum,
we get
. Substituting into the original sum,
we get ![]() .
.
See also
| 1987 AIME (Problems • Answer Key • Resources) | ||
| Preceded by Problem 14 |
Followed by Last Question | |
| 1 • 2 • 3 • 4 • 5 • 6 • 7 • 8 • 9 • 10 • 11 • 12 • 13 • 14 • 15 | ||
| All AIME Problems and Solutions | ||
The problems on this page are copyrighted by the Mathematical Association of America's American Mathematics Competitions.