2006 AMC 10B Problems/Problem 23
Problem
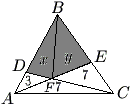
A triangle is partitioned into three triangles and a quadrilateral by drawing two lines from vertices to their opposite sides. The areas of the three triangles are 3, 7, and 7 as shown. What is the area of the shaded quadrilateral?
![]()
Solution
To help in finding the area of the quadrilateral, draw an auxillary line from the top vertex to the intersection of the two lines.
Doing so and labling the points yeilds this as the resulting diagram:
Since triangles ![]() and
and ![]() share an altitude from
share an altitude from ![]() and have equal area, their bases must be equal.
and have equal area, their bases must be equal.
So ![]() .
.
Since triangles ![]() and
and ![]() share an altitude from
share an altitude from ![]() and their respective bases are equal, their areas must be equal.
and their respective bases are equal, their areas must be equal.
So ![]() .
.
Since triangles ![]() and
and ![]() share an altitude from
share an altitude from ![]() and their respective areas are in the ratio
and their respective areas are in the ratio ![]() , their bases must be in the same ratio.
, their bases must be in the same ratio.
So ![]() .
.
Since triangles ![]() and
and ![]() share an altitude from
share an altitude from ![]() and their respective bases are in the ratio
and their respective bases are in the ratio ![]() , their areas must be in the same ratio.
, their areas must be in the same ratio.
So ![]() .
.
Substituting ![]() for
for ![]() :
:
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Therefore, the shaded area is ![]()