Difference between revisions of "2017 IMO Problems/Problem 4"
(→Solution) |
|||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
==Solution== | ==Solution== | ||
| + | [[File:2017 IMO 4.png|500px|right]] | ||
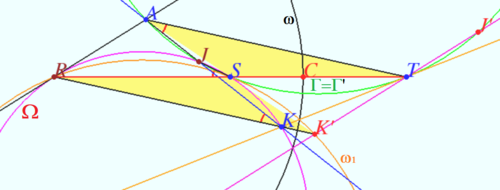
We construct inversion which maps <math>KT</math> into the circle <math>\omega_1</math> and <math>\Gamma</math> into <math>\Gamma.</math> Than we prove that <math>\omega_1</math> is tangent to <math>\Gamma.</math> | We construct inversion which maps <math>KT</math> into the circle <math>\omega_1</math> and <math>\Gamma</math> into <math>\Gamma.</math> Than we prove that <math>\omega_1</math> is tangent to <math>\Gamma.</math> | ||
Quadrungle <math>RJSK</math> is cyclic <math>\implies \angle RSJ = \angle RKJ.</math> | Quadrungle <math>RJSK</math> is cyclic <math>\implies \angle RSJ = \angle RKJ.</math> | ||
Quadrungle <math>AJST</math> is cyclic <math>\implies \angle RSJ = \angle TAJ \implies AT||RK.</math> | Quadrungle <math>AJST</math> is cyclic <math>\implies \angle RSJ = \angle TAJ \implies AT||RK.</math> | ||
| − | We construct circle <math>\omega</math> centered at <math>R</math> which maps <math>\Gamma</math> into <math>\Gamma.</math> Let <math>C = \omega \cap RT \implies RC^2 = RS \cdot RT.</math> Inversion with respect <math>\omega</math> swap <math>T</math> and <math>S \implies \Gamma</math> maps into <math>\Gamma.</math> | + | |
| + | We construct circle <math>\omega</math> centered at <math>R</math> which maps <math>\Gamma</math> into <math>\Gamma.</math> Let <math>C = \omega \cap RT \implies RC^2 = RS \cdot RT.</math> Inversion with respect <math>\omega</math> swap <math>T</math> and <math>S \implies \Gamma</math> maps into <math>\Gamma (\Gamma = \Gamma').</math> Let <math>O</math> be the center of <math>\Gamma.</math> | ||
| + | |||
Inversion with respect <math>\omega</math> maps <math>K</math> into <math>K'</math>. | Inversion with respect <math>\omega</math> maps <math>K</math> into <math>K'</math>. | ||
| + | <math>K</math> belong <math>KT \implies</math> circle <math>K'SR</math> is the image of <math>KT</math>. Let <math>Q</math> be the center of the circle <math>K'SR.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>K'T</math> is the image of <math>\Omega</math> at this inversion, <math>l = AR</math> is tangent line to <math>\Omega</math> at <math>R,</math> so <math>K'T||AR.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>K'</math> is image K at this inversion <math>\implies K \in RK' \implies RK'||AT \implies ARK'T</math> is parallelogramm. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>S</math> is the midpoint of <math>RT \implies S</math> is the center of symmetry of <math>ATK'R \implies</math> | ||
| + | <math>\triangle RSK'</math> is symmetrical to <math>\triangle TSA</math> with respect to <math>S \implies</math> | ||
| + | circumcircle <math>RSK'</math> is symmetrical to circumcircle <math>TSA</math> with respect to <math>S \implies</math> | ||
| + | <math>O</math> is symmetrycal <math>Q</math> with respect to <math>S, S</math> lies on <math>\Gamma</math> and on <math>|omega_1 \implies</math> | ||
| + | <math>\Gamma</math> is tangent <math>\omega_1 \implies S\Gamma</math> is tangent <math>\omega_1.</math> | ||
Revision as of 12:01, 26 August 2022
Let ![]() and
and ![]() be different points on a circle
be different points on a circle ![]() such that
such that ![]() is not a diameter. Let
is not a diameter. Let ![]() be the tangent line to
be the tangent line to ![]() at
at ![]() . Point
. Point ![]() is such that
is such that ![]() is the midpoint of the line segment
is the midpoint of the line segment ![]() . Point
. Point ![]() is chosen on the shorter arc
is chosen on the shorter arc ![]() of
of ![]() so that the circumcircle
so that the circumcircle ![]() of triangle
of triangle ![]() intersects
intersects ![]() at two distinct points. Let
at two distinct points. Let ![]() be the common point of
be the common point of ![]() and
and ![]() that is closer to
that is closer to ![]() . Line
. Line ![]() meets
meets ![]() again at
again at ![]() . Prove that the line
. Prove that the line ![]() is tangent to
is tangent to ![]() .
.
Solution
We construct inversion which maps ![]() into the circle
into the circle ![]() and
and ![]() into
into ![]() Than we prove that
Than we prove that ![]() is tangent to
is tangent to ![]()
Quadrungle ![]() is cyclic
is cyclic ![]() Quadrungle
Quadrungle ![]() is cyclic
is cyclic ![]()
We construct circle ![]() centered at
centered at ![]() which maps
which maps ![]() into
into ![]() Let
Let ![]() Inversion with respect
Inversion with respect ![]() swap
swap ![]() and
and ![]() maps into
maps into ![]() Let
Let ![]() be the center of
be the center of ![]()
Inversion with respect ![]() maps
maps ![]() into
into ![]() .
.
![]() belong
belong ![]() circle
circle ![]() is the image of
is the image of ![]() . Let
. Let ![]() be the center of the circle
be the center of the circle ![]()
![]() is the image of
is the image of ![]() at this inversion,
at this inversion, ![]() is tangent line to
is tangent line to ![]() at
at ![]() so
so ![]()
![]() is image K at this inversion
is image K at this inversion ![]() is parallelogramm.
is parallelogramm.
![]() is the midpoint of
is the midpoint of ![]() is the center of symmetry of
is the center of symmetry of ![]()
![]() is symmetrical to
is symmetrical to ![]() with respect to
with respect to ![]() circumcircle
circumcircle ![]() is symmetrical to circumcircle
is symmetrical to circumcircle ![]() with respect to
with respect to ![]()
![]() is symmetrycal
is symmetrycal ![]() with respect to
with respect to ![]() lies on
lies on ![]() and on
and on ![]()
![]() is tangent
is tangent ![]() is tangent
is tangent ![]()