Difference between revisions of "Mock AIME 6 2006-2007 Problems/Problem 13"
(Created page with "==Problem== Consider two circles of different sizes that do not intersect. The smaller circle has center <math>O</math>. Label the intersection of their common external tang...") |
|||
| (10 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Problem== | ==Problem== | ||
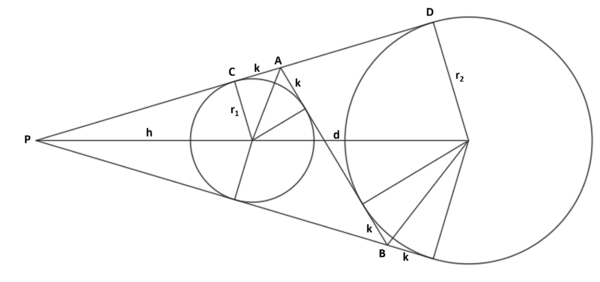
| − | Consider two circles of different sizes that do not intersect. The smaller circle has center <math>O</math>. Label the intersection of their common external tangents <math>P</math>. A common internal tangent | + | Consider two circles of different sizes that do not intersect. The smaller circle has center <math>O</math>. Label the intersection of their common external tangents <math>P</math>. A common internal tangent intersects the common external tangents at points <math>A</math> and <math>B</math>. Given that the radius of the larger circle is <math>11</math>, <math>PO=3</math>, and <math>AB=20\sqrt{2}</math>, what is the square of the area of triangle <math>PBA</math>? |
==Solution== | ==Solution== | ||
| − | {{ | + | |
| + | [[File:Mock_AIME_6_P13a.png|600px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>|AB|=|CD|=20\sqrt{2}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Let <math>d</math> be the distance between centers, and <math>h=|PO|=3</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>|CD|^2+(r_2-r_1)^2=d^2</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>(20\sqrt{2})^2+(r_2-r_1)^2=d^2</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>800+(r_2-r_1)^2=d^2</math> [Equation 1] | ||
| + | |||
| + | By similar triangles, | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\frac{r_1}{h}=\frac{r_2}{h+d}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | solving for <math>d</math> we have: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>d=\frac{(r_2-r_1)h}{r_1}</math> [Equation 2] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Substituting [Equation 2] into [Equation 1] we have: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>800+(r_2-r_1)^2=\frac{(r_2-r_1)^2h^2}{r_1^2}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>800+(11-r_1)^2=\frac{9(11-r_1)^2}{r_1^2}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Solving for <math>r_1</math> we get <math>r_1=1</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Since <math>r_1</math> is the radius of the incircle of <math>\Delta PBA</math> then, | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>r_1=\frac{A_1}{s}</math> where <math>A_1</math> is the area of <math>\Delta PBA</math> and <math>s</math> is half the perimeter of <math>\Delta PBA</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Then, <math>A_1=r_1s=s=\frac{|AB|+(\sqrt{(h+d)^2-r_2^2}-k)+(\sqrt{h^2-r_1^2}+k)}{2}=\frac{20\sqrt{2}+\left( \frac{r_2}{r_1}+1 \right)\sqrt{h^2-r_1^2}}{2}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>A_1=\frac{20\sqrt{2}+12\sqrt{3^2-1^2}}{2}=10\sqrt{2}+12\sqrt{2}=22\sqrt{2}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>A_1^2=(22\sqrt{2})^2=\boxed{968}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ~Tomas Diaz. orders@tomasdiaz.com | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{alternate solutions}} | ||
Latest revision as of 02:36, 26 November 2023
Problem
Consider two circles of different sizes that do not intersect. The smaller circle has center ![]() . Label the intersection of their common external tangents
. Label the intersection of their common external tangents ![]() . A common internal tangent intersects the common external tangents at points
. A common internal tangent intersects the common external tangents at points ![]() and
and ![]() . Given that the radius of the larger circle is
. Given that the radius of the larger circle is ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() , what is the square of the area of triangle
, what is the square of the area of triangle ![]() ?
?
Solution
![]()
Let ![]() be the distance between centers, and
be the distance between centers, and ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() [Equation 1]
[Equation 1]
By similar triangles,
![]()
solving for ![]() we have:
we have:
![]() [Equation 2]
[Equation 2]
Substituting [Equation 2] into [Equation 1] we have:
![]()
![]()
Solving for ![]() we get
we get ![]()
Since ![]() is the radius of the incircle of
is the radius of the incircle of ![]() then,
then,
![]() where
where ![]() is the area of
is the area of ![]() and
and ![]() is half the perimeter of
is half the perimeter of ![]()
Then, 
![]()
![]()
~Tomas Diaz. orders@tomasdiaz.com
Alternate solutions are always welcome. If you have a different, elegant solution to this problem, please add it to this page.