Difference between revisions of "2007 AIME I Problems/Problem 9"
m (more) |
Boxtheanswer (talk | contribs) m (→See also) |
||
| (38 intermediate revisions by 14 users not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
In [[right triangle]] <math>ABC</math> with [[right angle]] <math>C</math>, <math>CA = 30</math> and <math>CB = 16</math>. Its legs <math>CA</math> and <math>CB</math> are extended beyond <math>A</math> and <math>B</math>. [[Point]]s <math>O_1</math> and <math>O_2</math> lie in the exterior of the triangle and are the centers of two [[circle]]s with equal [[radius|radii]]. The circle with center <math>O_1</math> is tangent to the [[hypotenuse]] and to the extension of leg <math>CA</math>, the circle with center <math>O_2</math> is [[tangent]] to the hypotenuse and to the extension of [[leg]] <math>CB</math>, and the circles are externally tangent to each other. The length of the radius either circle can be expressed as <math>p/q</math>, where <math>p</math> and <math>q</math> are [[relatively prime]] [[positive]] [[integer]]s. Find <math>p+q</math>. | In [[right triangle]] <math>ABC</math> with [[right angle]] <math>C</math>, <math>CA = 30</math> and <math>CB = 16</math>. Its legs <math>CA</math> and <math>CB</math> are extended beyond <math>A</math> and <math>B</math>. [[Point]]s <math>O_1</math> and <math>O_2</math> lie in the exterior of the triangle and are the centers of two [[circle]]s with equal [[radius|radii]]. The circle with center <math>O_1</math> is tangent to the [[hypotenuse]] and to the extension of leg <math>CA</math>, the circle with center <math>O_2</math> is [[tangent]] to the hypotenuse and to the extension of [[leg]] <math>CB</math>, and the circles are externally tangent to each other. The length of the radius either circle can be expressed as <math>p/q</math>, where <math>p</math> and <math>q</math> are [[relatively prime]] [[positive]] [[integer]]s. Find <math>p+q</math>. | ||
| − | == Solution == | + | == Solutions == |
| − | {{ | + | === Solution 1 === |
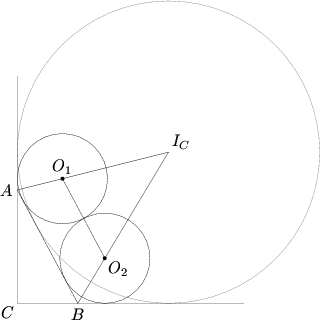
| − | Let the point where CB's extension hits the circle be | + | [[Image:AIME I 2007-9.png]] |
| + | |||
| + | Label the points as in the diagram above. If we draw <math>\overline{O_1A}</math> and <math>\overline{O_2B}</math>, we form two [[right triangle]]s. As <math>\overline{AF}</math> and <math>\overline{AD}</math> are both [[tangent]]s to the circle, we see that <math>\overline{O_1A}</math> is an [[angle bisector]]. Thus, <math>\triangle AFO_1 \cong \triangle ADO_1</math>. Call <math>x = AD = AF</math> and <math>y = EB = BG</math>. We know that <math>x + y + 2r = 34</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | If we call <math>\angle CAB = \theta</math>, then <math>\angle DAO_1 = \frac{180 - \theta}{2}</math>. Apply the [[trigonometric identities|tangent half-angle formula]] (<math>\tan \frac{\theta}{2} = \sqrt{\frac{1 - \cos \theta}{1 + \cos \theta}}</math>). We see that <math>\frac rx = \tan \frac{180 - \theta}{2} = \sqrt{\frac{1 - \cos (180 - \theta)}{1 + \cos (180 - \theta)}}</math><math> = \sqrt{\frac{1 + \cos \theta}{1 - \cos \theta}}</math>. Also, <math>\cos \theta = \frac{30}{34} = \frac{15}{17}</math>. Thus, <math>\frac rx = \sqrt{\frac{1 + \frac{15}{17}}{1 - \frac{15}{17}}}</math>, and <math>x = \frac{r}{4}</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Similarly, we find that <math>y = r/\sqrt{\frac{1 + \frac{8}{17}}{1 - \frac{8}{17}}} = \frac{3r}{5}</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Therefore, <math>x + y + 2r = \frac{r}{4} + \frac{3r}{5} + 2r = \frac{57r}{20} = 34 \Longrightarrow r = \frac{680}{57}</math>, and <math>p + q = 737</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Solution 2 === | ||
| + | Use a similar solution to the aforementioned solution. Instead, call <math>\angle CAB = 2\theta</math>, and then proceed by simplifying through identities. We see that <math>\frac rx = \tan \left(\frac{180 - 2\theta}{2}\right) = \tan (90 - \theta)</math>. In terms of <math>r</math>, we find that <math>x = \frac{r}{\cot \theta} = \frac{r\sin \theta}{\cos \theta}</math>. Similarly, we find that <math>y = \frac{r \sin(45 - \theta)}{\cos (45 - \theta)}</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Substituting, we find that <math>r\left(\frac{\sin \theta}{\cos \theta} + \frac{\sin(45 - \theta)}{\cos (45 - \theta)} + 2\right) = 34</math>. Under a common denominator, <math>r\left(\frac{\sin \theta \cos (45 - \theta) + \cos \theta \sin (45 - \theta)}{\cos \theta \cos (45 - \theta)} + 2\right) = 34</math>. [[Trigonometric identities]] simplify this to <math>r\left(\frac{\sin\left((\theta) + (45 - \theta)\right)}{\frac 12 \left(\cos (\theta + 45 - \theta) + \cos (\theta - 45 + \theta) \right)} + 2\right) = 34</math>. From here, it is possible to simplify: | ||
| + | :<math>r\left(\frac{2 \sin 45}{\cos 45 + \cos 2\theta \cos 45 + \sin 2\theta \sin 45} +2\right) = 34</math> | ||
| + | :<math>r\left(\frac{2}{\frac{17}{17} + \frac{8}{17} + \frac{15}{17}} + 2\right) = 34</math> | ||
| + | :<math>r\left(\frac{57}{20}\right) = 34</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Our answer is <math>34 \cdot \frac{20}{57} = \frac{680}{57}</math>, and <math>p + q = 737</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Solution 3 === | ||
| + | Let the point where CB's extension hits the circle be G, and the point where the hypotenuse hits that circle be E. Clearly <math>EB=GB</math>. Let <math>EB=x</math>. Draw the two [[perpendicular]] radii to G and E. Now we have a [[cyclic quadrilateral]]. Let the radius be length <math>r</math>. We see that since the cosine of angle ABC is <math>\frac{15}{17}</math> the cosine of angle EBG is <math>-\frac{15}{17}</math>. Since the measure of the angle opposite to EBG is the [[complement]] of this one, its cosine is <math>\frac{15}{17}</math>. Using the law of cosines, we see that <math>x^{2}+x^{2}+\frac{30x^{2}}{17}=r^{2}+r^{2}-\frac{30r^{2}}{17}</math> | ||
This tells us that <math>r=4x</math>. | This tells us that <math>r=4x</math>. | ||
| − | Now look at the other end of the hypotenuse. Call the point where CA hits the circle F and the point where the hypotenuse hits the circle | + | Now look at the other end of the hypotenuse. Call the point where CA hits the circle F and the point where the hypotenuse hits the circle D. Draw the radii to F and D and we have cyclic quadrilaterals once more. |
| − | Using the law of cosines again, we find that the length of our tangents is <math>2.4x</math>. Note that if we connect the centers of the circles we have a rectangle with sidelengths 8x and 4x. So, 8x+2.4x+x=34. Solving we find that <math>4x=\frac{680}{57}</math> so our answer is 737. | + | Using the law of cosines again, we find that the length of our tangents is <math>2.4x</math>. Note that if we connect the centers of the circles we have a rectangle with sidelengths 8x and 4x. So, <math>8x+2.4x+x=34</math>. Solving we find that <math>4x=\frac{680}{57}</math> so our answer is 737. |
| + | |||
| + | === Solution 4 === | ||
| + | [[Image:AIME I 2007-9b.png|left]] | ||
| + | By Pythagoras, <math>AB = 34</math>. Let <math>I_{C}</math> be the <math>C</math>-excenter of triangle <math>ABC</math>. Then the <math>C</math>-exradius <math>r_{C}</math> is given by | ||
| + | <math>r_{C}= \frac{K}{s-c}= \frac{240}{40-34}= 40</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The circle with center <math>O_{1}</math> is tangent to both <math>AB</math> and <math>AC</math>, which means that <math>O_{1}</math> lies on the external angle bisector of <math>\angle BAC</math>. Therefore, <math>O_{1}</math> lies on <math>AI_{C}</math>. Similarly, <math>O_{2}</math> lies on <math>BI_{C}</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Let <math>r</math> be the common radius of the circles with centers <math>O_{1}</math> and <math>O_{2}</math>. The distances from points <math>O_{1}</math> and <math>O_{2}</math> to <math>AB</math> are both <math>r</math>, so <math>O_{1}O_{2}</math> is parallel to <math>AB</math>, which means that triangles <math>I_{C}AB</math> and <math>I_{C}O_{1}O_{2}</math> are similar. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The distance from <math>I_{C}</math> to <math>AB</math> is <math>r_{C}= 40</math>, so the distance from <math>I_{C}</math> to <math>O_{1}O_{2}</math> is <math>40-r</math>. Therefore, | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\frac{40-r}{40}= \frac{O_{1}O_{2}}{AB}= \frac{2r}{34}\quad \Rightarrow \quad r = \frac{680}{57}</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Hence, the final answer is <math>680+57 = 737</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Solution 5 === | ||
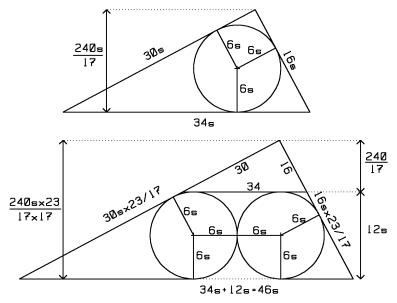
| + | [[Image:AIME I 2007-9c.gif|left]] | ||
| + | Start with a scaled 16-30-34 triangle. [[Inscribe]] a circle. The height, <math>h,</math> and radius, <math>r,</math> are found via <math>A=\frac{1}{2}\times 16s\times 30s=\frac{1}{2}\times 34s\times h=\frac{1}{2}\times rp,</math> where <math>p</math> is the [[perimeter]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Cut the figure through the circle and perpendicular to the hypotenuse. Slide the two pieces in opposite directions along the hypotenuse until they are one diameter of the circle apart. Complete the two partial circles. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The linear dimensions of the new triangle are <math>\frac{46s}{34s}=\frac{23}{17}</math> times the size of the original. The problem's 16-30-34 triangle sits above the circles. Equate heights and solve for <math>r=6s</math>: | ||
| + | <div style="text-align:center;"> | ||
| + | <math>\frac{240s}{17}\times\frac{23}{17} = \frac{240}{17}+12s</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>20s\times 23 = 20\times 17+s\times 17\times 17 </math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>s = \frac{340}{171}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>r = 6s = \frac{680}{57}</math></div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | The answer is <math>737</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Solution 6 === | ||
| + | [[Image:AIME_2007_-9.PNG]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Using [[homothety]] in the diagram above, as well as the [[auxiliary]] triangle, leads to the solution. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Solution 7 === | ||
| + | A different approach is to plot the triangle on the Cartesian Plane with | ||
| + | <math>C</math> at <math>(0,0)</math>, <math>A</math> at <math>(0,30)</math>, and <math>B</math> at <math>(16,0)</math>. We wish to find the coordinates of <math>O_1</math> and <math>O_2</math> in terms of the radius, which will be expressed as <math>r</math> in the rest of this solution. When we know the coordinates, we will set the distance between the 2 points equal to <math>2r</math>. All points <math>r</math> units away from <math>\overline{AB}</math> are on the line with slope <math>-\frac{15}{8}</math>, and y-intercept <math>30+ \frac{17}{8} r</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>O_1</math> will have x-coordinate <math>r</math> and likewise <math>O_2</math> will have y-coordinate <math>r</math> | ||
| + | plugging this into the equation for the line mentioned in the sentence above gives us: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>O_1 = \left(r,\frac14 r+30\right)</math> and <math>O_2 = \left(\frac35 r+16,r\right)</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | By the distance formula and the fact that the circles and tangent, we have: <math>\left(16-\frac25 r\right)^2 + \left(30-\frac34 r\right)^2 = (2r)^2</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | which simplifies into the quadratic equation: <math>1311 r^2 + 23120 r - 462400 = 0</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | And by the quadratic equation, the solutions are: <math>\frac{-23120 \pm 54400}{2622}</math> | ||
| + | The solution including the "<math>-</math>" is extraneous so we have the radius equal to | ||
| + | <math>\frac{31280}{2622}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Which simplifies to <math>\frac{680}{57}</math>. The sum of the numerator and the denominator is <math>\boxed{737}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Solution 8 (simple algebra)=== | ||
| + | It is known that <math>O_1O_2</math> is parallel to AB. Thus, extending <math>O_1F</math> and <math>GO_2</math> to intersect at H yields similar triangles <math>O_1O_2H</math> and BAC, so that <math>O_1O_2 = 2r</math>, <math>O_1H = \frac{16r}{17}</math>, and <math>HO_2 = \frac{30r}{17}</math>. It should be noted that <math>O_2G = r</math>. Also, FHGC is a rectangle, and so AF = <math>\frac{47r}{17} - 30</math> and similarly for BG. Because tangents to a circle are equal, the hypotenuse can be expressed in terms of r: <cmath>2r + \frac{47r}{17} - 30 + \frac{33r}{17} - 16 = 34</cmath> Thus, r = <math>\frac{680}{57}</math>, and the answer is <math>\boxed{737}.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Note=== | ||
| + | When drawing the diagram, it may seem that <math>H</math> lies on circle <math>O_1</math>, but it is actually not: <math>H</math> lies inside of circle <math>O_1</math>. We can see this from the similarity ratios: <math>\frac{O_1O_2}{BA}=\frac{HO_1}{CB}=\frac{HO_2}{CA}</math>. Taking a look at the first equation (<math>\tfrac{O_1O_2}{BA}=\tfrac{HO_1}{CB}</math>), <math>\frac{2r}{34}=\frac{HO_1}{16}</math> which simplifies to <math>\frac r{17}=\frac{HO_1}{16}</math>. Indeed, <math>HO_1</math> does not equal <math>r</math>, instead, <math>HO_1=\frac{16}{17}r</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ~BakedPotato66 | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Solution 9=== | ||
| + | Let the radius of the circle be <math>r</math>. It can be seen that <math>\Delta FHO_{1}</math> and <math>\Delta O_{2}GJ</math> are similar to <math>\Delta ACB</math>, and the length of the hypotenuses are <math>\frac{17}{8}r</math> and <math>\frac {17}{15}r</math>, respectively. Then, the entire length of <math>HJ</math> is going to be <math>(\frac{17}{8}+\frac{17}{15}+2)r = \frac{631}{120}r</math>. The length of the hypotenuse of <math>\Delta ACB</math> is 34, so the length of the height to <math>AB</math> is <math>\frac{16*30}{34} = \frac{240}{17}</math>. Thus, the height to <math>\Delta HCJ</math> is going to be <math>\frac{240}{17} + r</math>. <math>\Delta HCJ</math> is similar to <math>\Delta ACB</math> so we have the following: <math>\frac{\frac{631}{120}r}{34} = \frac{\frac{240}{17} + r}{\frac{240}{17}}</math>. Cross multiplying and simplifying, we get that <math>r = \frac{680}{57}</math> so the answer is <math>\boxed{737}</math>. | ||
| + | ~Leonard_my_dude~ | ||
== See also == | == See also == | ||
| + | [[Exradius]] (Solution 4) | ||
{{AIME box|year=2007|n=I|num-b=8|num-a=10}} | {{AIME box|year=2007|n=I|num-b=8|num-a=10}} | ||
[[Category:Intermediate Geometry Problems]] | [[Category:Intermediate Geometry Problems]] | ||
| + | {{MAA Notice}} | ||
Latest revision as of 19:10, 21 July 2024
Contents
Problem
In right triangle ![]() with right angle
with right angle ![]() ,
, ![]() and
and ![]() . Its legs
. Its legs ![]() and
and ![]() are extended beyond
are extended beyond ![]() and
and ![]() . Points
. Points ![]() and
and ![]() lie in the exterior of the triangle and are the centers of two circles with equal radii. The circle with center
lie in the exterior of the triangle and are the centers of two circles with equal radii. The circle with center ![]() is tangent to the hypotenuse and to the extension of leg
is tangent to the hypotenuse and to the extension of leg ![]() , the circle with center
, the circle with center ![]() is tangent to the hypotenuse and to the extension of leg
is tangent to the hypotenuse and to the extension of leg ![]() , and the circles are externally tangent to each other. The length of the radius either circle can be expressed as
, and the circles are externally tangent to each other. The length of the radius either circle can be expressed as ![]() , where
, where ![]() and
and ![]() are relatively prime positive integers. Find
are relatively prime positive integers. Find ![]() .
.
Solutions
Solution 1
Label the points as in the diagram above. If we draw ![]() and
and ![]() , we form two right triangles. As
, we form two right triangles. As ![]() and
and ![]() are both tangents to the circle, we see that
are both tangents to the circle, we see that ![]() is an angle bisector. Thus,
is an angle bisector. Thus, ![]() . Call
. Call ![]() and
and ![]() . We know that
. We know that ![]() .
.
If we call ![]() , then
, then ![]() . Apply the tangent half-angle formula (
. Apply the tangent half-angle formula (![]() ). We see that
). We see that 
![]() . Also,
. Also, ![]() . Thus,
. Thus,  , and
, and ![]() .
.
Similarly, we find that  .
.
Therefore, ![]() , and
, and ![]() .
.
Solution 2
Use a similar solution to the aforementioned solution. Instead, call ![]() , and then proceed by simplifying through identities. We see that
, and then proceed by simplifying through identities. We see that ![]() . In terms of
. In terms of ![]() , we find that
, we find that ![]() . Similarly, we find that
. Similarly, we find that ![]() .
.
Substituting, we find that ![]() . Under a common denominator,
. Under a common denominator, ![]() . Trigonometric identities simplify this to
. Trigonometric identities simplify this to ![]() . From here, it is possible to simplify:
. From here, it is possible to simplify:
Our answer is ![]() , and
, and ![]() .
.
Solution 3
Let the point where CB's extension hits the circle be G, and the point where the hypotenuse hits that circle be E. Clearly ![]() . Let
. Let ![]() . Draw the two perpendicular radii to G and E. Now we have a cyclic quadrilateral. Let the radius be length
. Draw the two perpendicular radii to G and E. Now we have a cyclic quadrilateral. Let the radius be length ![]() . We see that since the cosine of angle ABC is
. We see that since the cosine of angle ABC is ![]() the cosine of angle EBG is
the cosine of angle EBG is ![]() . Since the measure of the angle opposite to EBG is the complement of this one, its cosine is
. Since the measure of the angle opposite to EBG is the complement of this one, its cosine is ![]() . Using the law of cosines, we see that
. Using the law of cosines, we see that ![]() This tells us that
This tells us that ![]() .
.
Now look at the other end of the hypotenuse. Call the point where CA hits the circle F and the point where the hypotenuse hits the circle D. Draw the radii to F and D and we have cyclic quadrilaterals once more.
Using the law of cosines again, we find that the length of our tangents is ![]() . Note that if we connect the centers of the circles we have a rectangle with sidelengths 8x and 4x. So,
. Note that if we connect the centers of the circles we have a rectangle with sidelengths 8x and 4x. So, ![]() . Solving we find that
. Solving we find that ![]() so our answer is 737.
so our answer is 737.
Solution 4
By Pythagoras, ![]() . Let
. Let ![]() be the
be the ![]() -excenter of triangle
-excenter of triangle ![]() . Then the
. Then the ![]() -exradius
-exradius ![]() is given by
is given by
![]() .
.
The circle with center ![]() is tangent to both
is tangent to both ![]() and
and ![]() , which means that
, which means that ![]() lies on the external angle bisector of
lies on the external angle bisector of ![]() . Therefore,
. Therefore, ![]() lies on
lies on ![]() . Similarly,
. Similarly, ![]() lies on
lies on ![]() .
.
Let ![]() be the common radius of the circles with centers
be the common radius of the circles with centers ![]() and
and ![]() . The distances from points
. The distances from points ![]() and
and ![]() to
to ![]() are both
are both ![]() , so
, so ![]() is parallel to
is parallel to ![]() , which means that triangles
, which means that triangles ![]() and
and ![]() are similar.
are similar.
The distance from ![]() to
to ![]() is
is ![]() , so the distance from
, so the distance from ![]() to
to ![]() is
is ![]() . Therefore,
. Therefore,
![]() .
.
Hence, the final answer is ![]() .
.
Solution 5
Start with a scaled 16-30-34 triangle. Inscribe a circle. The height, ![]() and radius,
and radius, ![]() are found via
are found via ![]() where
where ![]() is the perimeter.
is the perimeter.
Cut the figure through the circle and perpendicular to the hypotenuse. Slide the two pieces in opposite directions along the hypotenuse until they are one diameter of the circle apart. Complete the two partial circles.
The linear dimensions of the new triangle are ![]() times the size of the original. The problem's 16-30-34 triangle sits above the circles. Equate heights and solve for
times the size of the original. The problem's 16-30-34 triangle sits above the circles. Equate heights and solve for ![]() :
:
![]()
![]()
![]()
The answer is ![]() .
.
Solution 6
Using homothety in the diagram above, as well as the auxiliary triangle, leads to the solution.
Solution 7
A different approach is to plot the triangle on the Cartesian Plane with
![]() at
at ![]() ,
, ![]() at
at ![]() , and
, and ![]() at
at ![]() . We wish to find the coordinates of
. We wish to find the coordinates of ![]() and
and ![]() in terms of the radius, which will be expressed as
in terms of the radius, which will be expressed as ![]() in the rest of this solution. When we know the coordinates, we will set the distance between the 2 points equal to
in the rest of this solution. When we know the coordinates, we will set the distance between the 2 points equal to ![]() . All points
. All points ![]() units away from
units away from ![]() are on the line with slope
are on the line with slope ![]() , and y-intercept
, and y-intercept ![]()
![]() will have x-coordinate
will have x-coordinate ![]() and likewise
and likewise ![]() will have y-coordinate
will have y-coordinate ![]() plugging this into the equation for the line mentioned in the sentence above gives us:
plugging this into the equation for the line mentioned in the sentence above gives us:
![]() and
and ![]()
By the distance formula and the fact that the circles and tangent, we have: ![]()
which simplifies into the quadratic equation: ![]()
And by the quadratic equation, the solutions are: ![]() The solution including the "
The solution including the "![]() " is extraneous so we have the radius equal to
" is extraneous so we have the radius equal to
![]()
Which simplifies to ![]() . The sum of the numerator and the denominator is
. The sum of the numerator and the denominator is ![]()
Solution 8 (simple algebra)
It is known that ![]() is parallel to AB. Thus, extending
is parallel to AB. Thus, extending ![]() and
and ![]() to intersect at H yields similar triangles
to intersect at H yields similar triangles ![]() and BAC, so that
and BAC, so that ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() . It should be noted that
. It should be noted that ![]() . Also, FHGC is a rectangle, and so AF =
. Also, FHGC is a rectangle, and so AF = ![]() and similarly for BG. Because tangents to a circle are equal, the hypotenuse can be expressed in terms of r:
and similarly for BG. Because tangents to a circle are equal, the hypotenuse can be expressed in terms of r: ![]() Thus, r =
Thus, r = ![]() , and the answer is
, and the answer is ![]()
Note
When drawing the diagram, it may seem that ![]() lies on circle
lies on circle ![]() , but it is actually not:
, but it is actually not: ![]() lies inside of circle
lies inside of circle ![]() . We can see this from the similarity ratios:
. We can see this from the similarity ratios: ![]() . Taking a look at the first equation (
. Taking a look at the first equation (![]() ),
), ![]() which simplifies to
which simplifies to ![]() . Indeed,
. Indeed, ![]() does not equal
does not equal ![]() , instead,
, instead, ![]() .
.
~BakedPotato66
Solution 9
Let the radius of the circle be ![]() . It can be seen that
. It can be seen that ![]() and
and ![]() are similar to
are similar to ![]() , and the length of the hypotenuses are
, and the length of the hypotenuses are ![]() and
and ![]() , respectively. Then, the entire length of
, respectively. Then, the entire length of ![]() is going to be
is going to be ![]() . The length of the hypotenuse of
. The length of the hypotenuse of ![]() is 34, so the length of the height to
is 34, so the length of the height to ![]() is
is ![]() . Thus, the height to
. Thus, the height to ![]() is going to be
is going to be ![]() .
. ![]() is similar to
is similar to ![]() so we have the following:
so we have the following: ![]() . Cross multiplying and simplifying, we get that
. Cross multiplying and simplifying, we get that ![]() so the answer is
so the answer is ![]() .
~Leonard_my_dude~
.
~Leonard_my_dude~
See also
Exradius (Solution 4)
| 2007 AIME I (Problems • Answer Key • Resources) | ||
| Preceded by Problem 8 |
Followed by Problem 10 | |
| 1 • 2 • 3 • 4 • 5 • 6 • 7 • 8 • 9 • 10 • 11 • 12 • 13 • 14 • 15 | ||
| All AIME Problems and Solutions | ||
The problems on this page are copyrighted by the Mathematical Association of America's American Mathematics Competitions.