Difference between revisions of "2013 AMC 10A Problems/Problem 20"
Countingkg (talk | contribs) |
m (→Solution 2) |
||
| (46 intermediate revisions by 16 users not shown) | |||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
<math> \textbf{(A)}\ 1 - \frac{\sqrt2}{2} + \frac{\pi}{4}\qquad\textbf{(B)}\ \frac{1}{2} + \frac{\pi}{4} \qquad\textbf{(C)}\ 2 - \sqrt2 + \frac{\pi}{4}\qquad\textbf{(D)}\ \frac{\sqrt2}{2} + \frac{\pi}{4} \qquad\textbf{(E)}\ 1 + \frac{\sqrt2}{4} + \frac{\pi}{8} </math> | <math> \textbf{(A)}\ 1 - \frac{\sqrt2}{2} + \frac{\pi}{4}\qquad\textbf{(B)}\ \frac{1}{2} + \frac{\pi}{4} \qquad\textbf{(C)}\ 2 - \sqrt2 + \frac{\pi}{4}\qquad\textbf{(D)}\ \frac{\sqrt2}{2} + \frac{\pi}{4} \qquad\textbf{(E)}\ 1 + \frac{\sqrt2}{4} + \frac{\pi}{8} </math> | ||
| + | [[Category: Introductory Geometry Problems]] | ||
| − | ==Solution== | + | ==Solution 1== |
First, we need to see what this looks like. Below is a diagram. | First, we need to see what this looks like. Below is a diagram. | ||
| Line 19: | Line 20: | ||
path arcrot=arc(origin,sqrt(2)/2,45+90*i,90*(i+1)); | path arcrot=arc(origin,sqrt(2)/2,45+90*i,90*(i+1)); | ||
draw(arcrot); | draw(arcrot); | ||
| − | fill(arcrot--( | + | fill(arcrot--(0,0)--cycle,grey); |
draw(arc(origin,sqrt(2)/2+1/8,50+90*i,90*(i+1)-10),EndArrow); | draw(arc(origin,sqrt(2)/2+1/8,50+90*i,90*(i+1)-10),EndArrow); | ||
} | } | ||
draw(square^^square2);</asy> | draw(square^^square2);</asy> | ||
| − | For this square with side length 1, the distance from center to vertex is <math>r = \frac | + | For this square with side length 1, the distance from center to vertex is <math>r = \frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}</math>, hence the area is composed of a semicircle of radius <math>r</math>, plus <math>4</math> times a parallelogram (or a kite with diagonals of <math>(\sqrt{2}-1)</math> and <math>r \text{ or} \frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}</math>) with height <math>\frac{1}{2}</math> and base <math>\frac{\sqrt{2}}{2(1+\sqrt{2})}</math>. That is to say, the total area is <math>\frac{1}{2} \pi \left(\frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\right)^2 + 4 \frac{\sqrt{2}}{4(1+\sqrt{2})} = \boxed{\textbf{(C) } 2 - \sqrt{2} + \frac{\pi}{4}}</math>. |
| + | |||
| + | <asy> | ||
| + | size(150);defaultpen(linewidth(0.8)); | ||
| + | path square=shift((-.5,-.5))*unitsquare,square2=rotate(45)*square;//fill(square^^square2,grey); | ||
| + | for(int i=0;i<=3;i=i+1){path arcrot=arc(origin,sqrt(2)/2,45+90*i,90*(i+1));draw(arcrot); | ||
| + | fill(arcrot--(0,0)--cycle,grey);} | ||
| + | //draw(arc(origin,sqrt(2)/2+1/8,50+90*i,90*(i+1)-10),EndArrow);} | ||
| + | draw(square^^square2); | ||
| + | //draw((-.5,.5)--(.5,-.5)^^(0,sqrt(.5))--(0,-sqrt(.5)),dotted);draw((.5,.5)--(-.5,-.5),dotted); | ||
| + | </asy> | ||
| + | (To turn each dart-shaped piece into a parallelogram, cut along the dashed line and flip over one half.) | ||
| + | <asy> | ||
| + | size(150,Aspect);real r=sqrt(2);real b=2-2/r; | ||
| + | draw((0,0)--(-1,1)--(b-1,1)--(0,r)--cycle);draw((0,1)--(b-1,1)--(b/2-1,1-b/2));draw((0,0)--(b-1,1),dashed); | ||
| + | fill((2,0)--(b+1,1)--(b+2,0)--cycle,lightgray);draw((.5,.5)--(1,.5),EndArrow); | ||
| + | draw((2,0)--(1,1)--(b+1,1)--(b+2,0)--(2,0)^^(b+1,1)--(b/2+1,1-b/2)^^(2,0)--(2+b/2,b/2)); | ||
| + | draw((2,0)--(b+1,1),dashed); | ||
| + | </asy> | ||
| + | Alternatively, you can move the dart-shaped piece to the other side and make a kite. | ||
| + | <asy> | ||
| + | size(75,Aspect);real r=sqrt(2);real b=2-2/r; | ||
| + | draw((r-1,1)--(b-1,1)); | ||
| + | draw((0,0)--(b-1,1)--(0,r)--(r-1,1)--cycle); | ||
| + | draw((0,r)--(0,0),dashed); | ||
| + | </asy> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Solution 2== | ||
| + | <asy> | ||
| + | size(200); | ||
| + | defaultpen(linewidth(0.8)); | ||
| + | path square=shift((-.5,-.5))*unitsquare,square2=rotate(45)*square; | ||
| + | for(int i=0;i<=6;i=i+1) | ||
| + | { | ||
| + | path arcrot=arc(origin,sqrt(2)/2,45+270*i,270*(i+1)); | ||
| + | draw(arcrot); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | draw(square^^square2);</asy> | ||
| + | <center><math>\textbf{(high res image; no labels)}</math></center> | ||
| + | [[Image:AMC 10A 2013 20.jpg]] | ||
| + | |||
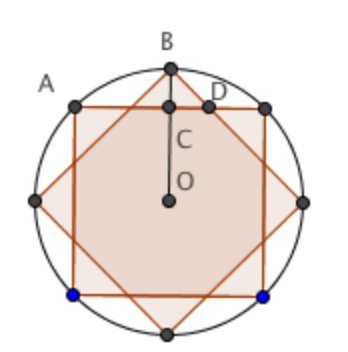
| + | Let <math>O</math> be the center of the square and <math>C</math> be the intersection of <math>OB</math> and <math>AD</math>. The desired area consists of the unit square, plus <math>4</math> regions congruent to the region bounded by arc <math>AB</math>, <math>\overline{AC}</math>, and <math>\overline{BC}</math>, plus <math>4</math> triangular regions congruent to right triangle <math>BCD</math>. The area of the region bounded by arc <math>AB</math>, <math>\overline{AC}</math>, and <math>\overline{BC}</math> is <math>\frac{\text{Area of Circle}-\text{Area of Square}}{8}</math>. Since the circle has radius <math>\dfrac{1}{\sqrt {2}}</math>, the area of the region is <math>\dfrac{\dfrac{\pi}{2}-1}{8}</math>, so 4 times the area of that region is <math>\dfrac{\pi}{4}-\dfrac{1}{2}</math>. Now we find the area of <math>\triangle BCD</math>. <math>BC=BO-OC=\dfrac{\sqrt {2}}{2}-\dfrac{1}{2}</math>. Since <math>\triangle BCD</math> is a <math>45-45-90</math> right triangle, the area of <math>\triangle BCD</math> is <math>\dfrac{BC^2}{2}=\dfrac {\left (\dfrac {\sqrt {2}}{2}-\dfrac{1}{2} \right)^2}{2}</math>, so <math>4</math> times the area of <math>\triangle BCD</math> is <math>\dfrac{3}{2}-\sqrt {2}</math>. Finally, the area of the whole region is <math>1+ \left(\dfrac {3}{2}-\sqrt {2} \right) + \left(\dfrac{\pi}{4}-\dfrac{1}{2} \right)=\dfrac{\pi}{4}+2-\sqrt {2}</math>, which we can rewrite as <math>\boxed{\textbf{(C) } 2 - \sqrt{2} + \frac{\pi}{4}}</math>. | ||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
{{AMC10 box|year=2013|ab=A|num-b=19|num-a=21}} | {{AMC10 box|year=2013|ab=A|num-b=19|num-a=21}} | ||
| + | {{MAA Notice}} | ||
Latest revision as of 16:55, 23 July 2021
Contents
Problem
A unit square is rotated ![]() about its center. What is the area of the region swept out by the interior of the square?
about its center. What is the area of the region swept out by the interior of the square?
![]()
Solution 1
First, we need to see what this looks like. Below is a diagram.
![[asy] size(200); defaultpen(linewidth(0.8)); path square=shift((-.5,-.5))*unitsquare,square2=rotate(45)*square; fill(square^^square2,grey); for(int i=0;i<=3;i=i+1) { path arcrot=arc(origin,sqrt(2)/2,45+90*i,90*(i+1)); draw(arcrot); fill(arcrot--(0,0)--cycle,grey); draw(arc(origin,sqrt(2)/2+1/8,50+90*i,90*(i+1)-10),EndArrow); } draw(square^^square2);[/asy]](http://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/2/c/e/2cef856b58cfff2a7283d5219d0dfdaa03042386.png)
For this square with side length 1, the distance from center to vertex is ![]() , hence the area is composed of a semicircle of radius
, hence the area is composed of a semicircle of radius ![]() , plus
, plus ![]() times a parallelogram (or a kite with diagonals of
times a parallelogram (or a kite with diagonals of ![]() and
and ![]() ) with height
) with height ![]() and base
and base ![]() . That is to say, the total area is
. That is to say, the total area is  .
.
![[asy] size(150);defaultpen(linewidth(0.8)); path square=shift((-.5,-.5))*unitsquare,square2=rotate(45)*square;//fill(square^^square2,grey); for(int i=0;i<=3;i=i+1){path arcrot=arc(origin,sqrt(2)/2,45+90*i,90*(i+1));draw(arcrot); fill(arcrot--(0,0)--cycle,grey);} //draw(arc(origin,sqrt(2)/2+1/8,50+90*i,90*(i+1)-10),EndArrow);} draw(square^^square2); //draw((-.5,.5)--(.5,-.5)^^(0,sqrt(.5))--(0,-sqrt(.5)),dotted);draw((.5,.5)--(-.5,-.5),dotted); [/asy]](http://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/1/8/4/184aa4bab0f1d089a1cc659b41a0c3fae9aa9e7a.png) (To turn each dart-shaped piece into a parallelogram, cut along the dashed line and flip over one half.)
(To turn each dart-shaped piece into a parallelogram, cut along the dashed line and flip over one half.)
![[asy] size(150,Aspect);real r=sqrt(2);real b=2-2/r; draw((0,0)--(-1,1)--(b-1,1)--(0,r)--cycle);draw((0,1)--(b-1,1)--(b/2-1,1-b/2));draw((0,0)--(b-1,1),dashed); fill((2,0)--(b+1,1)--(b+2,0)--cycle,lightgray);draw((.5,.5)--(1,.5),EndArrow); draw((2,0)--(1,1)--(b+1,1)--(b+2,0)--(2,0)^^(b+1,1)--(b/2+1,1-b/2)^^(2,0)--(2+b/2,b/2)); draw((2,0)--(b+1,1),dashed); [/asy]](http://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/4/f/5/4f5c5a5cf3a60dd0e7cdc32bb0caf1b6d792df89.png) Alternatively, you can move the dart-shaped piece to the other side and make a kite.
Alternatively, you can move the dart-shaped piece to the other side and make a kite.
![[asy] size(75,Aspect);real r=sqrt(2);real b=2-2/r; draw((r-1,1)--(b-1,1)); draw((0,0)--(b-1,1)--(0,r)--(r-1,1)--cycle); draw((0,r)--(0,0),dashed); [/asy]](http://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/4/9/a/49a54e3a86d6718092983262eb1a1ceb745723aa.png)
Solution 2
![[asy] size(200); defaultpen(linewidth(0.8)); path square=shift((-.5,-.5))*unitsquare,square2=rotate(45)*square; for(int i=0;i<=6;i=i+1) { path arcrot=arc(origin,sqrt(2)/2,45+270*i,270*(i+1)); draw(arcrot); } draw(square^^square2);[/asy]](http://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/3/9/b/39baf46e49824d8bc53a4b853563984045ce96b7.png)
Let ![]() be the center of the square and
be the center of the square and ![]() be the intersection of
be the intersection of ![]() and
and ![]() . The desired area consists of the unit square, plus
. The desired area consists of the unit square, plus ![]() regions congruent to the region bounded by arc
regions congruent to the region bounded by arc ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() , plus
, plus ![]() triangular regions congruent to right triangle
triangular regions congruent to right triangle ![]() . The area of the region bounded by arc
. The area of the region bounded by arc ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() is
is ![]() . Since the circle has radius
. Since the circle has radius ![]() , the area of the region is
, the area of the region is ![]() , so 4 times the area of that region is
, so 4 times the area of that region is ![]() . Now we find the area of
. Now we find the area of ![]() .
. ![]() . Since
. Since ![]() is a
is a ![]() right triangle, the area of
right triangle, the area of ![]() is
is  , so
, so ![]() times the area of
times the area of ![]() is
is ![]() . Finally, the area of the whole region is
. Finally, the area of the whole region is ![]() , which we can rewrite as
, which we can rewrite as ![]() .
.
See Also
| 2013 AMC 10A (Problems • Answer Key • Resources) | ||
| Preceded by Problem 19 |
Followed by Problem 21 | |
| 1 • 2 • 3 • 4 • 5 • 6 • 7 • 8 • 9 • 10 • 11 • 12 • 13 • 14 • 15 • 16 • 17 • 18 • 19 • 20 • 21 • 22 • 23 • 24 • 25 | ||
| All AMC 10 Problems and Solutions | ||
The problems on this page are copyrighted by the Mathematical Association of America's American Mathematics Competitions.