Difference between revisions of "Asymptote: Getting Started/Windows/Interactive Mode"
| Line 48: | Line 48: | ||
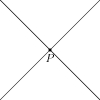
Finally, press Ctrl+A (or whatever hot key you assigned in step 6 above), and you should see the following image: | Finally, press Ctrl+A (or whatever hot key you assigned in step 6 above), and you should see the following image: | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | [[Image:PointX.jpg]] | |
| − | + | ||
| − | |||
If you wish to include such images directly inside your LaTeX documents, see the section under Advanced Configuration on \hyperlink{TeX}{LaTeX}. | If you wish to include such images directly inside your LaTeX documents, see the section under Advanced Configuration on \hyperlink{TeX}{LaTeX}. | ||
Now for the fun part - you are ready to learn the Asymptote language and produce beautiful figures! | Now for the fun part - you are ready to learn the Asymptote language and produce beautiful figures! | ||
Revision as of 12:41, 22 January 2007
When Asymptote is run, it looks for a file called config.asy in the folder
C:\Documents and Settings\%USERNAME\.asy\
where %USERNAME is your Windows user name. Browse to the folder
C:\Documents and Settings\%USERNAME\.asy\
and create a new folder. Rename this folder ".asy" (without the quotes). Double-click on the .asy folder, right click in the folder and choose New ![]() Text Document. This will create a file called New Text Document.txt. Right-click on this file to rename it as config.asy, then open this file with Notepad or a similar editor. Type or copy-and-paste the following lines into the document:
Text Document. This will create a file called New Text Document.txt. Right-click on this file to rename it as config.asy, then open this file with Notepad or a similar editor. Type or copy-and-paste the following lines into the document:
import settings; psviewer="C:\Program Files\Ghostgum\gsview\gsview32.exe"; dir="C:\Program Files\Asymptote";
This sets the eps viewer and Asymptote directory for your files. (IMPORTANT: If you installed any of gsview or Asymptote in a different directory than the default directory, the path names above must be changed to the ones that you chose. If you are not sure if you kept the default directories, browse to C:\Program Files and browse to each of the paths above.)
When you have finished this, save the file config.asy.
At this point, you are ready to use Asymptote in "Interactive Mode". To test that you have done the previous steps correctly:
- Run the program asy.exe. You will see a black window, prompting you with a > sign.
- Type:
asy
and press Enter.
- On the next line, type:
draw((0,0)--(100,100));
Press Enter again, and GSview should pop up, displaying a diagonal line about 1.3 inches in length. (The command drew the path connecting points (0,0) and (100,100) in Cartesian coordinates; to learn more about points, paths, and the draw command, see the Basics section.) If something went wrong, go back over the first steps in this section and make sure each path name in config.asy matches the location of the corresponding program.
One can continue to use Asymptote in this interactive mode, with each new draw or label command adding something to the diagram. However, this is horribly inefficient. In order to use Asymptote efficiently, it is best to use a powerful editor such as TeXnicCenter (see Art of Problem Solving's [instructions] in the LaTeX guide) or Crimson Editor to write files containing code for an entire diagram in Asymptote, and compile the file with Asymptote. There are many ways to do this, and many such editors available, but this guide will explain how to configure TeXnicCenter to quickly compile your Asymptote code, in order to be consistent with Art of Problem Solving's LaTeX guide.
Using TeXnicCenter for Asymptote
First, download and install TeXnicCenter according to the instructions given [here]. Now, use the following steps to set up TeXnicCenter to compile your Asymptote file with the press of a button:
- Go to the Tools menu, and click Customize.
- You will see a tab at the top of the Customize window that says Tools. Click on this tab.
- Click on the New (Insert) button - the one that looks like a dotted rectangle with a star - to create a new Tool. Name the tool whatever you like, say Asymptote.
- Click on your newly created Asymptote tool. There are three information blocks to fill in:
- In the Command block, type in "C:\Program Files\asy.exe" (with the quotes, to ensure that it is a single file name) if you used the default installation folder, or browse to the directory in which you installed Asymptote in order to enter the full path name of asy.exe.
- In the Arguments block, type or copy-and-paste the following line:
-batchView -tex "latex" -align C %tc
This tells Asymptote to produce and view an eps file given the corresponding Asymptote code in your current document.
- In the Initial directory block, type %dc.
- Now you will want to make a shortcut key, or hotkey, to run this tool. Click on the Keyboard tab in the Customize window.
- Set the Category to Tools, and your Asymptote tool will appear. Click on Asymptote and then on the Press New Shortcut Key block. Then press Ctrl+A (or any other convenient shortcut key that you wish to use), and click Assign.
Congratulations! You are now ready to create your first Asymptote document.
To do so, create a new file in TeXnicCenter and save it as test.asy. Type the following code into the document:
draw((0,0)--(100,100));
draw((0,100)--(100,0));
dot((50,50));}
label(" ",(50,50),S);
",(50,50),S);
Finally, press Ctrl+A (or whatever hot key you assigned in step 6 above), and you should see the following image:
If you wish to include such images directly inside your LaTeX documents, see the section under Advanced Configuration on \hyperlink{TeX}{LaTeX}.
Now for the fun part - you are ready to learn the Asymptote language and produce beautiful figures!