Difference between revisions of "2011 AIME II Problems/Problem 10"
Mr.sharkman (talk | contribs) |
Treehead123 (talk | contribs) (Added an analytic geometry solution with diagrams) |
||
| Line 122: | Line 122: | ||
-Mr.Sharkman | -Mr.Sharkman | ||
| + | Note: my solution was very long and tedious. It was definitely was the least elegant solution. The only thing I like about it is it contains no quadratic equations (unless you count LoC). | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Solution 7 Analytic Geometry== | ||
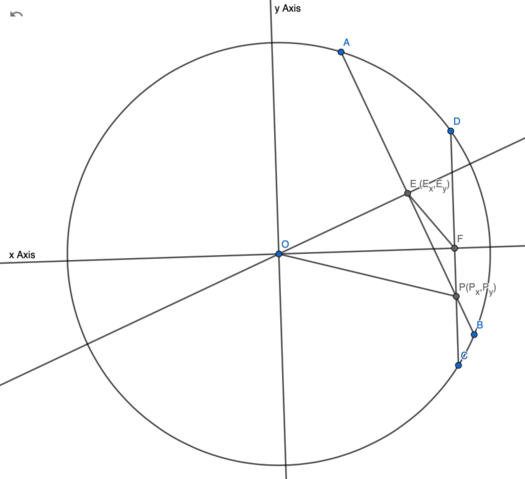
| + | [[Image:2011 AIMEII Problem 10 CASE 2.png|525px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Let <math>E</math> and <math>F</math> be the midpoints of <math>\overline{AB}</math> and <math>\overline{CD}</math>, respectively, such that <math>\overline{BE}</math> intersects <math>\overline{CF}</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Since <math>E</math> and <math>F</math> are midpoints, <math>BE = 15</math> and <math>CF = 7</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>B</math> and <math>C</math> are located on the circumference of the circle, so <math>OB = OC = 25</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Since <math>\overline{OE}\perp \overline{AB}</math> and <math>\overline{OF}\perp \overline{CD}</math>, | ||
| + | <math>OE = \sqrt{OB^2-BE^2}=20</math> and <math>OF = \sqrt{OC^2-OF^2}=24</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | With law of cosines, <math>\cos \angle EOF = \frac{OE^2+OF^2-EF^2}{2\cdot OE\cdot OF} = \frac{13}{15}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Since <math>EF < OF</math>, <math>\angle EOF</math> is acute angle. <math>\sin \angle EOF = \sqrt{1-\cos^2 \angle EOF} = \frac{\sqrt{56}}{15}</math> and <math>\tan \angle EOF = \frac{\sqrt{56}}{13}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Let <math>\overline{OF}</math> line be <math>x</math> axis. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Line <math>\overline{DC}</math> equation is <math>x = OF</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Since line <math>\overline{AB}</math> passes point <math>E</math> and perpendicular to <math>\overline{OD}</math>, its equation is <math>y - E_y = -\frac{1}{\tan \angle EOF} (x - E_x)</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | where <math>E_x = OE\cos{\angle EOF}</math> , <math>E_y = OE\sin{\angle EOF}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Since <math>P</math> is the intersection of <math>\overline{AB}</math> and <math>\overline{CD}</math>, | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>P_x = OF = 24</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>P_y = E_y -\frac{1}{\tan \angle EOF} (OF - E_x) = - \frac{3\sqrt{14}}{7}</math> (Negative means point <math>P</math> is between point <math>F</math> and <math>C</math>) | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>OP^2 = P_x^2 + P_y^2 = \frac{4050}{7}</math> and the answer is <math>\boxed{057}</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Note: if <math>EF</math> was longer, point <math>P</math> would be between point <math>D</math> and <math>F</math>. Then, <math>OP</math> would be the diagonal of quadrilateral <math>OEPF</math> not the diagonal. For example, | ||
| + | |||
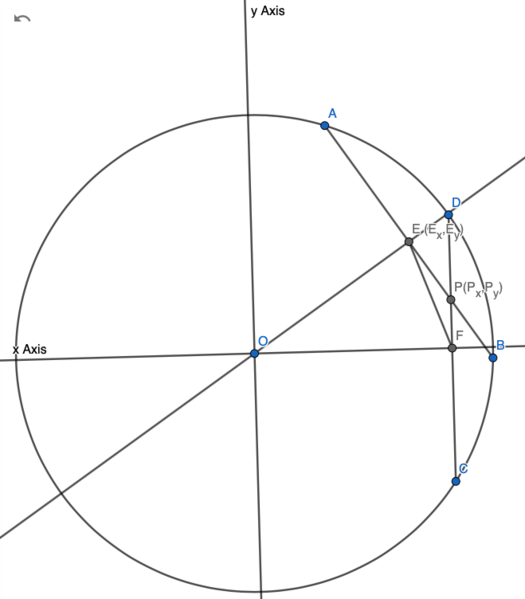
| + | [[Image:2011 AIMEII Problem 10 CASE 1.png|525px]] | ||
| − | |||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
{{AIME box|year=2011|n=II|num-b=9|num-a=11}} | {{AIME box|year=2011|n=II|num-b=9|num-a=11}} | ||
Revision as of 01:23, 18 December 2023
Contents
Problem 10
A circle with center ![]() has radius 25. Chord
has radius 25. Chord ![]() of length 30 and chord
of length 30 and chord ![]() of length 14 intersect at point
of length 14 intersect at point ![]() . The distance between the midpoints of the two chords is 12. The quantity
. The distance between the midpoints of the two chords is 12. The quantity ![]() can be represented as
can be represented as ![]() , where
, where ![]() and
and ![]() are relatively prime positive integers. Find the remainder when
are relatively prime positive integers. Find the remainder when ![]() is divided by 1000.
is divided by 1000.
Solution 1
Let ![]() and
and ![]() be the midpoints of
be the midpoints of ![]() and
and ![]() , respectively, such that
, respectively, such that ![]() intersects
intersects ![]() .
.
Since ![]() and
and ![]() are midpoints,
are midpoints, ![]() and
and ![]() .
.
![]() and
and ![]() are located on the circumference of the circle, so
are located on the circumference of the circle, so ![]() .
.
The line through the midpoint of a chord of a circle and the center of that circle is perpendicular to that chord, so ![]() and
and ![]() are right triangles (with
are right triangles (with ![]() and
and ![]() being the right angles). By the Pythagorean Theorem,
being the right angles). By the Pythagorean Theorem, ![]() , and
, and ![]() .
.
Let ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() be lengths
be lengths ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() , respectively. OEP and OFP are also right triangles, so
, respectively. OEP and OFP are also right triangles, so ![]() , and
, and ![]()
We are given that ![]() has length 12, so, using the Law of Cosines with
has length 12, so, using the Law of Cosines with ![]() :
:
![]()
Substituting for ![]() and
and ![]() , and applying the Cosine of Sum formula:
, and applying the Cosine of Sum formula:
![]()
![]() and
and ![]() are acute angles in right triangles, so substitute opposite/hypotenuse for sines and adjacent/hypotenuse for cosines:
are acute angles in right triangles, so substitute opposite/hypotenuse for sines and adjacent/hypotenuse for cosines:

Combine terms and multiply both sides by ![]() :
: ![]()
Combine terms again, and divide both sides by 64: ![]()
Square both sides: ![]()
This reduces to ![]() ;
; ![]() .
.
Solution 2 - Fastest
We begin as in the first solution. Once we see that ![]() has side lengths
has side lengths ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() , we can compute its area with Heron's formula:
, we can compute its area with Heron's formula:
![]()
Thus, the circumradius of triangle ![]() is
is ![]() . Looking at
. Looking at ![]() , we see that
, we see that ![]() , which makes it a cyclic quadrilateral. This means
, which makes it a cyclic quadrilateral. This means ![]() 's circumcircle and
's circumcircle and ![]() 's inscribed circle are the same.
's inscribed circle are the same.
Since ![]() is cyclic with diameter
is cyclic with diameter ![]() , we have
, we have ![]() , so
, so ![]() and the answer is
and the answer is ![]() .
.
Solution 3
We begin as the first solution have ![]() and
and ![]() . Because
. Because ![]() , Quadrilateral
, Quadrilateral ![]() is inscribed in a Circle. Assume point
is inscribed in a Circle. Assume point ![]() is the center of this circle.
is the center of this circle.
![]()
![]() point
point ![]() is on
is on ![]()
Link ![]() and
and ![]() , Made line
, Made line ![]() , then
, then ![]()
On the other hand, ![]()
![]()
As a result, ![]()
Therefore, ![]()
As a result, ![]()
Solution 4
Let ![]() .
.
Proceed as the first solution in finding that quadrilateral ![]() has side lengths
has side lengths ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() , and diagonals
, and diagonals ![]() and
and ![]() .
.
We note that quadrilateral ![]() is cyclic and use Ptolemy's theorem to solve for
is cyclic and use Ptolemy's theorem to solve for ![]() :
:
![]()
Solving, we have ![]() so the answer is
so the answer is ![]() .
.
-Solution by blueberrieejam
~bluesoul changes the equation to a right equation, the previous equation isn't solvable
Solution 5 (Quick Angle Solution)
Let ![]() be the midpoint of
be the midpoint of ![]() and
and ![]() of
of ![]() . As
. As ![]() , quadrilateral
, quadrilateral ![]() is cyclic with diameter
is cyclic with diameter ![]() . By Cyclic quadrilaterals note that
. By Cyclic quadrilaterals note that ![]() .
.
The area of ![]() can be computed by Herons as
can be computed by Herons as ![]() The area is also
The area is also ![]() . Therefore,
. Therefore,
![\begin{align*} \sin{\angle MNO} &= \frac{2[MNO]}{ON \cdot MN} \\ &= \frac{2}{9}\sqrt{14} \\ \sin{\angle MNO} &= \frac{OM}{OP} \\ &= \frac{2}{9}\sqrt{14} \\ OP &= \frac{90\sqrt{14}}{14} \\ OP^2 &= \frac{4050}{7} \implies \boxed{057}. \end{align*}](http://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/c/9/a/c9ac27140d40c3ee394c8efb3e156e2c36a45941.png)
~ Aaryabhatta1
Solution 6
Define ![]() and
and ![]() as the midpoints of
as the midpoints of ![]() and
and ![]() , respectively. Because
, respectively. Because ![]() , we have that
, we have that ![]() is a cyclic quadrilateral. Hence,
is a cyclic quadrilateral. Hence, ![]() Then, let these two angles be denoted as
Then, let these two angles be denoted as ![]() .
Now, assume WLOG that
.
Now, assume WLOG that ![]() and
and ![]() (We can do this because one of
(We can do this because one of ![]() or
or ![]() must be less than 7, and similarly for
must be less than 7, and similarly for ![]() and
and ![]() ). Then, by Power of a Point on P with respect to the circle with center
). Then, by Power of a Point on P with respect to the circle with center ![]() , we have that
, we have that
![]()
![]() Then, let
Then, let ![]() . From Law of Cosines on
. From Law of Cosines on ![]() , we have that
, we have that
![]()
![]() Plugging in
Plugging in ![]() in gives
in gives
![]()
![]()
![]() Hence,
Hence,
![]() Then, we also know that
Then, we also know that
![]() Squaring this, we get
Squaring this, we get
![]() Equating our expressions for
Equating our expressions for ![]() , we get
, we get
![]() Solving gives us that
Solving gives us that
![]() .
Since
.
Since ![]() , from the Pythagorean Theorem,
, from the Pythagorean Theorem,
![]() ,
and thus the answer is
,
and thus the answer is ![]() , which when divided by a thousand leaves a remainder of
, which when divided by a thousand leaves a remainder of ![]()
-Mr.Sharkman
Note: my solution was very long and tedious. It was definitely was the least elegant solution. The only thing I like about it is it contains no quadratic equations (unless you count LoC).
Solution 7 Analytic Geometry
Let ![]() and
and ![]() be the midpoints of
be the midpoints of ![]() and
and ![]() , respectively, such that
, respectively, such that ![]() intersects
intersects ![]() .
.
Since ![]() and
and ![]() are midpoints,
are midpoints, ![]() and
and ![]() .
.
![]() and
and ![]() are located on the circumference of the circle, so
are located on the circumference of the circle, so ![]() .
.
Since ![]() and
and ![]() ,
,
![]() and
and ![]()
With law of cosines, ![]()
Since ![]() ,
, ![]() is acute angle.
is acute angle. ![]() and
and ![]()
Let ![]() line be
line be ![]() axis.
axis.
Line ![]() equation is
equation is ![]() .
.
Since line ![]() passes point
passes point ![]() and perpendicular to
and perpendicular to ![]() , its equation is
, its equation is ![]()
where ![]() ,
, ![]()
Since ![]() is the intersection of
is the intersection of ![]() and
and ![]() ,
,
![]()
![]() (Negative means point
(Negative means point ![]() is between point
is between point ![]() and
and ![]() )
)
![]() and the answer is
and the answer is ![]() .
.
Note: if ![]() was longer, point
was longer, point ![]() would be between point
would be between point ![]() and
and ![]() . Then,
. Then, ![]() would be the diagonal of quadrilateral
would be the diagonal of quadrilateral ![]() not the diagonal. For example,
not the diagonal. For example,
See also
| 2011 AIME II (Problems • Answer Key • Resources) | ||
| Preceded by Problem 9 |
Followed by Problem 11 | |
| 1 • 2 • 3 • 4 • 5 • 6 • 7 • 8 • 9 • 10 • 11 • 12 • 13 • 14 • 15 | ||
| All AIME Problems and Solutions | ||
The problems on this page are copyrighted by the Mathematical Association of America's American Mathematics Competitions.