Difference between revisions of "DVI exam"
(→2024 1 Problem 2) |
(→2024 var 3 Problem 6) |
||
| Line 526: | Line 526: | ||
Answer: <math>11,23.</math> | Answer: <math>11,23.</math> | ||
| − | ==2024 var | + | ==2024 var 243 Problem 6== |
Solve the system of equations in the positive <math>x, y, z:</math> | Solve the system of equations in the positive <math>x, y, z:</math> | ||
<cmath>\left\{ | <cmath>\left\{ | ||
Revision as of 13:17, 15 July 2024
DVI is an exam in mathematics at the Moscow State University named after M.V. Lomonosov. The first four problems have a standard level. Problem 5 is advanced level of geometry. Problem 6 is an advanced level equation or inequality. Problem 7 is advanced level of stereometry.
Below are the most difficult problems of this exam in recent years. The headings indicate the year when the problem was used, the variant option of the exam, and the number of the problem.
Contents
[hide]- 1 2011 Problem 8
- 2 2012 Problem 8
- 3 2014 1 Problem 6
- 4 2014 1 Problem 8
- 5 2015 1 Problem 7
- 6 2016 2 Problem 7
- 7 2016 2 Problem 8
- 8 2020 201 problem 6
- 9 2020 202 problem 6
- 10 2020 203 problem 6
- 11 2020 204 problem 6
- 12 2020 205 problem 6
- 13 2020 206 problem 6
- 14 2021 215 problem 7
- 15 2022 221 problem 7
- 16 2022 222 problem 7
- 17 2022 222 problem 6
- 18 2022 224 problem 6
- 19 2023 231 problem 6
- 20 2023 231 EM problem 6
- 21 2023 232 problem 6
- 22 2023 233 problem 6
- 23 2024 Problem 18 (EGE)
- 24 2024 Test problem 7
- 25 2024 241 Problem 2
- 26 2024 var 243 Problem 6
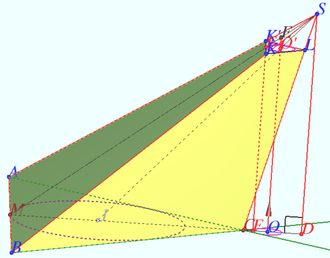
2011 Problem 8
Solve the system of equations
![]() Standard Solution
Standard Solution
![]() Denote
Denote
![]() We get
We get ![]() First equation define inner points of the circle with radius
First equation define inner points of the circle with radius ![]() and the circle.
The distance from the straight line to the origin of the coordinate system
and the circle.
The distance from the straight line to the origin of the coordinate system ![]() is
is
![]() so the system of the equations define the only tangent point of the circle and the line.
so the system of the equations define the only tangent point of the circle and the line.
![]() Short Solution
Short Solution
![]()
![]()
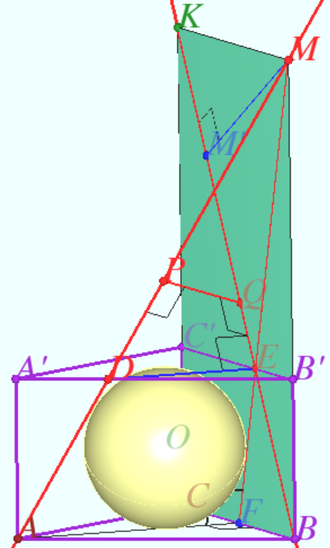
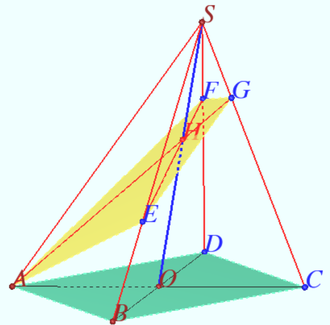
2012 Problem 8
Let the tetrahedron ![]() be given.
be given.
A right circular cylinder is located so that the circle of its upper base touches each of the faces which contains vertex ![]()
The circle of the lower base lies in the ![]() plane and touches straight lines
plane and touches straight lines ![]() and
and ![]()
Find the height ![]() of the cylinder.
of the cylinder.
Solution
Denote ![]() the midpoint
the midpoint ![]() Plane
Plane ![]() is the bisector plane of segment
is the bisector plane of segment ![]()
![]()
The inradius of ![]() equal to
equal to ![]() distance from incenter
distance from incenter ![]() to vertex
to vertex ![]() is
is ![]()
Denote ![]() the foot from
the foot from ![]() to
to ![]()
Denote ![]() the crosssection of
the crosssection of ![]() by plane of the upper base of cylinder,
by plane of the upper base of cylinder, ![]() is the incenter
is the incenter ![]() is the point of tangency incircle of
is the point of tangency incircle of ![]() and
and ![]()
Denote ![]() and
and ![]() the foots from
the foots from ![]() and
and ![]() to
to ![]() Denote the radius
Denote the radius ![]()
The circle of the lower base inscribed in angle equal to ![]() so
so
![]()
![]() Projection from the point
Projection from the point ![]() maps
maps ![]() onto
onto ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Answer: ![]()
2014 1 Problem 6
Find all pares of real numbers ![]() satisfying the system of equations
satisfying the system of equations
![]() Solution
Solution
Denote ![]()
![]() Denote
Denote ![]()
![]()
![]() is the solution. Let
is the solution. Let
![]() If
If ![]() then
then ![]() if
if ![]() then
then ![]() therefore
therefore ![]() is the single root.
is the single root.
2014 1 Problem 8
Let ![]()
Find ![]() and
and ![]()
Solution
![]()
![]()
![]() where
where ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Answer:![]()
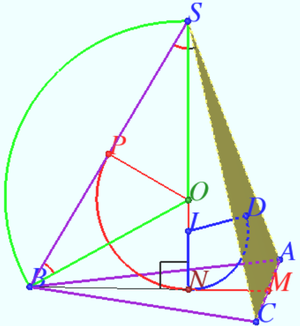
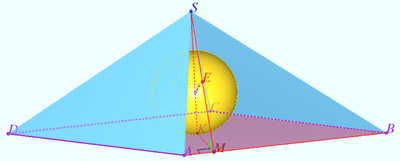
2015 1 Problem 7
A sphere is inscribed in a regular triangular prism with bases ![]() Find its radius if the distance between straight lines
Find its radius if the distance between straight lines ![]() and
and ![]() is equal to
is equal to ![]() where
where ![]() and
and ![]() are points lying on
are points lying on ![]() and
and ![]() , respectively, and
, respectively, and ![]()
Solution
The distance from the center of the sphere to the centers of the prism faces is equal to ![]() so
so ![]()
In order to find the distance ![]() between the lines
between the lines ![]() and
and ![]() , one can find the length of two perpendiculars
, one can find the length of two perpendiculars ![]() and
and ![]() to the line
to the line ![]() that are perpendicular to each other. Then
that are perpendicular to each other. Then
![]() since, when viewed along a straight line
since, when viewed along a straight line ![]() , the segment
, the segment ![]() is the altitude of a right triangle with legs
is the altitude of a right triangle with legs ![]() and
and ![]()
The plane ![]() containe the straight line
containe the straight line ![]() The straight line
The straight line ![]() crossed
crossed ![]() at the point
at the point ![]()
![]() In a right triangle
In a right triangle ![]()
![]()
![]() is the height falling on the hypotenuse,
is the height falling on the hypotenuse, ![]()
Let ![]() be the projection of
be the projection of ![]() onto plane
onto plane ![]()
Therefore ![]() is the projection of
is the projection of ![]() onto plane
onto plane ![]() at the point
at the point ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() Answer:
Answer:![]()
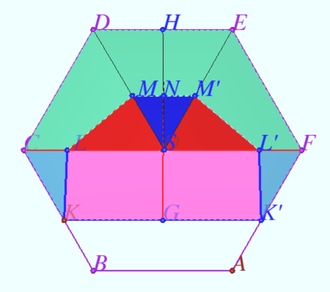
2016 2 Problem 7
Let the base of the regular pyramid with vertex ![]() be the hexagon
be the hexagon ![]() with side
with side ![]() The plane
The plane ![]() is parallel to the edge
is parallel to the edge ![]() , perpendicular to the plane
, perpendicular to the plane ![]() and intersects the edge
and intersects the edge ![]() at point
at point ![]() so that
so that ![]() The lines along which
The lines along which ![]() intersects the
intersects the ![]() plane and the base plane are perpendicular.
plane and the base plane are perpendicular.
Find the area of the triangle cut off by the plane ![]() from the face
from the face ![]()
Solution
Denote ![]()
![]() are the midpoints of
are the midpoints of ![]() respectively.
respectively.
Plane ![]() is the plane symmetry of pyramid,
is the plane symmetry of pyramid, ![]()
By condition ![]() so exist point
so exist point ![]()
![]() is the line along which
is the line along which ![]() intersects the
intersects the ![]() plane,
plane, ![]() is the line along which
is the line along which ![]() intersects the base plane, so
intersects the base plane, so ![]()
We use the top wiew and get
![]()
![]()
![]() Denote
Denote ![]() and use the side wiew.
and use the side wiew.
![]()
![]() Triangle
Triangle ![]() is the regular triangle with side
is the regular triangle with side ![]() , so
, so
![]()
![]()
![]() Answer: 8.
Answer: 8.
2016 2 Problem 8
Find the smallest value of the expression
![]() Solution
Solution
![]()
![]()
![]() Denote
Denote ![]()
![]()
![]() The shortest length of a broken line
The shortest length of a broken line ![]() with fixed ends is equal to the distance between points
with fixed ends is equal to the distance between points ![]() and
and ![]() which is
which is ![]() and is achieved if points
and is achieved if points ![]() and
and ![]() are collinear.
are collinear.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() Answer:
Answer:![]()
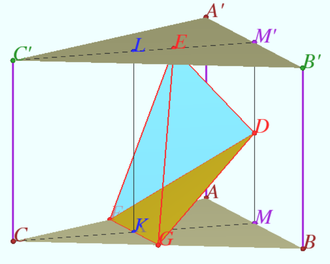
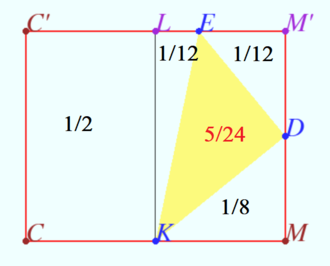
2020 201 problem 6
Let a triangular prism ![]() with a base
with a base ![]() be given,
be given, ![]() Find the ratio in which the plane
Find the ratio in which the plane ![]() divides the segment
divides the segment ![]() if
if ![]()
![]()
Solution
Let ![]() be the parallel projections of
be the parallel projections of ![]() on the plane
on the plane ![]()
![]()
We use and get
![]()
![]() Let
Let ![]()
Similarly ![]()
Answer: ![]()
2020 202 problem 6
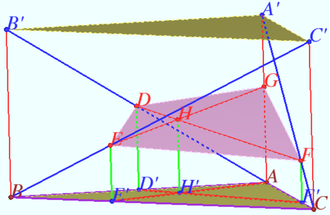
Let a tetrahedron ![]() be given,
be given, ![]() Find the cosine of the angle
Find the cosine of the angle ![]() between the edges
between the edges ![]() and
and ![]()
Solution
Let us describe a parallelepiped ![]() around a given tetrahedron
around a given tetrahedron ![]()
![]() and
and ![]() are equal rectangles.
are equal rectangles.
![]() and
and ![]() are equal rectangles.
are equal rectangles.
Denote ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() Answer:
Answer: ![]()
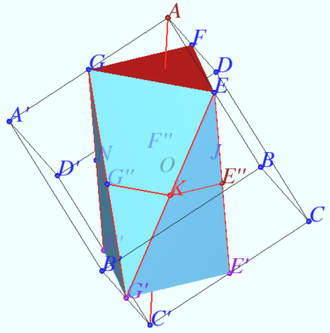
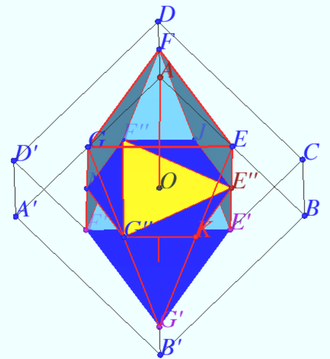
2020 203 problem 6
Let a cube ![]() with the base
with the base ![]() and side edges
and side edges ![]() be given. Find the volume of a polyhedron whose vertices are the midpoints of the edges
be given. Find the volume of a polyhedron whose vertices are the midpoints of the edges ![]()
Solution
Denote the vertices of polyhedron ![]() Triangles
Triangles ![]() and
and ![]() are equilateral triangles with sides
are equilateral triangles with sides ![]() and areas
and areas ![]()
This triangles lies in parallel planes, which are normal to cube diagonal ![]() The distance
The distance ![]() between this planes is
between this planes is ![]() So the volume of the regular prism with base
So the volume of the regular prism with base ![]() and height
and height ![]() is
is
![]()
Let the area ![]() be the quadratic function of
be the quadratic function of ![]() Let
Let
![]()
![]()
![]() Suppose, we move point
Suppose, we move point ![]() along axis
along axis ![]() and cross the solid by plane contains
and cross the solid by plane contains ![]() and normal to axis. Distance from
and normal to axis. Distance from ![]() to each crosspoint this plane with the edge change proportionally position
to each crosspoint this plane with the edge change proportionally position ![]() along axes, so the area is quadratic function from
along axes, so the area is quadratic function from ![]() position.
position.
![]()
![]()
Answer: ![]()
2020 204 problem 6
Let a regular triangular pyramid be given. The circumcenter of the sphere ![]() is equidistant from the edge and from the plane of the base of the pyramid. Find the radius of the sphere inscribed in this pyramid if the length of the edge of its base is
is equidistant from the edge and from the plane of the base of the pyramid. Find the radius of the sphere inscribed in this pyramid if the length of the edge of its base is ![]()
Solution
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() Answer:
Answer: ![]()
2020 205 problem 6
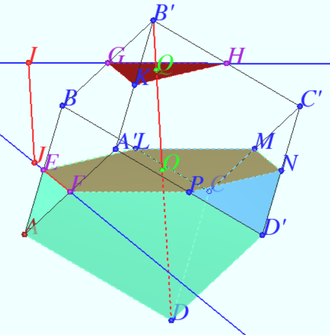
Let the quadrangular pyramid ![]() with the base parallelogram
with the base parallelogram ![]() be given.
be given.
Point ![]() Point
Point ![]()
Find the ratio in which the plane ![]() divides the volume of the pyramid.
divides the volume of the pyramid.
Solution
Let plane ![]() cross edge
cross edge ![]() at point
at point ![]() We make the central projection from point
We make the central projection from point ![]() The images of points
The images of points ![]() are
are ![]() respectively.
The image of
respectively.
The image of ![]() is the crosspoint of
is the crosspoint of ![]() and
and ![]() So lines
So lines ![]() and
and ![]() are crossed at point
are crossed at point ![]()
![]()
![]() Let’s compare volumes of some tetrachedrons, denote the volume of
Let’s compare volumes of some tetrachedrons, denote the volume of ![]() as
as ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() Answer: 1 : 6.
Answer: 1 : 6.
2020 206 problem 6
Given a cube ![]() with the base
with the base ![]() and side edges
and side edges ![]() Find the distance between the line passing through the midpoints of the edges
Find the distance between the line passing through the midpoints of the edges ![]() and
and ![]() and the line passing through the midpoints of the edges
and the line passing through the midpoints of the edges ![]() and
and ![]()
Solution
Let points ![]() be the midpoints of
be the midpoints of ![]() respectively. We need to prove that planes
respectively. We need to prove that planes ![]() and
and ![]() are parallel, perpendicular to
are parallel, perpendicular to ![]() Therefore,
Therefore, ![]()
Point ![]() is the midpoint
is the midpoint ![]()
![]()
![]() For proof we can use one of the following methods:
For proof we can use one of the following methods:
1. Vectors: ![]()
![]() Scalar product
Scalar product ![]() Similarly,
Similarly, ![]()
2. ![]()
3. Rotating the cube around its axis ![]() we find that the point
we find that the point ![]() move to
move to ![]() , then to
, then to ![]() then to
then to ![]()
Answer: ![]()
2021 215 problem 7
The sphere touches all edges of the tetrahedron ![]() It is known that the products of the lengths of crossing edges are equal. It is also known that
It is known that the products of the lengths of crossing edges are equal. It is also known that ![]() Find
Find ![]()
Solution
The tangent segments from the common point to the sphere are equal.
Let us denote the segments from the vertex ![]() to the sphere by
to the sphere by ![]()
Similarly, we define ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() If
If ![]() then
then ![]()
If ![]()
The tetrahedron ![]() is a regular pyramid with a regular triangle with side
is a regular pyramid with a regular triangle with side ![]() at the base and side edges equal to
at the base and side edges equal to ![]()
Answer: 3.
2022 221 problem 7
The volume of a triangular prism ![]() with base
with base ![]() and side edges
and side edges ![]() is equal to
is equal to ![]() Find the volume of the tetrahedron
Find the volume of the tetrahedron ![]() where
where ![]() is the centroid of the face
is the centroid of the face ![]() is the point of intersection of the medians of
is the point of intersection of the medians of ![]() is the midpoint of the edge
is the midpoint of the edge ![]() and
and ![]() is the midpoint of the edge
is the midpoint of the edge ![]()
Solution
Let us consider the uniform triangular prism ![]() Let
Let ![]() be the midpoint of
be the midpoint of ![]() be the midpoint of
be the midpoint of ![]() be the midpoint of
be the midpoint of ![]() be the midpoint of
be the midpoint of ![]()
The area ![]() of
of ![]() in the sum with the areas of triangles
in the sum with the areas of triangles ![]() is half the area of rectangle
is half the area of rectangle ![]() so
so
![]()
![]() Denote the distance between these lines
Denote the distance between these lines ![]() The volume of the tetrahedron is
The volume of the tetrahedron is ![]()
![]() The volume of the prism is
The volume of the prism is ![]()
![]()
An arbitrary prism is obtained from a regular one as a result of an affine transformation.
All points on the tetrahedron are defined affinely, which means that the volume ratio will be preserved.
Answer: 5.
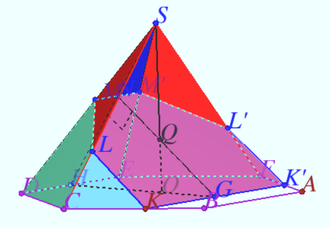
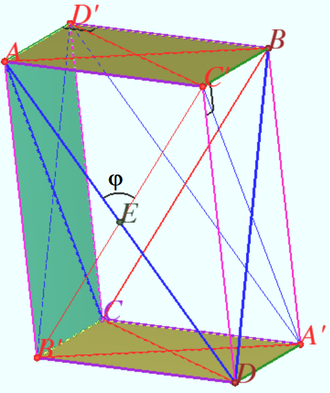
2022 222 problem 7
A sphere of diameter ![]() is inscribed in a pyramid at the base of which lies a rhombus with an acute angle
is inscribed in a pyramid at the base of which lies a rhombus with an acute angle ![]() and side
and side ![]() Find the angle
Find the angle ![]() if it is known that all lateral faces of the pyramid are inclined to plane of its base at an angle of
if it is known that all lateral faces of the pyramid are inclined to plane of its base at an angle of ![]()
Solution 1
Denote rhombus ![]() is the vertex of a pyramid
is the vertex of a pyramid ![]() is the center of the sphere,
is the center of the sphere, ![]() is the tangent point of
is the tangent point of ![]() and sphere,
and sphere, ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() Solution 2
Solution 2
The area of the rhombus ![]()
The area of the lateral surface is ![]()
![]()
![]() Answer:
Answer:![]()
2022 222 problem 6
Find all possible values of the product ![]() if it is known that
if it is known that ![]() and it is true
and it is true
![]()
Solution
Let ![]() then for each
then for each ![]() equation is true,
equation is true, ![]() Let
Let ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() no solution.
no solution.
Answer:![]()
2022 224 problem 6
Find all triples of real numbers ![]() in the interval
in the interval ![]() satisfying the system of equations
satisfying the system of equations
![]()
Solution
Denote ![]()
![]()
![]() Similarly,
Similarly, ![]()
 Therefore
Therefore
![]()
![]() Answer:
Answer:![]()
2023 231 problem 6
Let positive numbers ![]() be such that
be such that ![]()
Find the maximum value of ![]()
Solution
![]()
![]() Similarly
Similarly
![]() Adding this equations, we get:
Adding this equations, we get:
![]() If
If ![]() then
then ![]()
Answer:![]()
Explanation for students
For the function under study ![]() it is required to find the majorizing function
it is required to find the majorizing function ![]() This function must be a linear combination of the given function
This function must be a linear combination of the given function ![]() and a constant,
and a constant, ![]()
At the supposed extremum point ![]() the functions and their derivatives must coincide
the functions and their derivatives must coincide ![]()
![]()
![]()
2023 231 EM problem 6
![]() Find the maximum value
Find the maximum value ![]() and all argument values
and all argument values ![]() such that
such that ![]() .
.
Solution
![]()
![]()
![]() because
because ![]() and signs of
and signs of ![]() and
and ![]() are different, so
are different, so ![]() Therefore
Therefore ![]()
2023 232 problem 6
Let positive numbers ![]() be such that
be such that ![]() Find the maximum value of
Find the maximum value of ![]()
Solution
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() It is clear that
It is clear that ![]() and
and ![]() Denote
Denote ![]() So
So ![]()
![]() If
If ![]() then
then ![]()
Answer:![]()
2023 233 problem 6
Let positive numbers ![]() be such that
be such that ![]()
Find the maximum value of ![]()
Solution
Let ![]() Then
Then
![]()
![]()
Equality is achieved if ![]()
Answer: ![]()
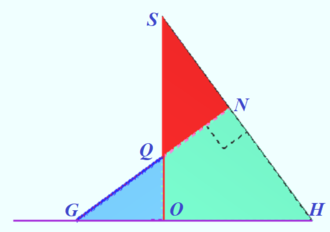
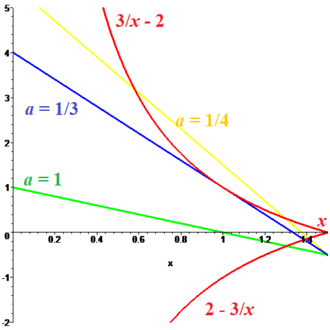
2024 Problem 18 (EGE)
Find those values of the parameter a for which the system of equations has exactly one solution:
![]() Solution
Solution
1. Special case ![]() exactly one solution.
exactly one solution.
2. ![]()
3. We solve the first equation with respect ![]() and get
and get ![]()
This solution is shown in the diagram by red curve.
We solve the second equation with respect ![]() and get
and get
![]() This solution is shown in the diagram by segments which connect point
This solution is shown in the diagram by segments which connect point ![]() with axis
with axis ![]()
Each solution of the system is shown by the point of crosspoint red curve with segment.
If ![]() then segment (colored by blue) is tangent to red curve (discriminant is zero), so we have two solutions (1,1) and
then segment (colored by blue) is tangent to red curve (discriminant is zero), so we have two solutions (1,1) and ![]()
If ![]() we get three solutions (colored by yellow).
we get three solutions (colored by yellow).
In other cases the system has exactly one solution.
Answer: ![]()
2024 Test problem 7
Find all values of the parameter a for which there is at least one solution to the inequality ![]() on the interval
on the interval ![]()
Solution
![]() where
where ![]() where
where ![]()
The equation ![]() has solutions
has solutions ![]() and
and ![]()
![]()
![]() if
if ![]() so given inequality has the solution
so given inequality has the solution ![]() for these
for these ![]()
![]()
![]() if
if ![]() so given inequality has the solution
so given inequality has the solution ![]() for these
for these ![]()
![]() no solution of the given inequality.
no solution of the given inequality.
![]() no solution of the inequality if
no solution of the inequality if ![]()
![]() If
If ![]() no solution of the inequality.
no solution of the inequality.
![]() If
If ![]() no solution of the given inequality.
no solution of the given inequality.
![]() If
If ![]() no solution of the given inequality.
no solution of the given inequality.
2024 241 Problem 2
The natural numbers ![]() form a strictly increasing arithmetic progression. Find all possible values of
form a strictly increasing arithmetic progression. Find all possible values of ![]() if it is known that
if it is known that ![]() is odd,
is odd, ![]() and
and ![]()
Solution
![]() is odd, so
is odd, so ![]()
Let ![]() the common difference may be
the common difference may be ![]() increasing arithmetic progression exist.
increasing arithmetic progression exist.
Let ![]() the common difference may be
the common difference may be ![]() increasing arithmetic progression exist.
increasing arithmetic progression exist.
Let ![]() can not be the natural number.
can not be the natural number.
Answer: ![]()
2024 var 243 Problem 6
Solve the system of equations in the positive ![]()
![]()
Solution (after Natalia Zakharova)
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() Answer:
Answer: ![]()