Barycentric coordinates
This can be used in mass points. http://mathworld.wolfram.com/BarycentricCoordinates.html This article is a stub. Help us out by expanding it.
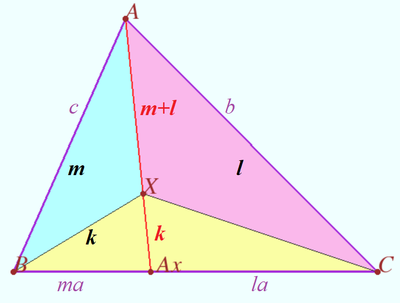
Barycentric coordinates are triples of numbers ![]() corresponding to masses placed at the vertices of a reference triangle
corresponding to masses placed at the vertices of a reference triangle ![]() . These masses then determine a point
. These masses then determine a point ![]() , which is the geometric centroid of the three masses and is identified with coordinates
, which is the geometric centroid of the three masses and is identified with coordinates ![]() . The vertices of the triangle are given by
. The vertices of the triangle are given by ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() . Barycentric coordinates were discovered by Möbius in 1827 (Coxeter 1969, p. 217; Fauvel et al. 1993).
. Barycentric coordinates were discovered by Möbius in 1827 (Coxeter 1969, p. 217; Fauvel et al. 1993).
The Central NC Math Group published a lecture concerning this topic at https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KQim7-wrwL0 if you would like to view it.
Useful formulas
Notation
Let the triangle ![]() be a given triangle,
be a given triangle, ![]() be the lengths of
be the lengths of ![]()
We use the following Conway symbols:
![]() is semiperimeter,
is semiperimeter, ![]() is twice the area of
is twice the area of ![]()
![]() where
where ![]() is the inradius,
is the inradius, ![]() is the circumradius,
is the circumradius,
![]() is the cosine of the Brocard angle,
is the cosine of the Brocard angle,
![]()
Main
For any point in the plane ![]() there are barycentric coordinates(BC):
there are barycentric coordinates(BC): ![]() :
:
![]()
![]() The normalized (absolute) barycentric coordinates NBC satisfy the condition
The normalized (absolute) barycentric coordinates NBC satisfy the condition ![]() they are uniquely determined:
they are uniquely determined:
![]()
![]() Triangle vertices
Triangle vertices ![]()
The barycentric coordinates of a point do not change under an affine transformation.
Lines
The straight line in barycentric coordinates (BC) is given by the equation ![]()
The lines given in the BC by the equations ![]() and
and ![]() intersect at the point
intersect at the point
![]()
These lines are parallel iff ![]()
The sideline ![]() contains the points
contains the points ![]() its equation is
its equation is ![]()
The line ![]() has equation
has equation ![]() it intersects the sideline
it intersects the sideline ![]() at the point
at the point ![]()
Iff ![]() then
then ![]()
Let NBC of points ![]() and
and ![]() be
be ![]()
Then the square of distance ![]()
![]() The equation of bisector of
The equation of bisector of ![]() is:
is:
![]() Nagel line :
Nagel line : ![]()
Circles
Any circle is given by an equation of the form ![]()
Circumcircle contains the points ![]() the equation of this circle:
the equation of this circle: ![]()
The incircle contains the tangent points of the incircle with the sides:
![]()
The equation of the incircle is
![]() where
where ![]()
The radical axis of two circles given by equations of this form is:
![]() Conjugate
Conjugate
The point ![]() is isotomically conjugate with respect to
is isotomically conjugate with respect to ![]() with the point
with the point ![]()
The point ![]() is isogonally conjugate with respect to
is isogonally conjugate with respect to ![]() with the point
with the point ![]()
The point ![]() is isocircular conjugate with respect to
is isocircular conjugate with respect to ![]() with the point
with the point ![]()
Triangle centers
The median ![]() centroid is
centroid is ![]()
The simmedian point ![]() is isogonally conjugate with respect to
is isogonally conjugate with respect to ![]() with the point
with the point ![]()
The bisector ![]() the incenter is
the incenter is ![]()
The excenters are ![]()
The circumcenter ![]() lies at the intersection of the bisectors
lies at the intersection of the bisectors ![]() and
and ![]() its BC coordinates
its BC coordinates ![]()
The orthocenter ![]() is isogonally conjugate with respect to
is isogonally conjugate with respect to ![]() with the point
with the point ![]()
Let Nagel point ![]() lies at line
lies at line ![]()
The Gergonne point is the isotomic conjugate of the Nagel point, so ![]()
vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss
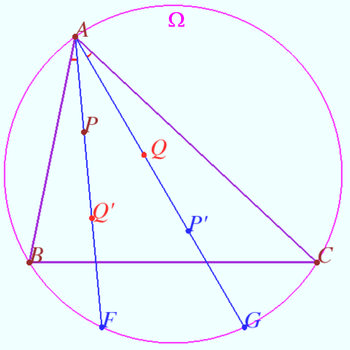
Product of isogonal segments
Let triangle ![]() the circumcircle
the circumcircle ![]() and isogonals
and isogonals ![]() and
and ![]() of the
of the ![]() be given.
Let point
be given.
Let point ![]() and
and ![]() be the isogonal conjugate of a point
be the isogonal conjugate of a point ![]() and
and ![]() with respect to
with respect to ![]() Prove that
Prove that ![]()
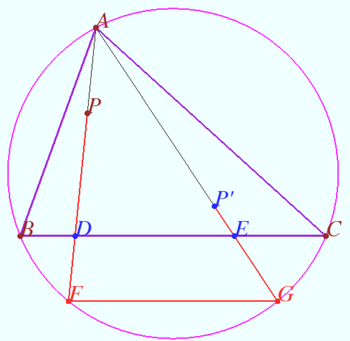
Proof
We fixed ![]() and the point
and the point ![]() So isogonal
So isogonal ![]() is fixed.
is fixed.
Denote ![]()
We need to prove that ![]() do not depends from
do not depends from ![]()
Line ![]() has the equation
has the equation ![]()
To find the point ![]() we solve the system this equation and equation for circumcircle:
we solve the system this equation and equation for circumcircle: ![]()
![]() We use the formula for isogonal cobnjugate point and get
We use the formula for isogonal cobnjugate point and get
![]() and then
and then ![]()
![]() We calculate distances (using NBC) and get:
We calculate distances (using NBC) and get:
![]()
![]() where
where ![]() has sufficiently big formula.
has sufficiently big formula.
Therefore ![]() vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss
vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss