Getting Started With Python Programming
This guide takes you through the process of getting started with programming using the Python language. The sections flow from one to the next so it's recommended to read through this document linearly.
Contents
[hide]Installing Python
1. Download the installer:
- For Windows 32-bit (if you're uncertain, this is probably the version you should download) : http://www.python.org/ftp/python/3.1.2/python-3.1.2.msi
- For Windows 64-bit: http://www.python.org/ftp/python/3.1.2/python-3.1.2.amd64.msi
- For Mac OS X: http://www.python.org/ftp/python/3.1.2/python-3.1.2-macosx10.3-2010-03-24.dmg
2. Run the installer.
3. Click next for every option in the setup wizard (i.e. use the defaults).
Using the Python Shell
The Python installation comes with an easy-to-use text editor called IDLE. You should start by playing around with this. You should be able to find IDLE wherever Python was installed. On Mac this should be in the Applications folder while on Windows it should be accessible from the Start menu in a folder named Python or something close to that.
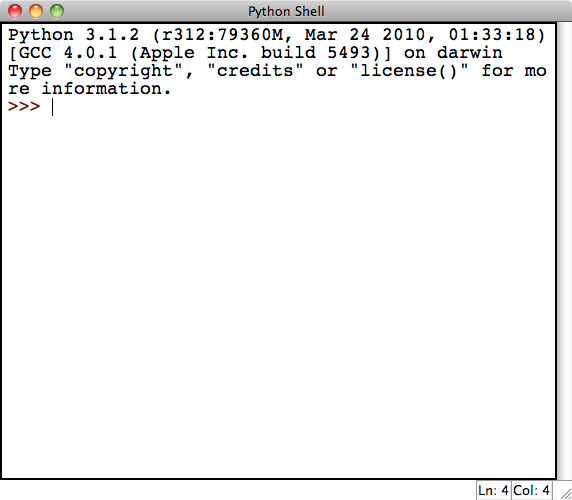
When you first open IDLE, you'll see the Python Shell:
Note that the screenshots in this article are taken using IDLE on a Mac with the font increased. Thus IDLE may look a little bit different for you but should still function similarly. Another thing to note is that in the lower left hand corner of the Python Shell you can see that it says "Ln: 4 Col: 4". This is just telling you where in the document your cursor is. In this case it's on line 4 and over in column 4.
The Python Shell is very useful for quick math and short sequences of commands:
Here we see a number of familiar operations: + for add, - for subtraction, * for multiplication, and / for division. The last operation shown in the example, denoted by **, happens to be exponentiation. One neat feature to note about Python is that it can store arbitrarily large numbers (limited by the amount of memory your computer has). Trying some hefty exponentiation, we can see that we can compute with some pretty big numbers such as ![]() as illustrated below.
as illustrated below.
While Python can make for a pretty good calculator, it can do a whole lot more. One example is when dealing with strings as follows:
Here we are concatenating the three strings "python", "is", and "cool" by using the + operator. Notice that previously we used + to add numbers but now with strings, Python concatenates them! You may also note that the output of the operation gives us a string with single quotes around it. In Python, you are able to use single quotes or double quotes to denote a string. You can use them interchangeably.
As a final example, we can even write code in the Python Shell that extends beyond a single line as shown below. We also see our first example of a ![]() loop.
loop.
Take some time to play around with the Python Shell. You'll want to go through a more extensive introduction to programming to learn the full extent of what you can do with Python, but you can still do some pretty nifty stuff by just playing around.
The IDLE Text Editor and Your First Python Program
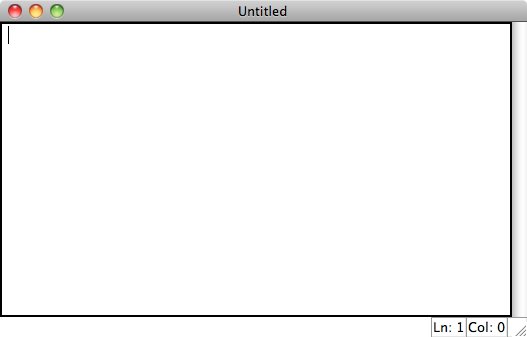
For most programming needs, you'll want to edit your program in a separate document and then run it. In the file menu click on New Window which should give you a blank document with the title "Untitled" as shown below:
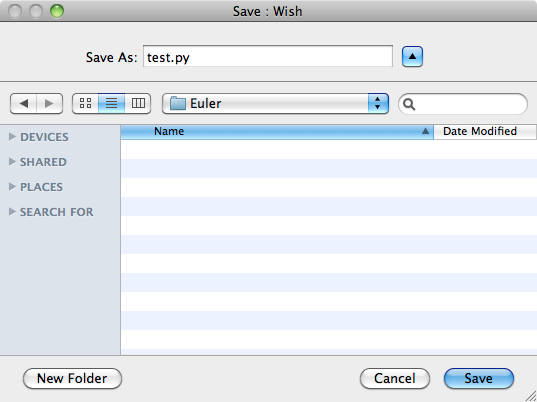
You'll need to save your file before running it, so you might as well save it now. Make sure that you name your file with a name that ends in .py so that you get proper syntax highlighting. Here we save ours as test.py:
To get acquainted with the text editor, let's write our first Python program! We'll write a program to solve the | first Euler Project problem which asks:
Find the sum of all the multiples of 3 or 5 below 1000.
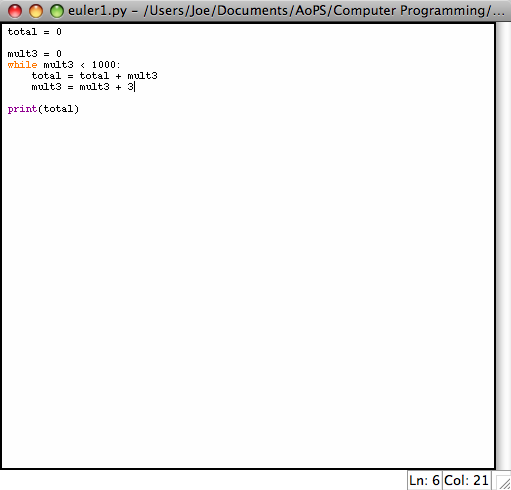
To do this, we first want to sum up all of the multiples of 3 less below 1000. We can do this with the following code:
The first step is to define two variables, total and mult3, which we set to 0. Total is what will eventually be the answer while mult3 is going to be what we use to keep track of the multiples of 3. The next step is that we create a while loop. A while loop has two components:
- The first is the condition that it checks every step. In this case we check to see that mult3 is less than 1000. Thus, we keep iterating over this loop until mult3 is not less than 1000 anymore.
- The second component is the code in the loop that we execute. In this case we add mult3 to the total and then increment mult3 to be the next multiple of 3.
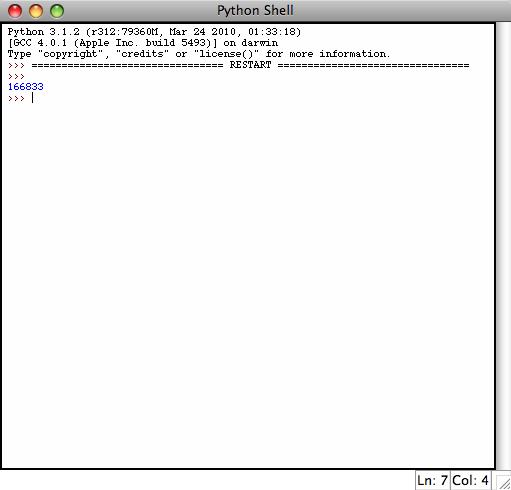
After the while loop we print out our total. Now that we've written this code, we probably want to run it and test it out. We can do so by going to the Run menu and hitting Run Module (shortcut F5). The program should execute and print out the answer to the command line:
At this point, you should know enough to finish off the program. We have yet to account for the multiples of 5 and any double counting that may have occurred. Try finishing this up on your own. The answer you should get is 233168 so you can check your work.
One thing you may want to note is that it can be tedious to write statements such as:
total = total + mult3.
Python has a shorthand for this which you can use:
total += mult3.
Try it out for yourself!
What's Next?
Now that you've learned the very basics of getting Python going, there's a bunch of tutorials you can look at which are [listed | http://wiki.python.org/moin/BeginnersGuide/NonProgrammers] on the Python website. Go check them out!