Difference between revisions of "Steiner line"
(→Collings Clime) |
(→Steiner line) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Steiner line== | ==Steiner line== | ||
| − | Let <math>ABC</math> be a triangle with orthocenter <math>H. | + | [[File:Steiner and Simson lines.png|500px|right]] |
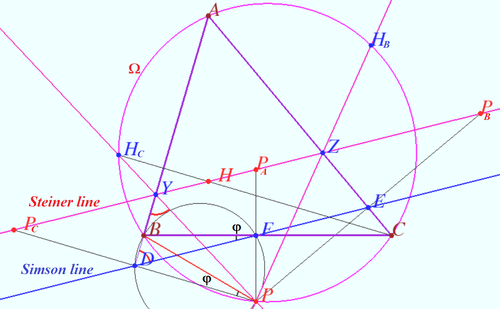
| + | Let <math>ABC</math> be a triangle with orthocenter <math>H. P</math> is a point on the circumcircle <math>\Omega</math> of <math>\triangle ABC.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Let <math>P_A, P_B, </math> and <math>P_C</math> be the reflections of <math>P</math> in three lines which contains edges <math>BC, AC,</math> and <math>AB,</math> respectively. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Prove that <math>P_A, P_B, P_C,</math> and <math>H</math> are collinear. Respective line is known as the Steiner line of point <math>P</math> with respect to <math>\triangle ABC.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <i><b>Proof</b></i> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Let <math>D, E,</math> and <math>F</math> be the foots of the perpendiculars dropped from <math>P</math> to lines <math>AB, AC,</math> and <math>BC,</math> respectively. | ||
| + | |||
| + | WLOG, Steiner line cross <math>AB</math> at <math>Y</math> and <math>AC</math> at <math>Z.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | The line <math>DEF</math> is Simson line of point <math>P</math> with respect of <math>\triangle ABC.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>D</math> is midpoint of segment <math>PP_C \implies</math> homothety centered at <math>P</math> with ratio <math>2</math> sends point <math>D</math> to a point <math>P_C.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Similarly, this homothety sends point <math>E</math> to a point <math>P_B</math>, point <math>F</math> to a point <math>P_A,</math> therefore this homothety send Simson line to line <math>P_AP_BP_C.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Let <math>\angle ABC = \beta, \angle BFD = \varphi \implies \angle BDF = \beta – \varphi.</math> | ||
| + | <cmath>P_CP_A||DF \implies \angle P_CYB = \beta – \varphi.</cmath> | ||
| + | <math>P</math> is simmetric to <math>P_C \implies \angle PYD = \beta – \varphi.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Quadrungle <math>BDPF</math> is cyclic <math>\implies \angle BPD = \varphi \implies \angle BPY = 90^\circ – \angle BYP – \angle BPD = 90^\circ – \beta.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\angle BCH = \angle BPY \implies PY \cap CH</math> at point <math>H_C \in \Omega.</math> | ||
| + | Similarly, line <math>BH \cap PZ</math> at <math>H_B \in \Omega.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | According the Collins Claim <math>YZ</math> is <math>H-line,</math> therefore <math>H \in P_AP_B.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss''' | ||
| + | |||
==Collings Clime== | ==Collings Clime== | ||
[[File:Steiner H line.png|500px|right]] | [[File:Steiner H line.png|500px|right]] | ||
Revision as of 12:09, 7 December 2022
Steiner line
Let ![]() be a triangle with orthocenter
be a triangle with orthocenter ![]() is a point on the circumcircle
is a point on the circumcircle ![]() of
of ![]()
Let ![]() and
and ![]() be the reflections of
be the reflections of ![]() in three lines which contains edges
in three lines which contains edges ![]() and
and ![]() respectively.
respectively.
Prove that ![]() and
and ![]() are collinear. Respective line is known as the Steiner line of point
are collinear. Respective line is known as the Steiner line of point ![]() with respect to
with respect to ![]()
Proof
Let ![]() and
and ![]() be the foots of the perpendiculars dropped from
be the foots of the perpendiculars dropped from ![]() to lines
to lines ![]() and
and ![]() respectively.
respectively.
WLOG, Steiner line cross ![]() at
at ![]() and
and ![]() at
at ![]()
The line ![]() is Simson line of point
is Simson line of point ![]() with respect of
with respect of ![]()
![]() is midpoint of segment
is midpoint of segment ![]() homothety centered at
homothety centered at ![]() with ratio
with ratio ![]() sends point
sends point ![]() to a point
to a point ![]()
Similarly, this homothety sends point ![]() to a point
to a point ![]() , point
, point ![]() to a point
to a point ![]() therefore this homothety send Simson line to line
therefore this homothety send Simson line to line ![]()
Let ![]()
![]()
![]() is simmetric to
is simmetric to ![]()
Quadrungle ![]() is cyclic
is cyclic ![]()
![]() at point
at point ![]() Similarly, line
Similarly, line ![]() at
at ![]()
According the Collins Claim ![]() is
is ![]() therefore
therefore ![]()
vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss
Collings Clime
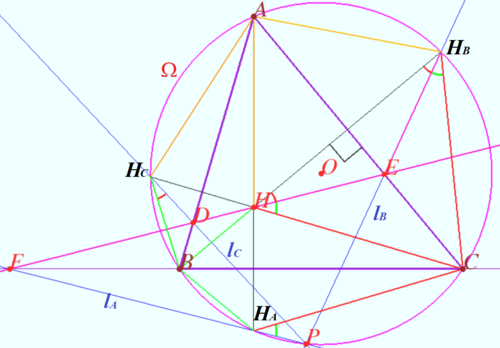
Let triangle ![]() be the triangle with the orthocenter
be the triangle with the orthocenter ![]() and circumcircle
and circumcircle ![]() Denote
Denote ![]() any line containing point
any line containing point ![]()
Let ![]() and
and ![]() be the reflections of
be the reflections of ![]() in the edges
in the edges ![]() and
and ![]() respectively.
respectively.
Prove that lines ![]() and
and ![]() are concurrent and the point of concurrence lies on
are concurrent and the point of concurrence lies on ![]()
Proof
Let ![]() and
and ![]() be the crosspoints of
be the crosspoints of ![]() with
with ![]() and
and ![]() respectively.
respectively.
WLOG ![]() Let
Let ![]() and
and ![]() be the points symmetric to
be the points symmetric to ![]() with respect
with respect ![]() and
and ![]() respectively.
respectively.
Therefore ![]()
![]()
![]()
Let ![]() be the crosspoint of
be the crosspoint of ![]() and
and ![]() is cyclic
is cyclic ![]()
Similarly ![]() is cyclic
is cyclic ![]() the crosspoint of
the crosspoint of ![]() and
and ![]() is point
is point ![]()
Usually the point ![]() is called the anti-Steiner point of the
is called the anti-Steiner point of the ![]() with respect to
with respect to ![]()
vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss