Difference between revisions of "2018 AIME I Problems/Problem 13"
Math101010 (talk | contribs) m |
Mathboy282 (talk | contribs) (vid solution) |
||
| (38 intermediate revisions by 13 users not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
Let <math>\triangle ABC</math> have side lengths <math>AB=30</math>, <math>BC=32</math>, and <math>AC=34</math>. Point <math>X</math> lies in the interior of <math>\overline{BC}</math>, and points <math>I_1</math> and <math>I_2</math> are the incenters of <math>\triangle ABX</math> and <math>\triangle ACX</math>, respectively. Find the minimum possible area of <math>\triangle AI_1I_2</math> as <math>X</math> varies along <math>\overline{BC}</math>. | Let <math>\triangle ABC</math> have side lengths <math>AB=30</math>, <math>BC=32</math>, and <math>AC=34</math>. Point <math>X</math> lies in the interior of <math>\overline{BC}</math>, and points <math>I_1</math> and <math>I_2</math> are the incenters of <math>\triangle ABX</math> and <math>\triangle ACX</math>, respectively. Find the minimum possible area of <math>\triangle AI_1I_2</math> as <math>X</math> varies along <math>\overline{BC}</math>. | ||
| − | ==Solution== | + | ==Solution 1 (Official MAA)== |
| − | First note that <cmath>\angle I_1AI_2 = \angle I_1AX + \angle XAI_2 = \frac{\angle BAX}2 + \frac{\angle CAX}2 = \frac{\angle A}2</cmath> is a constant not depending on <math>X</math>, so by <math>[AI_1I_2] = \tfrac12(AI_1)(AI_2)\sin\angle I_1AI_2</math> it suffices to minimize <math>(AI_1)(AI_2)</math>. Let <math>a = BC</math>, <math>b = AC</math>, <math>c = AB</math>, and <math>\alpha = \angle AXB</math>. Remark that <cmath>\angle AI_1B = 180^\circ - (\angle I_1AB + \angle I_1BA) = 180^\circ - \tfrac12(180^\circ - \alpha) = 90^\circ + \tfrac\alpha 2.</cmath> Applying the Law of Sines to <math>\triangle ABI_1</math> gives <cmath>\frac{AI_1}{AB} = \frac{\sin\angle ABI_1}{\sin\angle AI_1B}\qquad\Rightarrow\qquad AI_1 = \frac{c\sin\frac B2}{\cos\frac\alpha 2}.</cmath> Analogously one can derive <math>AI_2 = \tfrac{b\sin\frac C2}{\sin\frac\alpha 2}</math>, and so <cmath>[AI_1I_2] = \frac{bc\sin\frac A2 \sin\frac B2\sin\frac C2}{2\cos\frac\alpha 2\sin\frac\alpha 2} = \frac{bc\sin\frac A2 \sin\frac B2\sin\frac C2}{\sin\alpha}\geq bc\sin\frac A2 \sin\frac B2\sin\frac C2,</cmath> with equality when <math>\alpha = 90^\circ</math>, that is, when <math>X</math> is the foot of the perpendicular from <math>A</math> to <math>\overline{BC}</math>. In this case the desired area is <math>bc\sin\tfrac A2\sin\tfrac B2\sin\tfrac C2</math>. To make this feasible to compute, note that <cmath>\sin\frac A2=\sqrt{\frac{1 | + | First note that <cmath>\angle I_1AI_2 = \angle I_1AX + \angle XAI_2 = \frac{\angle BAX}2 + \frac{\angle CAX}2 = \frac{\angle A}2</cmath> is a constant not depending on <math>X</math>, so by <math>[AI_1I_2] = \tfrac12(AI_1)(AI_2)\sin\angle I_1AI_2</math> it suffices to minimize <math>(AI_1)(AI_2)</math>. Let <math>a = BC</math>, <math>b = AC</math>, <math>c = AB</math>, and <math>\alpha = \angle AXB</math>. Remark that <cmath>\angle AI_1B = 180^\circ - (\angle I_1AB + \angle I_1BA) = 180^\circ - \tfrac12(180^\circ - \alpha) = 90^\circ + \tfrac\alpha 2.</cmath> Applying the Law of Sines to <math>\triangle ABI_1</math> gives <cmath>\frac{AI_1}{AB} = \frac{\sin\angle ABI_1}{\sin\angle AI_1B}\qquad\Rightarrow\qquad AI_1 = \frac{c\sin\frac B2}{\cos\frac\alpha 2}.</cmath> Analogously one can derive <math>AI_2 = \tfrac{b\sin\frac C2}{\sin\frac\alpha 2}</math>, and so <cmath>[AI_1I_2] = \frac{bc\sin\frac A2 \sin\frac B2\sin\frac C2}{2\cos\frac\alpha 2\sin\frac\alpha 2} = \frac{bc\sin\frac A2 \sin\frac B2\sin\frac C2}{\sin\alpha}\geq bc\sin\frac A2 \sin\frac B2\sin\frac C2,</cmath> with equality when <math>\alpha = 90^\circ</math>, that is, when <math>X</math> is the foot of the perpendicular from <math>A</math> to <math>\overline{BC}</math>. In this case the desired area is <math>bc\sin\tfrac A2\sin\tfrac B2\sin\tfrac C2</math>. To make this feasible to compute, note that <cmath>\sin\frac A2=\sqrt{\frac{1-\cos A}2}=\sqrt{\frac{1-\frac{b^2+c^2-a^2}{2bc}}2} = \sqrt{\dfrac{(a-b+c)(a+b-c)}{4bc}}.</cmath> Applying similar logic to <math>\sin \tfrac B2</math> and <math>\sin\tfrac C2</math> and simplifying yields a final answer of <cmath> |
| + | |||
| + | *Notice that we truly did minimize the area for <math>[A I_1 I_2]</math> because <math>b, c, \angle A, \angle B, \angle C</math> are all constants while only <math>\sin \alpha</math> is variable, so maximizing <math>\sin \alpha</math> would minimize the area. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Solution 2 (Similar to Official MAA)== | ||
| + | It's clear that <math>\angle I_{1}AI_{2}=\frac{1}{2}\angle BAX+\frac{1}{2}\angle CAX=\frac{1}{2}\angle A</math>. Thus <cmath> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==Solution 3 (A lengthier, but less trigonometric approach)== | ||
| + | |||
| + | First, instead of using angles to find <math>[AI_1I_2]</math>, let's try to find the area of other, simpler figures, and subtract that from <math>[ABC]</math>. However, to do this, we need to be able to figure out the length of the inradii, and so, we need to find <math>AX</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | To minimize <math>[AI_1I_2]</math>, intuitively, we should try to minimize the length of <math>AX</math>, since, after using the <math>rs=A</math> formula for the area of a triangle, we'll be able to minimize the inradii lengths, and thus, eventually minimize the area of <math>[AI_1I_2]</math>. (Proof needed here). | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | We need to minimize <math>AX</math>. Let <math>AX=d</math>, <math>BX=s</math>, and <math>CX=32-s</math>. After an application of Stewart's Theorem, we will get that <cmath>d=\sqrt{s^2-24s+900}</cmath> To minimize this quadratic, <math>s=12</math> whereby we conclude that <math>d=6\sqrt{21}</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | From here, draw perpendiculars down from <math>I_1</math> and <math>I_2</math> to <math>AB</math> and <math>AC</math> respectively, and label the foot of these perpendiculars <math>D</math> and <math>E</math> respectively. After, draw the inradii from <math>I_1</math> to <math>BX</math>, and from <math>I_2</math> to <math>CX</math>, and draw in <math>I_1I_2</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Label the foot of the inradii to <math>BX</math> and <math>CX</math>, <math>F</math> and <math>G</math>, respectively. From here, we see that to find <math>[AI_1I_2]</math>, we need to find <math>[ABC]</math>, and subtract off the sum of <math>[DBCEI_2I_1], [ADI_1],</math> and <math>[AEI_2]</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <math>[DBCEI_2I_1]</math> can be found by finding the area of two quadrilaterals <math>[DBFI_1]+[ECGI_2]</math> as well as the area of a trapezoid <math>[FGI_2I_1]</math>. If we let the inradius of <math>ABX</math> be <math>r_1</math> and if we let the inradius of <math>ACX</math> be <math>r_2</math>, we'll find, after an application of basic geometry and careful calculations on paper, that <math>[DBCEI_2I_1]=13r_1+19r_2</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | The area of two triangles can be found in a similar fashion, however, we must use <math>XYZ</math> substitution to solve for <math>AD</math> as well as <math>AE</math>. After doing this, we'll get a similar sum in terms of <math>r_1</math> and <math>r_2</math> for the area of those two triangles which is equal to <cmath>\frac{(9+3\sqrt{21})(r_1)}{2} + \frac{(7+3\sqrt{21})(r_2)}{2}.</cmath> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Now we're set. Summing up the area of the Hexagon and the two triangles and simplifying, we get that the formula for <math>[AI_1I_2]</math> is just <cmath>[ABC]-\left(\frac{(35+3\sqrt{21})(r_1)}{2}+\frac{(45+3r_2\sqrt{21})(r_2)}{2}\right).</cmath> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Using Heron's formula, <math>[ABC]=96\sqrt{21}</math>. Solving for <math>r_1</math> and <math>r_2</math> using Heron's in <math>ABX</math> and <math>ACX</math>, we get that <math>r_1=3\sqrt{21}-9</math> and <math>r_2=3\sqrt{21}-7</math>. From here, we just have to plug into our above equation and solve. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Doing so gets us that the minimum area of <math>AI_1I_2=\boxed{126}.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | -Azeem H.(Mathislife52) ~edited by phoenixfire | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Video Solution by Osman Nal== | ||
| + | https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=sT-wxV2rYqs | ||
| + | |||
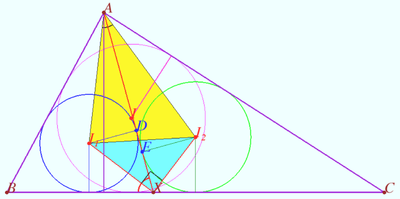
| + | ==Solution 4 (Geometry only)== | ||
| + | [[File:2018 AIME I 13.png|400px|right]] | ||
| + | Let <math>BC = a, s</math> be semiperimeter of <math>\triangle ABC, s = 48, h</math> be the height of <math>\triangle ABC</math> dropped from <math>A.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Let <math>r, r_1, r_2</math> be inradius of the <math>\triangle ABC, \triangle ABX,</math> and <math>\triangle ACX,</math> respectively. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Using the Lemma (below), we get the area | ||
| + | <cmath>[ AI_1 I_2] = \frac{AX \cdot r }{2} \ge \frac { hr}{2} =\frac{ r^2 s}{a},</cmath> | ||
| + | <cmath> [ AI_1 I_2]= \frac{(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)}{a} = \frac{18 \cdot 16 \cdot 14}{32} = 9 \cdot 14 = \boxed {126}. </cmath> | ||
| + | <i><b>Lemma </b></i> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <cmath>[AI_1 I_2] = \frac{AX \cdot r }{2}</cmath> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <i><b>Proof </b></i> | ||
| + | <cmath>\angle AXI_1 = \angle BXI_1, \angle AXI_2 = \angle CXI_2, \angle BXC = 180^\circ \implies \angle I_1 X I_2 = 90^\circ.</cmath> | ||
| + | WLOG <math>\hspace{70mm} \sin \angle AXB = \frac {h}{AX}.</math> | ||
| + | <cmath>[AI_1 X] =\frac{ AX\cdot r_1}{2}, \hspace{20mm} [AI_2 X] =\frac{ AX\cdot r_2}{2},\hspace{20mm}[XI_1 I_2] =\frac{XI_1 \cdot XI_2}{2},</cmath> | ||
| + | <cmath>XI_1 \cdot XI_2 = \frac{r_1}{\sin \angle AXI_1} \cdot \frac{r_2}{\sin \angle AXI_2} = \frac{2 r_1 r_2}{\sin \angle AXB} = \frac{2 AX \cdot r_1 \cdot r_2 }{h}.</cmath> | ||
| + | <math> \hspace{20mm} [AI_1 I_2] = [AI_1 X] + [AI_2 X] - [XI_1 I_2] = AX (r_1 + r_2 - \frac{2 r_1 r_2 }{h}) = \frac{AX \cdot r }{2}</math> if and only if | ||
| + | |||
| + | <i><b>Claim </b></i> | ||
| + | <cmath>r_1 + r_2 - \frac{2 r_1 r_2 }{h} = r.</cmath> | ||
| + | <i><b>Proof </b></i> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Let <math> \hspace{30mm} AX = t, AC = b, AB = c, x_1 = BX, x_2 = CX, \frac{c+t}{x_1} = u, \frac{b+t}{x_2} = v.</math> | ||
| + | <cmath>r_1 + r_2 - \frac{2 r_1 r_2 }{h} = r \iff \frac{h}{r_2} + \frac{h}{r_1}- 2 = \frac{h}{r_2} \frac{h}{r_1} \frac{r}{h}.</cmath> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <cmath>2[ABX] = r_1 (c + t + x_1) = h x_1 \implies \frac{h}{r_1} = 1 + u,</cmath> | ||
| + | <cmath>2[ACX] = r_2 (b + t + x_2) = h x_2 \implies \frac{h}{r_2} = 1 + v,</cmath> | ||
| + | <cmath>\frac{h}{r_2} + \frac{h}{r_1}- 2 = \frac{h}{r_2} \frac{h}{r_1} \frac{r}{h} \iff (u+v)(a+b+c)=(u+1)(v+1)a \iff (u+v)(b+c)=(uv+1)a,</cmath> | ||
| + | <cmath>c^2 x_2 + b^2 x_1 = t^2 x_1 + t^2 x_2 + x_1^2 x_2 + x_1 x_2^2,</cmath> | ||
| + | <cmath>(b^2 -t^2 -x_2^2)x_1 + (c^2 –t^2 -x_1^2)x_2 = 0,</cmath> | ||
| + | We use Cosine Law for <math>\triangle ABX</math> and <math>\triangle ACX</math> and get | ||
| + | <cmath>2 t x_1 x_2 \cos \angle AXB + 2 t x_1 x_2 \cos \angle AXC = 0 \iff \cos \angle AXB + \cos \angle AXC = 0.</cmath> | ||
| + | Last is evident, the claim has been proven. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss''' | ||
| + | |||
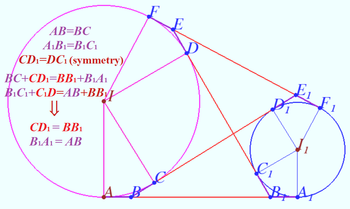
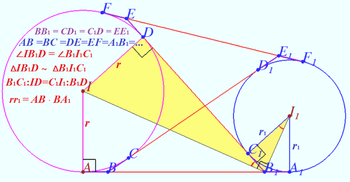
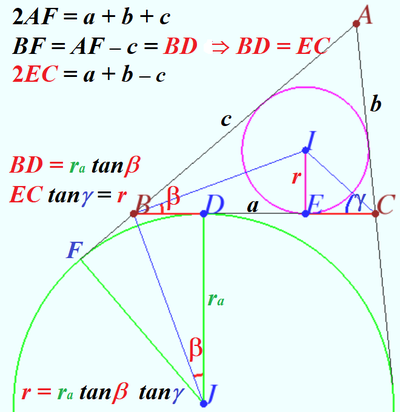
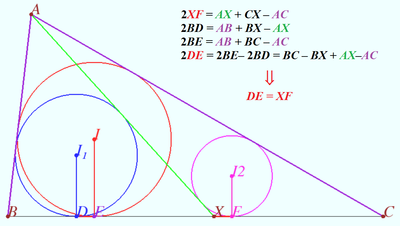
| + | ==Solution 4a== | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:2018 AIME I 13e.png|350px|right]] | ||
| + | [[File:2018 AIME I 13c.png|350px|right]] | ||
| + | |||
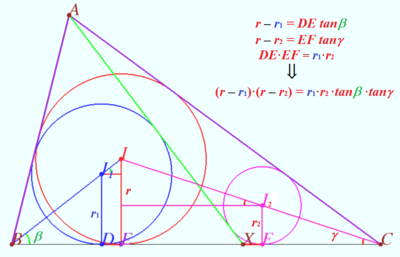
| + | Geometry proof of the equation <math>r_1 + r_2 - \frac{2 r_1 r_2 }{h} = r.</math> | ||
| + | <math>\frac{r^2}{r_1 r_2}-\frac{r}{r_1} -\frac{r}{r_2} +1 = 1 - \frac{2r}{h} \implies | ||
| + | \frac {(r-r_1)\cdot (r-r_2)}{r_1 \cdot r_2} = 1-\frac{2r}{h}.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Using diagrams, we can recall known facts and using those facts for making sequence of equations. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <cmath>\frac {(r-r_1)\cdot (r-r_2)}{r_1 \cdot r_2} =\tan\beta \tan\gamma.</cmath> | ||
| + | |||
| + | The twice area of <math>\triangle ABC</math> is | ||
| + | <math>r(a+b+c) = ha = r_a (b+c-a)\implies </math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <cmath>1 -\frac{2r}{h} = \frac {b+c-a}{b+c+a} = \frac {r}{r_a} = \tan\beta \tan\gamma .</cmath> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Therefore <cmath>r_1 + r_2 - \frac{2 r_1 r_2 }{h} = r.</cmath> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:2018 AIME I 13g.png|400px|right]] | ||
| + | [[File:2018 AIME I 13d.png|400px]] | ||
| + | [[File:2018 AIME I 13f.png|400px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Video Solution by MOP 2024== | ||
| + | https://youtube.com/watch?v=ALzZA13PuZk | ||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
{{AIME box|year=2018|n=I|num-b=12|num-a=14}} | {{AIME box|year=2018|n=I|num-b=12|num-a=14}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Intermediate Geometry Problems]] | ||
{{MAA Notice}} | {{MAA Notice}} | ||
Revision as of 20:36, 6 January 2024
Contents
[hide]Problem
Let ![]() have side lengths
have side lengths ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() . Point
. Point ![]() lies in the interior of
lies in the interior of ![]() , and points
, and points ![]() and
and ![]() are the incenters of
are the incenters of ![]() and
and ![]() , respectively. Find the minimum possible area of
, respectively. Find the minimum possible area of ![]() as
as ![]() varies along
varies along ![]() .
.
Solution 1 (Official MAA)
First note that ![]() is a constant not depending on
is a constant not depending on ![]() , so by
, so by ![]() it suffices to minimize
it suffices to minimize ![]() . Let
. Let ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() . Remark that
. Remark that ![]() Applying the Law of Sines to
Applying the Law of Sines to ![]() gives
gives ![]() Analogously one can derive
Analogously one can derive ![]() , and so
, and so ![]() with equality when
with equality when ![]() , that is, when
, that is, when ![]() is the foot of the perpendicular from
is the foot of the perpendicular from ![]() to
to ![]() . In this case the desired area is
. In this case the desired area is ![]() . To make this feasible to compute, note that
. To make this feasible to compute, note that ![\[\sin\frac A2=\sqrt{\frac{1-\cos A}2}=\sqrt{\frac{1-\frac{b^2+c^2-a^2}{2bc}}2} = \sqrt{\dfrac{(a-b+c)(a+b-c)}{4bc}}.\]](http://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/6/9/7/697053dfbaa5f36e17c51a597f420e04697c805b.png) Applying similar logic to
Applying similar logic to ![]() and
and ![]() and simplifying yields a final answer of
and simplifying yields a final answer of 
- Notice that we truly did minimize the area for
![$[A I_1 I_2]$](//latex.artofproblemsolving.com/3/0/2/302829b0408652028edad4394003ccca90041a5d.png) because
because  are all constants while only
are all constants while only  is variable, so maximizing
is variable, so maximizing  would minimize the area.
would minimize the area.
Solution 2 (Similar to Official MAA)
It's clear that ![]() . Thus
. Thus  By the Law of Sines on
By the Law of Sines on ![]() ,
, ![]() Similarly,
Similarly, ![]() It is well known that
It is well known that ![]() Denote
Denote ![]() and
and ![]() , with
, with ![]() . Thus
. Thus ![]() and
and  Thus
Thus ![]() so
so ![\begin{align*}[AI_{1}I_{2}]&=\frac{1}{2}\cdot AI_{1}\cdot AI_{2}\cdot\sin\left(\frac{1}{2}\angle A\right) \\ &=\frac{AB\sin\left(\frac{1}{2}\angle B\right)\cdot AC\sin\left(\frac{1}{2}\angle C\right)\cdot\sin\left(\frac{1}{2}\angle A\right)}{2\sin\alpha\cos\alpha} \\ &=\frac{AB\sin\left(\frac{1}{2}\angle B\right)\cdot AC\sin\left(\frac{1}{2}\angle C\right)\cdot\sin\left(\frac{1}{2}\angle A\right)}{\sin(2\alpha)}.\end{align*}](http://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/5/7/5/5758639747d71ebabec2a359869569638af77434.png) We intend to minimize this expression, which is equivalent to maximizing
We intend to minimize this expression, which is equivalent to maximizing ![]() , and that occurs when
, and that occurs when ![]() , or
, or ![]() . Ergo,
. Ergo, ![]() is the foot of the altitude from
is the foot of the altitude from ![]() to
to ![]() . In that case, we intend to compute
. In that case, we intend to compute ![]() Recall that
Recall that ![]() and similarly for angles
and similarly for angles ![]() and
and ![]() . Applying the Law of Cosines to each angle of
. Applying the Law of Cosines to each angle of ![]() gives
gives  Thus
Thus  Thus the answer is
Thus the answer is 
Solution 3 (A lengthier, but less trigonometric approach)
First, instead of using angles to find ![]() , let's try to find the area of other, simpler figures, and subtract that from
, let's try to find the area of other, simpler figures, and subtract that from ![]() . However, to do this, we need to be able to figure out the length of the inradii, and so, we need to find
. However, to do this, we need to be able to figure out the length of the inradii, and so, we need to find ![]() .
.
To minimize ![]() , intuitively, we should try to minimize the length of
, intuitively, we should try to minimize the length of ![]() , since, after using the
, since, after using the ![]() formula for the area of a triangle, we'll be able to minimize the inradii lengths, and thus, eventually minimize the area of
formula for the area of a triangle, we'll be able to minimize the inradii lengths, and thus, eventually minimize the area of ![]() . (Proof needed here).
. (Proof needed here).
We need to minimize ![]() . Let
. Let ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() . After an application of Stewart's Theorem, we will get that
. After an application of Stewart's Theorem, we will get that ![]() To minimize this quadratic,
To minimize this quadratic, ![]() whereby we conclude that
whereby we conclude that ![]() .
.
From here, draw perpendiculars down from ![]() and
and ![]() to
to ![]() and
and ![]() respectively, and label the foot of these perpendiculars
respectively, and label the foot of these perpendiculars ![]() and
and ![]() respectively. After, draw the inradii from
respectively. After, draw the inradii from ![]() to
to ![]() , and from
, and from ![]() to
to ![]() , and draw in
, and draw in ![]() .
.
Label the foot of the inradii to ![]() and
and ![]() ,
, ![]() and
and ![]() , respectively. From here, we see that to find
, respectively. From here, we see that to find ![]() , we need to find
, we need to find ![]() , and subtract off the sum of
, and subtract off the sum of ![]() and
and ![]() .
.
![]() can be found by finding the area of two quadrilaterals
can be found by finding the area of two quadrilaterals ![]() as well as the area of a trapezoid
as well as the area of a trapezoid ![]() . If we let the inradius of
. If we let the inradius of ![]() be
be ![]() and if we let the inradius of
and if we let the inradius of ![]() be
be ![]() , we'll find, after an application of basic geometry and careful calculations on paper, that
, we'll find, after an application of basic geometry and careful calculations on paper, that ![]() .
.
The area of two triangles can be found in a similar fashion, however, we must use ![]() substitution to solve for
substitution to solve for ![]() as well as
as well as ![]() . After doing this, we'll get a similar sum in terms of
. After doing this, we'll get a similar sum in terms of ![]() and
and ![]() for the area of those two triangles which is equal to
for the area of those two triangles which is equal to ![]()
Now we're set. Summing up the area of the Hexagon and the two triangles and simplifying, we get that the formula for ![]() is just
is just ![\[[ABC]-\left(\frac{(35+3\sqrt{21})(r_1)}{2}+\frac{(45+3r_2\sqrt{21})(r_2)}{2}\right).\]](http://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/e/d/7/ed75de39d2544c5acbbad80d0d2c955f3e141ce6.png)
Using Heron's formula, ![]() . Solving for
. Solving for ![]() and
and ![]() using Heron's in
using Heron's in ![]() and
and ![]() , we get that
, we get that ![]() and
and ![]() . From here, we just have to plug into our above equation and solve.
. From here, we just have to plug into our above equation and solve.
Doing so gets us that the minimum area of ![]()
-Azeem H.(Mathislife52) ~edited by phoenixfire
Video Solution by Osman Nal
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=sT-wxV2rYqs
Solution 4 (Geometry only)
Let ![]() be semiperimeter of
be semiperimeter of ![]() be the height of
be the height of ![]() dropped from
dropped from ![]()
Let ![]() be inradius of the
be inradius of the ![]() and
and ![]() respectively.
respectively.
Using the Lemma (below), we get the area
![]()
![]() Lemma
Lemma
![]()
Proof
![]() WLOG
WLOG ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() if and only if
if and only if
Claim
![]() Proof
Proof
Let ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() We use Cosine Law for
We use Cosine Law for ![]() and
and ![]() and get
and get
![]() Last is evident, the claim has been proven.
Last is evident, the claim has been proven.
vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss
Solution 4a
Geometry proof of the equation ![]()
![]()
Using diagrams, we can recall known facts and using those facts for making sequence of equations.
![]()
The twice area of ![]() is
is
![]()
![]()
Therefore ![]()
vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss
Video Solution by MOP 2024
https://youtube.com/watch?v=ALzZA13PuZk
See Also
| 2018 AIME I (Problems • Answer Key • Resources) | ||
| Preceded by Problem 12 |
Followed by Problem 14 | |
| 1 • 2 • 3 • 4 • 5 • 6 • 7 • 8 • 9 • 10 • 11 • 12 • 13 • 14 • 15 | ||
| All AIME Problems and Solutions | ||
The problems on this page are copyrighted by the Mathematical Association of America's American Mathematics Competitions.