Difference between revisions of "Asymptote: Basics"
(→Syntax) |
|||
| (29 intermediate revisions by 17 users not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
== Syntax == | == Syntax == | ||
| − | + | On AoPS, all Asymptote diagrams are declared with the "[asy]" tag and ended with the "[/asy]" tag. Each command in Asymptote must be separated by a semicolon (;), similar to programming languages like C and Java. This convention tells Asymptote where each command ends. | |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Commands do not necessarily need to be on separate lines, since semicolons are the only method by which Asymptote interprets new commands. However, putting the commands on separate lines is often useful to separate your commands to organize your code and improve readability for other AoPSers looking to interpret your code. Whitespaces before and after commands are also not read by Asymptote, so any line can be indented as far as desired for clarity's sake. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | To write comments (Lines that are not interpreted by Asymptote), start a line with two forward slashes. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Multi-line comments can be declared with /* and ended with */. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Applying what we've learned, we can now write clear, legible, Asymptote code: | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | /* | ||
| + | This is a program | ||
| + | that draws a triangle | ||
| + | */ | ||
| + | //Below, we draw the first segment. | ||
draw((0,0)--(50,50)); | draw((0,0)--(50,50)); | ||
| − | draw((0,50)--( | + | //And the next two segments, written without a line break between them |
| − | + | draw((50,0)--(50,50));draw((50,0)--(0,0)); | |
| − | |||
==Variables and Data Types== | ==Variables and Data Types== | ||
| − | + | When coding in Asymptote, it's often helpful to store data in '''data types'''. For example, a ''real'' number like <math>1.5</math> or a ''pair'' of numbers like <math>(2,3)</math>. Each new variable that you create must be declared using a data type, with the command <tt>[datatype] [variable];</tt>. For example, if you wanted to declare the variable <math>n</math> to have type integer, you can use the command | |
int n; | int n; | ||
| − | After it | + | After it's declared, you can store a specific value in a variable using the = symbol, as in |
n=3; | n=3; | ||
| − | These two commands can be abbreviated by the single command <tt>int n=3;</tt>, and several integers can also be declared at once (<tt>int m,n,d;</tt>). | + | These two commands can be abbreviated by the single command <tt>int n=3;</tt>, and several integers can also be declared at once (<tt>int m,n,d;</tt>) or even many declarations and assignations at once: <tt>int a,b=2,c,d=5;</tt>. |
| − | + | The most commonly used data types in Asymptote are given in the following table: | |
| − | + | <center>[[Image:Table1.gif]]</center> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ==Size and Unitsize== | |
| − | + | Asymptote is a primarily coordinate-based graphics language. Each point is a pair <math>(a,b)</math> where <math>a</math> is the <math>x</math>-coordinate and <math>b</math> is the <math>y</math>-coordinate. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | However, there are many ways to choose a Cartesian coordinate system for the plane; one must pick the placement of origin and the scale on each of the <math>x</math>- and <math>y</math>-axis. Asymptote will place your image in the center of your output page after it is drawn, so placement of origin is actually irrelevant. By default, the unit length in both the <math>x</math> and <math>y</math> directions is the PostScript bigpoint, which has length <math>1/72</math> inches. Thus, if you do not change the scaling on the picture, the points <math>(0,0)</math> and <math>(72,0)</math> are exactly one inch apart when drawn in Asymptote. However, drawing in bigpoints is inconvenient if you wish to draw a figure that is exactly 3cm wide. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | The function <tt>unitsize</tt> can be used to specify the unit length for your picture. This function takes up to 3 arguments: the picture you want to scale the axes for (if this isn't specified, it defaults to <tt>currentpicture</tt>, the picture you are drawing on), the unit length in the x direction, and the unit length in the y direction. If only one real argument is given, both the x and y unit sizes are set to this number. Thus the command | |
| − | + | unitsize(72); | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
will tell Asymptote that from now on, your unit length is <math>1</math> inch. Be careful when you are redefining your unit length - now that unitsize is set to <math>72</math>, the points <math>(0,0)</math> and <math>(72,0)</math> are actually <math>72</math> inches apart! | will tell Asymptote that from now on, your unit length is <math>1</math> inch. Be careful when you are redefining your unit length - now that unitsize is set to <math>72</math>, the points <math>(0,0)</math> and <math>(72,0)</math> are actually <math>72</math> inches apart! | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | Asymptote has the built-in constants <tt>pt</tt> (1/72.27 inches), <tt>inch</tt>, <tt>cm</tt>, and <tt>mm</tt> for convenience when defining lengths, so the above command can also be stated | |
| − | + | unitsize(1inch); | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | The other useful function is <tt>size</tt>, which specifies the exact width and height of the box that your picture (if unspecified as a first argument, this will again default to <tt>currentpicture</tt>) will be fit into. If only one number is given, both the width and the height will be set to this number. For example, the command | |
| − | + | size(5cm,5cm); | |
| − | + | or just | |
| − | + | size(5cm); | |
| − | + | will fit the diagram to a 5cm x 5cm box regardless of the specified unitsizes. | |
| − | + | ||
| + | As an example, make an Asymptote document containing the following two lines: | ||
| + | unitsize(2inch); | ||
| + | draw(unitsquare); | ||
| + | and see what happens as you change the <math>2</math> inch size to several other values. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[Asymptote: Drawing | Next: Drawing]] | ||
Latest revision as of 13:11, 5 July 2024
Syntax
On AoPS, all Asymptote diagrams are declared with the "[asy]" tag and ended with the "[/asy]" tag. Each command in Asymptote must be separated by a semicolon (;), similar to programming languages like C and Java. This convention tells Asymptote where each command ends.
Commands do not necessarily need to be on separate lines, since semicolons are the only method by which Asymptote interprets new commands. However, putting the commands on separate lines is often useful to separate your commands to organize your code and improve readability for other AoPSers looking to interpret your code. Whitespaces before and after commands are also not read by Asymptote, so any line can be indented as far as desired for clarity's sake.
To write comments (Lines that are not interpreted by Asymptote), start a line with two forward slashes.
Multi-line comments can be declared with /* and ended with */.
Applying what we've learned, we can now write clear, legible, Asymptote code:
/* This is a program that draws a triangle */ //Below, we draw the first segment. draw((0,0)--(50,50)); //And the next two segments, written without a line break between them draw((50,0)--(50,50));draw((50,0)--(0,0));
Variables and Data Types
When coding in Asymptote, it's often helpful to store data in data types. For example, a real number like ![]() or a pair of numbers like
or a pair of numbers like ![]() . Each new variable that you create must be declared using a data type, with the command [datatype] [variable];. For example, if you wanted to declare the variable
. Each new variable that you create must be declared using a data type, with the command [datatype] [variable];. For example, if you wanted to declare the variable ![]() to have type integer, you can use the command
to have type integer, you can use the command
int n;
After it's declared, you can store a specific value in a variable using the = symbol, as in
n=3;
These two commands can be abbreviated by the single command int n=3;, and several integers can also be declared at once (int m,n,d;) or even many declarations and assignations at once: int a,b=2,c,d=5;.
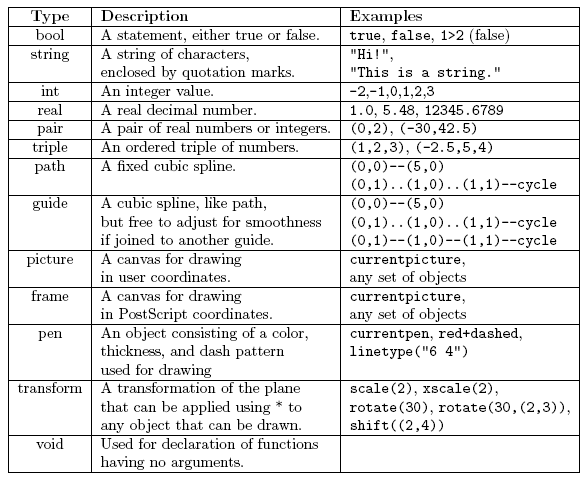
The most commonly used data types in Asymptote are given in the following table:
Size and Unitsize
Asymptote is a primarily coordinate-based graphics language. Each point is a pair ![]() where
where ![]() is the
is the ![]() -coordinate and
-coordinate and ![]() is the
is the ![]() -coordinate.
-coordinate.
However, there are many ways to choose a Cartesian coordinate system for the plane; one must pick the placement of origin and the scale on each of the ![]() - and
- and ![]() -axis. Asymptote will place your image in the center of your output page after it is drawn, so placement of origin is actually irrelevant. By default, the unit length in both the
-axis. Asymptote will place your image in the center of your output page after it is drawn, so placement of origin is actually irrelevant. By default, the unit length in both the ![]() and
and ![]() directions is the PostScript bigpoint, which has length
directions is the PostScript bigpoint, which has length ![]() inches. Thus, if you do not change the scaling on the picture, the points
inches. Thus, if you do not change the scaling on the picture, the points ![]() and
and ![]() are exactly one inch apart when drawn in Asymptote. However, drawing in bigpoints is inconvenient if you wish to draw a figure that is exactly 3cm wide.
are exactly one inch apart when drawn in Asymptote. However, drawing in bigpoints is inconvenient if you wish to draw a figure that is exactly 3cm wide.
The function unitsize can be used to specify the unit length for your picture. This function takes up to 3 arguments: the picture you want to scale the axes for (if this isn't specified, it defaults to currentpicture, the picture you are drawing on), the unit length in the x direction, and the unit length in the y direction. If only one real argument is given, both the x and y unit sizes are set to this number. Thus the command
unitsize(72);
will tell Asymptote that from now on, your unit length is ![]() inch. Be careful when you are redefining your unit length - now that unitsize is set to
inch. Be careful when you are redefining your unit length - now that unitsize is set to ![]() , the points
, the points ![]() and
and ![]() are actually
are actually ![]() inches apart!
inches apart!
Asymptote has the built-in constants pt (1/72.27 inches), inch, cm, and mm for convenience when defining lengths, so the above command can also be stated
unitsize(1inch);
The other useful function is size, which specifies the exact width and height of the box that your picture (if unspecified as a first argument, this will again default to currentpicture) will be fit into. If only one number is given, both the width and the height will be set to this number. For example, the command
size(5cm,5cm);
or just
size(5cm);
will fit the diagram to a 5cm x 5cm box regardless of the specified unitsizes.
As an example, make an Asymptote document containing the following two lines:
unitsize(2inch); draw(unitsquare);
and see what happens as you change the ![]() inch size to several other values.
inch size to several other values.









