Difference between revisions of "2015 AIME I Problems/Problem 6"
m (→Solution) |
m |
||
| (24 intermediate revisions by 15 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Problem== | ==Problem== | ||
| − | Point <math>A,B,C,D,</math> and <math>E</math> are equally spaced on a minor arc of a | + | Point <math>A,B,C,D,</math> and <math>E</math> are equally spaced on a minor arc of a circle. Points <math>E,F,G,H,I</math> and <math>A</math> are equally spaced on a minor arc of a second circle with center <math>C</math> as shown in the figure below. The angle <math>\angle ABD</math> exceeds <math>\angle AHG</math> by <math>12^\circ</math>. Find the degree measure of <math>\angle BAG</math>. |
<asy> | <asy> | ||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
label("$G$",G,dir(260)); | label("$G$",G,dir(260)); | ||
label("$H$",H,dir(280)); | label("$H$",H,dir(280)); | ||
| − | label("$I$",I,dir(315));</asy> | + | label("$I$",I,dir(315)); |
| + | </asy> | ||
| − | ==Solution== | + | ==Solution 1== |
| − | Let O be the center of the circle with ABCDE on it. | + | Let <math>O</math> be the center of the circle with <math>ABCDE</math> on it. |
| − | Let <math>x | + | Let <math>x</math> be the degree measurement of <math>\overarc{ED}=\overarc{DC}=\overarc{CB}=\overarc{BA}</math> in circle <math>O</math> |
| − | <math>\angle ECA</math> is therefore <math>5y</math> by way of circle <math>C</math> and < | + | |
| − | <math>\angle ABD</math> is <math>180 - \frac{3x}{2}</math> by way of circle O, and < | + | and <math>y</math> be the degree measurement of <math>\overarc{EF}=\overarc{FG}=\overarc{GH}=\overarc{HI}=\overarc{IA}</math> in circle <math>C</math>. |
| + | |||
| + | <math>\angle ECA</math> is, therefore, <math>5y</math> by way of circle <math>C</math> and <cmath>\frac{360-4x}{2}=180-2x</cmath> by way of circle <math>O</math>. | ||
| + | <math>\angle ABD</math> is <math>180 - \frac{3x}{2}</math> by way of circle <math>O</math>, and <cmath>\angle AHG = 180 - \frac{3y}{2}</cmath> by way of circle <math>C</math>. | ||
This means that: | This means that: | ||
| − | + | <cmath>180-\frac{3x}{2}=180-\frac{3y}{2}+12</cmath> | |
| − | + | which when simplified yields <cmath>\frac{3x}{2}+12=\frac{3y}{2}</cmath> or <cmath>x+8=y</cmath> | |
Since: | Since: | ||
| − | < | + | <cmath>5y=180-2x</cmath> and <cmath>5x+40=180-2x</cmath> |
So: | So: | ||
| − | < | + | <cmath>7x=140\Longleftrightarrow x=20</cmath> |
| − | < | + | <cmath>y=28</cmath> |
| − | <math>\angle BAG</math> is equal to <math>\angle BAE</math> + <math>\angle EAG</math>, which equates to 3x | + | <math>\angle BAG</math> is equal to <math>\angle BAE</math> + <math>\angle EAG</math>, which equates to <math>\frac{3x}{2} + y</math>. |
| − | Plugging in yields <math>30+28</math>, or <math>058</math> | + | Plugging in yields <math>30+28</math>, or <math>\boxed{058}</math>. |
| + | |||
| + | ==Solution 2== | ||
| + | Let <math>m</math> be the degree measurement of <math>\angle GCH</math>. Since <math>G,H</math> lie on a circle with center <math>C</math>, <math>\angle GHC=\frac{180-m}{2}=90-\frac{m}{2}</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Since <math>\angle ACH=2 \angle GCH=2m</math>, <math>\angle AHC=\frac{180-2m}{2}=90-m</math>. Adding <math>\angle GHC</math> and <math>\angle AHC</math> gives <math>\angle AHG=180-\frac{3m}{2}</math>, and <math>\angle ABD=\angle AHG+12=192-\frac{3m}{2}</math>. Since <math>AE</math> is parallel to <math>BD</math>, <math>\angle DBA=180-\angle ABD=\frac{3m}{2}-12=</math><math>\overarc{BE}</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | We are given that <math>A,B,C,D,E</math> are evenly distributed on a circle. Hence, | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\overarc{ED}=\overarc{DC}=\overarc{CB}=\overarc{BA}</math><math>=\frac{\angle DBA}{3}=\frac{m}{2}-4</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Here comes the key: Draw a line through <math>C</math> parallel to <math>AE</math>, and select a point <math>X</math> to the right of point <math>C</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\angle ACX</math> = <math>\overarc{AB}</math> + <math>\overarc{BC}</math> = <math>m-8</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Let the midpoint of <math>\overline{HG}</math> be <math>Y</math>, then <math>\angle YCX=\angle ACX+\angle ACY=(m-8)+\frac{5m}{2}=90</math>. Solving gives <math>m=28</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | The rest of the solution proceeds as in solution 1, which gives <math>\boxed{058}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==Solution 3== | ||
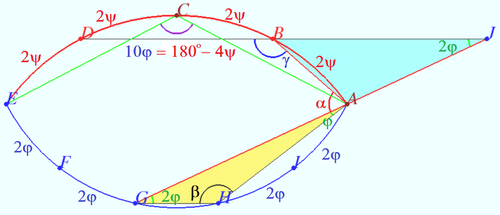
| + | [[File:2015 AIME I 6.png|500px|right]] | ||
| + | Let <math>\angle GAH = \varphi \implies \overset{\Large\frown} {GH} = 2\varphi \implies</math> | ||
| + | <cmath>\overset{\Large\frown} {EF} = \overset{\Large\frown} {FG} = \overset{\Large\frown} {HI} = \overset{\Large\frown} {IA} = 2\varphi \implies</cmath> | ||
| + | <cmath>\angle AGH = 2\varphi, \angle ACE = 10 \varphi.</cmath> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <cmath>BD||GH \implies \angle AJB = \angle AGH = 2 \varphi.</cmath> | ||
| + | <cmath>\triangle AHG: \hspace{10mm} \angle AHG = \beta = 180^\circ – 3 \varphi.</cmath> | ||
| + | <math>\hspace{10mm} \triangle ABJ: \hspace{10mm} \angle BAG + \angle ABD = \alpha + \gamma = 180^\circ + 2 \varphi. </math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Let arc <math> \overset{\Large\frown} {AB} = 2\psi \implies</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\angle ACE = \frac {360^\circ – 8 \psi}{2}= 180^\circ – 4 \psi, \angle ABD = \gamma =\frac {360^\circ – 6 \psi}{2} =180^\circ – 3 \psi.</math> | ||
| + | <math>\gamma – \beta = 3(\varphi – \psi) = 12^\circ \implies \psi = \varphi – 4^\circ \implies 10 \varphi = 180^\circ – 4(\varphi – 4^\circ) \implies 14 \varphi = 196^\circ \implies \varphi = 14^\circ.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Therefore <math>\gamma = 180^\circ – 3 \cdot (14^\circ – 4^\circ) = 150^\circ \implies \alpha = 180^\circ + 2 \cdot 14^\circ – 150^\circ = \boxed{\textbf{058}}.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==Video Solution== | ||
| + | |||
| + | https://youtu.be/IuwkX2Dv25s | ||
| + | |||
| + | ~MathProblemSolvingSkills.com | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
{{AIME box|year=2015|n=I|num-b=5|num-a=7}} | {{AIME box|year=2015|n=I|num-b=5|num-a=7}} | ||
{{MAA Notice}} | {{MAA Notice}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Introductory Geometry Problems]] | ||
Latest revision as of 15:04, 21 July 2023
Problem
Point ![]() and
and ![]() are equally spaced on a minor arc of a circle. Points
are equally spaced on a minor arc of a circle. Points ![]() and
and ![]() are equally spaced on a minor arc of a second circle with center
are equally spaced on a minor arc of a second circle with center ![]() as shown in the figure below. The angle
as shown in the figure below. The angle ![]() exceeds
exceeds ![]() by
by ![]() . Find the degree measure of
. Find the degree measure of ![]() .
.
![[asy] pair A,B,C,D,E,F,G,H,I,O; O=(0,0); C=dir(90); B=dir(70); A=dir(50); D=dir(110); E=dir(130); draw(arc(O,1,50,130)); real x=2*sin(20*pi/180); F=x*dir(228)+C; G=x*dir(256)+C; H=x*dir(284)+C; I=x*dir(312)+C; draw(arc(C,x,200,340)); label("$A$",A,dir(0)); label("$B$",B,dir(75)); label("$C$",C,dir(90)); label("$D$",D,dir(105)); label("$E$",E,dir(180)); label("$F$",F,dir(225)); label("$G$",G,dir(260)); label("$H$",H,dir(280)); label("$I$",I,dir(315)); [/asy]](http://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/5/5/9/5590bc90f068d76cce0399a7cf16b9bcf4f72c94.png)
Solution 1
Let ![]() be the center of the circle with
be the center of the circle with ![]() on it.
on it.
Let ![]() be the degree measurement of
be the degree measurement of ![]() in circle
in circle ![]()
and ![]() be the degree measurement of
be the degree measurement of ![]() in circle
in circle ![]() .
.
![]() is, therefore,
is, therefore, ![]() by way of circle
by way of circle ![]() and
and ![]() by way of circle
by way of circle ![]() .
.
![]() is
is ![]() by way of circle
by way of circle ![]() , and
, and ![]() by way of circle
by way of circle ![]() .
.
This means that:
![]()
which when simplified yields ![]() or
or ![]() Since:
Since:
![]() and
and ![]() So:
So:
![]()
![]()
![]() is equal to
is equal to ![]() +
+ ![]() , which equates to
, which equates to ![]() .
Plugging in yields
.
Plugging in yields ![]() , or
, or ![]() .
.
Solution 2
Let ![]() be the degree measurement of
be the degree measurement of ![]() . Since
. Since ![]() lie on a circle with center
lie on a circle with center ![]() ,
, ![]() .
.
Since ![]() ,
, ![]() . Adding
. Adding ![]() and
and ![]() gives
gives ![]() , and
, and ![]() . Since
. Since ![]() is parallel to
is parallel to ![]() ,
, ![]()
![]() .
.
We are given that ![]() are evenly distributed on a circle. Hence,
are evenly distributed on a circle. Hence,
![]()
![]()
Here comes the key: Draw a line through ![]() parallel to
parallel to ![]() , and select a point
, and select a point ![]() to the right of point
to the right of point ![]() .
.
![]() =
= ![]() +
+ ![]() =
= ![]() .
.
Let the midpoint of ![]() be
be ![]() , then
, then ![]() . Solving gives
. Solving gives ![]()
The rest of the solution proceeds as in solution 1, which gives ![]()
Solution 3
Let ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Let arc ![]()
![]()
![]()
Therefore ![]()
Video Solution
~MathProblemSolvingSkills.com
See Also
| 2015 AIME I (Problems • Answer Key • Resources) | ||
| Preceded by Problem 5 |
Followed by Problem 7 | |
| 1 • 2 • 3 • 4 • 5 • 6 • 7 • 8 • 9 • 10 • 11 • 12 • 13 • 14 • 15 | ||
| All AIME Problems and Solutions | ||
The problems on this page are copyrighted by the Mathematical Association of America's American Mathematics Competitions.