Difference between revisions of "2005 AMC 12A Problems/Problem 16"
(→Problem) |
(→Solution 1) |
||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
[[Image:2005_12A_AMC-16b.png]] | [[Image:2005_12A_AMC-16b.png]] | ||
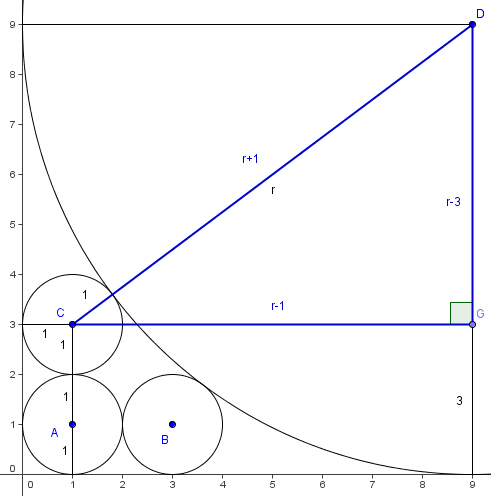
| − | Draw the segment between the center of the third circle and the large circle; this has length <math>r+1</math>. We then draw the [[radius]] of the large circle that is perpendicular to the [[x-axis]], and draw the perpendicular from this radius to the center of the third circle. This gives us a [[right triangle]] with legs <math>r-3,r-1</math> and [[hypotenuse]] <math>r+1</math>. The [[Pythagorean Theorem]] yields: | + | Set <math>s =1</math> so that we only have to find <math>r</math>. Draw the segment between the center of the third circle and the large circle; this has length <math>r+1</math>. We then draw the [[radius]] of the large circle that is perpendicular to the [[x-axis]], and draw the perpendicular from this radius to the center of the third circle. This gives us a [[right triangle]] with legs <math>r-3,r-1</math> and [[hypotenuse]] <math>r+1</math>. The [[Pythagorean Theorem]] yields: |
<div style="text-align:center;"><math>(r-3)^2 + (r-1)^2 = (r+1)^2</math><br /><math>r^2 - 10r + 9 = 0</math><br /><math>r = 1, 9</math></div> | <div style="text-align:center;"><math>(r-3)^2 + (r-1)^2 = (r+1)^2</math><br /><math>r^2 - 10r + 9 = 0</math><br /><math>r = 1, 9</math></div> | ||
Quite obviously <math>r > 1</math>, so <math>r = 9 \boxed{(D)}</math>. | Quite obviously <math>r > 1</math>, so <math>r = 9 \boxed{(D)}</math>. | ||
Revision as of 00:56, 10 January 2021
Problem
Three circles of radius ![]() are drawn in the first quadrant of the
are drawn in the first quadrant of the ![]() -plane. The first circle is tangent to both axes, the second is tangent to the first circle and the
-plane. The first circle is tangent to both axes, the second is tangent to the first circle and the ![]() -axis, and the third is tangent to the first circle and the
-axis, and the third is tangent to the first circle and the ![]() -axis. A circle of radius
-axis. A circle of radius ![]() is tangent to both axes and to the second and third circles. What is
is tangent to both axes and to the second and third circles. What is ![]() ?
?
![[asy] unitsize(3mm); defaultpen(linewidth(.8pt)+fontsize(10pt)); dotfactor=3; pair O0=(9,9), O1=(1,1), O2=(3,1), O3=(1,3); pair P0=O0+9*dir(-45), P3=O3+dir(70); pair[] ps={O0,O1,O2,O3}; dot(ps); draw(Circle(O0,9)); draw(Circle(O1,1)); draw(Circle(O2,1)); draw(Circle(O3,1)); draw(O0--P0,linetype("3 3")); draw(O3--P3,linetype("2 2")); draw((0,0)--(18,0)); draw((0,0)--(0,18)); label("$r$",midpoint(O0--P0),NE); label("$s$",(-1.5,4)); draw((-1,4)--midpoint(O3--P3));[/asy]](http://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/6/5/7/657afd2eef0760abe2ccc3fe7453a83a0b22e681.png)
![]()
Solution
Solution 1
Set ![]() so that we only have to find
so that we only have to find ![]() . Draw the segment between the center of the third circle and the large circle; this has length
. Draw the segment between the center of the third circle and the large circle; this has length ![]() . We then draw the radius of the large circle that is perpendicular to the x-axis, and draw the perpendicular from this radius to the center of the third circle. This gives us a right triangle with legs
. We then draw the radius of the large circle that is perpendicular to the x-axis, and draw the perpendicular from this radius to the center of the third circle. This gives us a right triangle with legs ![]() and hypotenuse
and hypotenuse ![]() . The Pythagorean Theorem yields:
. The Pythagorean Theorem yields:
Quite obviously ![]() , so
, so ![]() .
.