Difference between revisions of "Asymptote (Vector Graphics Language)"
(→See also) |
(→See also) |
||
| Line 57: | Line 57: | ||
*[[LaTeX]] | *[[LaTeX]] | ||
* [http://artofproblemsolving.com/wiki/index.php?title=LaTeX:LaTeX_on_AoPS AoPS's Getting Started with LaTeX guide] | * [http://artofproblemsolving.com/wiki/index.php?title=LaTeX:LaTeX_on_AoPS AoPS's Getting Started with LaTeX guide] | ||
| − | * | + | * http://www.artofproblemsolving.com/community/c68_latex_and_asymptote Asymptote Forum on AoPS |
[[Asymptote: Getting Started | Next: Getting Started]] | [[Asymptote: Getting Started | Next: Getting Started]] | ||
Revision as of 21:04, 17 July 2018
Asymptote is a powerful vector graphics language designed for creating mathematical diagrams and figures. It can output images in either eps or pdf format, and is compatible with the standard mathematics typesetting language, LaTeX. It is also a complete programming language, and has cleaner syntax than its predecessor, MetaPost, which was a language used only for two-dimensional graphics.
Here is an example of an image that can be produced using Asymptote:
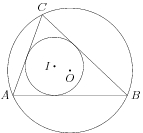
In a sense, Asymptote is the ruler and compass of typesetting.
You can use Asymptote on the AoPSWiki right now, by enclosing the Asymptote code within <asy>...</asy> tags. For example, the following code
<asy>
draw((0,0)--(3,7),red);
dot((0,0));
dot((3,7));
label("Produced with Asymptote "+version.VERSION,point(S),2S);
</asy>
created the picture
![[asy] draw((0,0)--(3,7),red); dot((0,0)); dot((3,7)); label("Produced with Asymptote "+version.VERSION,point(S),2S); [/asy]](http://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/d/8/8/d88f3bbba665110715eb36189c8dc425965c3be9.png)
And on the AoPS forums you can use [asy]..[/asy]
Another example:
[asy] pair A,B,C,X,Y,Z; A = (0,0); B = (1,0); C = (0.3,0.8); draw(A--B--C--A); X = (B+C)/2; Y = (A+C)/2; Z = (A+B)/2; draw(A--X, red); draw(B--Y,red); draw(C--Z,red); [/asy]
![[asy] pair A,B,C,X,Y,Z; A = (0,0); B = (1,0); C = (0.3,0.8); draw(A--B--C--A); X = (B+C)/2; Y = (A+C)/2; Z = (A+B)/2; draw(A--X, red); draw(B--Y,red); draw(C--Z,red);[/asy]](http://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/b/5/7/b57775c768cabba6a2ac4465219858d7f0636b41.png)









