Difference between revisions of "2006 AIME II Problems/Problem 1"
m (→See also) |
m (→Solution: argh) |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
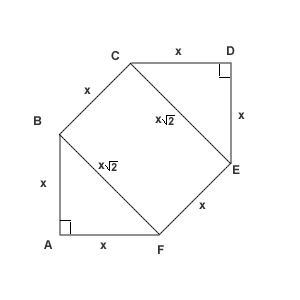
Let the side length be called <math>x</math>, so <math>x=AB=BC=CD=DE=EF=AF</math>. | Let the side length be called <math>x</math>, so <math>x=AB=BC=CD=DE=EF=AF</math>. | ||
| − | [[Image: | + | [[Image:2006_II_AIME-1.png]] |
The diagonal <math>BF=\sqrt{AB^2+AF^2}=\sqrt{x^2+x^2}=x\sqrt{2}</math>. Then the areas of the triangles AFB and CDE in total are <math>\frac{x^2}{2}\cdot 2</math>, | The diagonal <math>BF=\sqrt{AB^2+AF^2}=\sqrt{x^2+x^2}=x\sqrt{2}</math>. Then the areas of the triangles AFB and CDE in total are <math>\frac{x^2}{2}\cdot 2</math>, | ||
Revision as of 19:37, 25 September 2007
Problem
In convex hexagon ![]() , all six sides are congruent,
, all six sides are congruent, ![]() and
and ![]() are right angles, and
are right angles, and ![]() and
and ![]() are congruent. The area of the hexagonal region is
are congruent. The area of the hexagonal region is ![]() Find
Find ![]() .
.
Solution
Let the side length be called ![]() , so
, so ![]() .
.
The diagonal ![]() . Then the areas of the triangles AFB and CDE in total are
. Then the areas of the triangles AFB and CDE in total are ![]() ,
and the area of the rectangle BCEF equals
,
and the area of the rectangle BCEF equals ![]()
Then we have to solve the equation
![]() .
.
![]()
![]()
Therefore, ![]() is
is ![]() .
.
See also
| 2006 AIME II (Problems • Answer Key • Resources) | ||
| Preceded by First Question |
Followed by Problem 2 | |
| 1 • 2 • 3 • 4 • 5 • 6 • 7 • 8 • 9 • 10 • 11 • 12 • 13 • 14 • 15 | ||
| All AIME Problems and Solutions | ||