Difference between revisions of "2016 USAMO Problems/Problem 3"
(→Solution) |
(→See also) |
||
| (22 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
2. Show that <math>I_AY^2-I_AZ^2=OY^2-OZ^2,</math> which implies <math>\overline{OI_A}\perp\overline{YZ}.</math> This can be proved by multiple applications of the Pythagorean Thm. | 2. Show that <math>I_AY^2-I_AZ^2=OY^2-OZ^2,</math> which implies <math>\overline{OI_A}\perp\overline{YZ}.</math> This can be proved by multiple applications of the Pythagorean Thm. | ||
| − | {{ | + | ==Solution 2== |
| + | [[File:2016 USAMO 3a.png|300px|right]] | ||
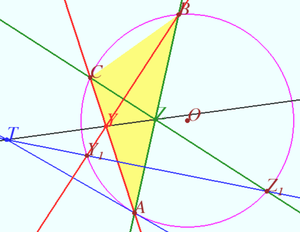
| + | We find point <math>T</math> on line <math>YZ,</math> we prove that <math>TY \perp OI_A</math> and state that <math>P</math> is the point <math>X(24)</math> from ENCYCLOPEDIA OF TRIANGLE, therefore <math>P \in OI_A.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Let <math>\omega</math> be circumcircle of <math>\triangle ABC</math> centered at <math>O.</math> | ||
| + | Let <math>Y_1,</math> and <math>Z_1</math> be crosspoints of <math>\omega</math> and <math>BY,</math> and <math>CZ,</math> respectively. | ||
| + | Let <math>T</math> be crosspoint of <math>YZ</math> and <math>Y_1 Z_1.</math> | ||
| + | In accordance the Pascal theorem for pentagon <math>AZ_1BCY_1,</math> <math>AT</math> is tangent to <math>\omega</math> at <math>A.</math> | ||
| + | |||
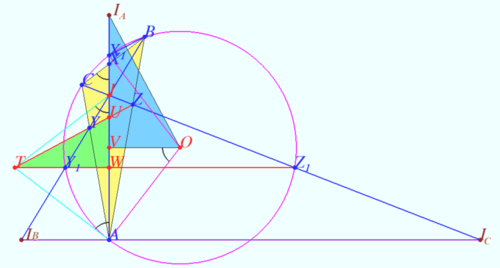
| + | [[File:2016 USAMO 3b.png|500px|right]] | ||
| + | Let <math>I_A, I_B, I_C</math> be <math>A, B,</math> and <math>C</math>-excenters of <math>\triangle ABC.</math> | ||
| + | Denote <cmath>a = BC, b = AC, c = AB, 2\alpha = \angle CAB, 2\beta = \angle ABC, 2\gamma = \angle ACB,</cmath> | ||
| + | <cmath>\psi = 90^\circ – \gamma + \beta, X = AI_A \cap \omega, X_1 = BC \cap AI_A,</cmath> | ||
| + | <cmath>I = BI_B \cap CI_C, U= YZ \cap AI_A, W = Y_1Z_1 \cap AI_A,</cmath> | ||
| + | <math>V</math> is the foot ot perpendicular from <math>O</math> to <math>AI_A.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>I</math> is ortocenter of <math>\triangle I_A I_B I_C</math> and incenter of <math>\triangle ABC.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\omega</math> is the Nine–point circle of <math>\triangle I_A I_B I_C.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>Y_1</math> is the midpoint of <math>II_B, Z_1</math> is the midpoint of <math>II_C</math> in accordance with property of Nine–point circle <math>\implies</math> | ||
| + | <cmath>Y_1Z_1 || I_B AI_C || VO, IW = AW \implies TW \perp AI.</cmath> | ||
| + | <cmath>\angle AXC = 180 ^\circ – 2\gamma – \alpha = 90 ^\circ – \gamma + \beta = \psi.</cmath> | ||
| + | <cmath>\angle TAI = \angle VOA = 2\beta + \alpha = 90 ^\circ – \gamma + \beta = \psi.</cmath> | ||
| + | <cmath>I_A X_1 = IX_1 = BX_1 = 2R \sin \alpha \implies</cmath> | ||
| + | <cmath>\cot \angle OI_A A = \frac {VI_A}{VO} = \frac {R \sin \psi + 2R \sin \alpha}{R \cos \psi} = \tan \psi + \frac{2 \sin\alpha}{\cos \psi}.</cmath> | ||
| + | <cmath>CX = \frac {ab}{b+c} \implies \frac {AI}{IX}= \frac {AC}{CX}= \frac {b+c}{a} \implies AI = AX \frac {b+c}{a+b+c},</cmath> | ||
| + | <cmath>AW = \frac {AI}{2}, UW = AU – AW,</cmath> | ||
| + | In <math>\triangle ABC</math> segment <math>YZ</math> cross segment <math>AX \implies \frac {AU}{UX} = \frac {m + nk}{k+1},</math> where <math>n = \frac {a}{b}, m = \frac{a}{c}, k=\frac {b}{c},</math> | ||
| + | <cmath>\frac {AU}{UX} = \frac{2a}{b+c} \implies AU = AX \cdot \frac {b+c}{2a +b +c}.</cmath> | ||
| + | <cmath>\frac {AU – AW}{AW} = \frac {b+c} {2a + b + c}.</cmath> | ||
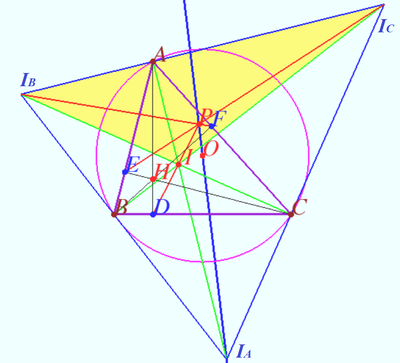
| + | [[File:2016 USAMO 3c.png|400px|right]] | ||
| + | <cmath>\cot \angle UTW = \frac {TW}{UW} = \frac {AW \cdot \tan \psi}{AU – AW} = \tan \psi \cdot \frac {2a +b+c}{b+c} =</cmath> | ||
| + | <cmath>=\tan \psi \cdot \frac {2a}{b+c} + \tan \psi = \frac {2 \sin \alpha}{\sin \psi} \tan \psi + \tan \psi = \tan \psi + \frac{2 \sin\alpha}{\cos \psi}</cmath> | ||
| + | <cmath>\implies \angle UTW = \angle OI_AA .</cmath> | ||
| + | <cmath>TW \perp AI_A \implies TYZ \perp OI_A.</cmath> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Let <math>\triangle II_B I_C</math> be the base triangle with orthocenter <math>I_A,</math> center of Nine-points circle <math>O \implies OI_A</math> be the Euler line of <math>\triangle II_B I_C.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\triangle ABC</math> is orthic triangle of <math>\triangle II_B I_C,</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\triangle DEF</math> is orthic-of-orthic triangle. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>P</math> is perspector of base triangle and orthic-of-orthic triangle. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Therefore <math>P</math> is point <math>X(24)</math> of ENCYCLOPEDIA OF TRIANGLE CENTERS which lies on Euler line of the base triangle. | ||
| + | [[https://artofproblemsolving.com/wiki/index.php/Kimberling%E2%80%99s_point_X(24)]] | ||
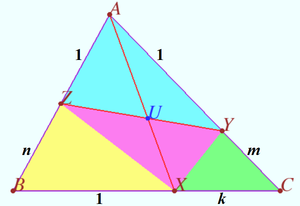
| + | [[File:2016 USAMO 3d.png|300px|right]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | <i><b>Claim</b></i> <cmath>\frac {AU}{UX} = \frac {m + nk}{k + 1}.</cmath> | ||
| + | <i><b>Proof</b></i> | ||
| + | <cmath>\frac {[AYZ]}{[ABC]} = \frac {AZ \cdot AY}{AB \cdot AC} = \frac {1}{(n + 1) \cdot (m+1)}, </cmath> | ||
| + | <cmath>\frac {[BXZ]}{[ABC]} = \frac {BZ \cdot BX}{AB \cdot BC} = \frac {n}{(n + 1) \cdot (k+1)}, </cmath> | ||
| + | <cmath>\frac {[CXY]}{[ABC]} = \frac {CY \cdot CX}{AC \cdot BC} = \frac {mk}{(m + 1) \cdot (k+1)},</cmath> | ||
| + | <cmath>\frac {[XYZ]}{[ABC]} = 1 - \frac {[AYZ]}{[ABC]} – \frac {[BXZ]}{[ABC]} – \frac {[CXY]}{[ABC]} = \frac {m+nk}{(m + 1) \cdot (k+1)\cdot (n+1)}, </cmath> | ||
| + | <cmath>\frac {AU}{UX} = \frac {[AYZ]}{[XYZ]} = \frac {m + nk}{k + 1}.</cmath> | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss''' | ||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
{{USAMO newbox|year=2016|num-b=2|num-a=4}} | {{USAMO newbox|year=2016|num-b=2|num-a=4}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{MAA Notice}} | ||
Latest revision as of 21:36, 17 October 2022
Contents
[hide]Problem
Let ![]() be an acute triangle, and let
be an acute triangle, and let ![]() and
and ![]() denote its
denote its ![]() -excenter,
-excenter, ![]() -excenter, and circumcenter, respectively. Points
-excenter, and circumcenter, respectively. Points ![]() and
and ![]() are selected on
are selected on ![]() such that
such that ![]() and
and ![]() Similarly, points
Similarly, points ![]() and
and ![]() are selected on
are selected on ![]() such that
such that ![]() and
and ![]()
Lines ![]() and
and ![]() meet at
meet at ![]() Prove that
Prove that ![]() and
and ![]() are perpendicular.
are perpendicular.
Solution
This problem can be proved in the following two steps.
1. Let ![]() be the
be the ![]() -excenter, then
-excenter, then ![]() and
and ![]() are colinear. This can be proved by the Trigonometric Form of Ceva's Theorem for
are colinear. This can be proved by the Trigonometric Form of Ceva's Theorem for ![]()
2. Show that ![]() which implies
which implies ![]() This can be proved by multiple applications of the Pythagorean Thm.
This can be proved by multiple applications of the Pythagorean Thm.
Solution 2
We find point ![]() on line
on line ![]() we prove that
we prove that ![]() and state that
and state that ![]() is the point
is the point ![]() from ENCYCLOPEDIA OF TRIANGLE, therefore
from ENCYCLOPEDIA OF TRIANGLE, therefore ![]()
Let ![]() be circumcircle of
be circumcircle of ![]() centered at
centered at ![]() Let
Let ![]() and
and ![]() be crosspoints of
be crosspoints of ![]() and
and ![]() and
and ![]() respectively.
Let
respectively.
Let ![]() be crosspoint of
be crosspoint of ![]() and
and ![]() In accordance the Pascal theorem for pentagon
In accordance the Pascal theorem for pentagon ![]()
![]() is tangent to
is tangent to ![]() at
at ![]()
Let ![]() be
be ![]() and
and ![]() -excenters of
-excenters of ![]() Denote
Denote ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() is the foot ot perpendicular from
is the foot ot perpendicular from ![]() to
to ![]()
![]() is ortocenter of
is ortocenter of ![]() and incenter of
and incenter of ![]()
![]() is the Nine–point circle of
is the Nine–point circle of ![]()
![]() is the midpoint of
is the midpoint of ![]() is the midpoint of
is the midpoint of ![]() in accordance with property of Nine–point circle
in accordance with property of Nine–point circle ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() In
In ![]() segment
segment ![]() cross segment
cross segment ![]() where
where ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Let ![]() be the base triangle with orthocenter
be the base triangle with orthocenter ![]() center of Nine-points circle
center of Nine-points circle ![]() be the Euler line of
be the Euler line of ![]()
![]() is orthic triangle of
is orthic triangle of ![]()
![]() is orthic-of-orthic triangle.
is orthic-of-orthic triangle.
![]() is perspector of base triangle and orthic-of-orthic triangle.
is perspector of base triangle and orthic-of-orthic triangle.
Therefore ![]() is point
is point ![]() of ENCYCLOPEDIA OF TRIANGLE CENTERS which lies on Euler line of the base triangle.
[[1]]
of ENCYCLOPEDIA OF TRIANGLE CENTERS which lies on Euler line of the base triangle.
[[1]]
Claim ![]() Proof
Proof
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss
See also
| 2016 USAMO (Problems • Resources) | ||
| Preceded by Problem 2 |
Followed by Problem 4 | |
| 1 • 2 • 3 • 4 • 5 • 6 | ||
| All USAMO Problems and Solutions | ||
The problems on this page are copyrighted by the Mathematical Association of America's American Mathematics Competitions. ![]()