Difference between revisions of "1996 AHSME Problems/Problem 30"
Isabelchen (talk | contribs) (→Solution 4) |
Isabelchen (talk | contribs) (→Solution 4) |
||
| Line 56: | Line 56: | ||
[[File:1996AHSMEP30.png|400px|center]] | [[File:1996AHSMEP30.png|400px|center]] | ||
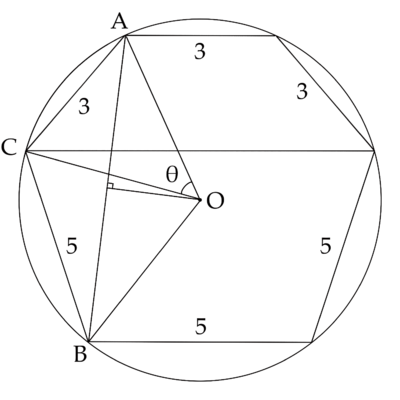
| − | Note that <math>\overarc{AB}</math> is a third of the circumference, therefore, <math>\angle AOB = 120^{\circ}</math> | + | Note that minor arc <math>\overarc{AB}</math> is a third of the circumference, therefore, <math>\angle AOB = 120^{\circ}</math>. minor arc <math>\overarc{AB} =240^{\circ}</math>, <math>\angle ACB = 120^{\circ}</math> |
By the Law of Cosine, <math>AB = \sqrt{ 3^2 + 5^2 - 2 \cdot 3 \cdot 5 \cdot \cos 120^{\circ}} = \sqrt{ 9 + 25 + 15 } = 7</math> | By the Law of Cosine, <math>AB = \sqrt{ 3^2 + 5^2 - 2 \cdot 3 \cdot 5 \cdot \cos 120^{\circ}} = \sqrt{ 9 + 25 + 15 } = 7</math> | ||
| − | <math> | + | <math>\frac{\angle AOB}{2} = 60^{\circ}</math>, therefore, <math>r = \frac{\frac{AB}{2}}{\sin 60^{\circ}} = \frac{\frac{7}{2}}{ \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2} } = \frac{7\sqrt{3}}{3}</math> |
<math>\sin \frac{\theta}{2} = \frac{\frac32}{r} = \frac{3}{2r} = \frac{3}{2 \cdot \frac{7\sqrt{3}}{3}} = \frac{3 \sqrt{3}}{14}</math> | <math>\sin \frac{\theta}{2} = \frac{\frac32}{r} = \frac{3}{2r} = \frac{3}{2 \cdot \frac{7\sqrt{3}}{3}} = \frac{3 \sqrt{3}}{14}</math> | ||
| Line 66: | Line 66: | ||
Let <math>x</math> be the length of the chord, <math>\sin \frac{3 \theta}{2} = \frac{\frac{x}{2}}{r}</math> | Let <math>x</math> be the length of the chord, <math>\sin \frac{3 \theta}{2} = \frac{\frac{x}{2}}{r}</math> | ||
| − | By the triple angle formula, <math>\sin \frac{3 \theta}{2} = 3 \cdot \frac{\theta}{2} - 4 \cdot (\frac{\theta}{2})^3 = 3 \cdot \frac{3 \sqrt{3}}{14} - 4 \cdot (\frac{3 \sqrt{3}}{14})^3</math> | + | By the triple angle formula, <math>\sin \frac{3 \theta}{2} = 3 \cdot \frac{\sin \theta}{2} - 4 \cdot (\frac{\sin \theta}{2})^3 = 3 \cdot \frac{3 \sqrt{3}}{14} - 4 \cdot (\frac{3 \sqrt{3}}{14})^3</math> |
<math>x = 2 \cdot \frac{7\sqrt{3}}{3} \cdot [3 \cdot \frac{3 \sqrt{3}}{14} - 4 \cdot (\frac{3 \sqrt{3}}{14})^3] = 2 \cdot \frac{7\sqrt{3}}{3} \cdot (\frac{9\sqrt{3}}{14} - \frac{82\sqrt{3}}{2 \cdot 7^3}) = 9 - \frac{81}{49} = \frac{360}{49}</math> | <math>x = 2 \cdot \frac{7\sqrt{3}}{3} \cdot [3 \cdot \frac{3 \sqrt{3}}{14} - 4 \cdot (\frac{3 \sqrt{3}}{14})^3] = 2 \cdot \frac{7\sqrt{3}}{3} \cdot (\frac{9\sqrt{3}}{14} - \frac{82\sqrt{3}}{2 \cdot 7^3}) = 9 - \frac{81}{49} = \frac{360}{49}</math> | ||
Revision as of 11:30, 30 September 2023
Problem
A hexagon inscribed in a circle has three consecutive sides each of length 3 and three consecutive sides each of length 5. The chord of the circle that divides the hexagon into two trapezoids, one with three sides each of length 3 and the other with three sides each of length 5, has length equal to ![]() , where
, where ![]() and
and ![]() are relatively prime positive integers. Find
are relatively prime positive integers. Find ![]() .
.
![]()
Solution 1
In hexagon ![]() , let
, let ![]() and let
and let ![]() . Since arc
. Since arc ![]() is one third of the circumference of the circle, it follows that
is one third of the circumference of the circle, it follows that ![]() . Similarly,
. Similarly, ![]() . Let
. Let ![]() be the intersection of
be the intersection of ![]() and
and ![]() ,
, ![]() that of
that of ![]() and
and ![]() , and
, and ![]() that of
that of ![]() and
and ![]() . Triangles
. Triangles ![]() and
and ![]() are equilateral, and by symmetry, triangle
are equilateral, and by symmetry, triangle ![]() is isosceles and thus also equilateral.
is isosceles and thus also equilateral.
![[asy] import olympiad; import geometry; size(150); defaultpen(linewidth(0.8)); real angleUnit = 15; draw(Circle(origin,1)); pair D = dir(22.5); pair C = dir(3*angleUnit + degrees(D)); pair B = dir(3*angleUnit + degrees(C)); pair A = dir(3*angleUnit + degrees(B)); pair F = dir(5*angleUnit + degrees(A)); pair E = dir(5*angleUnit + degrees(F)); draw(A--B--C--D--E--F--cycle); dot("$A$",A,A); dot("$B$",B,B); dot("$C$",C,C); dot("$D$",D,D); dot("$E$",E,E); dot("$F$",F,F); draw(A--D^^B--E^^C--F); label("$3$",D--C,SW); label("$3$",B--C,S); label("$3$",A--B,SE); label("$5$",A--F,NE); label("$5$",F--E,N); label("$5$",D--E,NW); [/asy]](http://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/3/8/c/38c2702b62f79dd9c81d7d73f557e3e7be4daa85.png)
Furthermore, ![]() and
and ![]() subtend the same arc, as do
subtend the same arc, as do ![]() and
and ![]() . Hence triangles
. Hence triangles ![]() and
and ![]() are similar. Therefore,
are similar. Therefore, ![]() It follows that
It follows that ![]() Solving the two equations simultaneously yields
Solving the two equations simultaneously yields ![]() so
so ![]()
Solution 2
All angle measures are in degrees.
Let the first trapezoid be ![]() , where
, where ![]() . Then the second trapezoid is
. Then the second trapezoid is ![]() , where
, where ![]() . We look for
. We look for ![]() .
.
Since ![]() is an isosceles trapezoid, we know that
is an isosceles trapezoid, we know that ![]() and, since
and, since ![]() , if we drew
, if we drew ![]() , we would see
, we would see ![]() . Anyway,
. Anyway, ![]() (
(![]() means arc AB). Using similar reasoning,
means arc AB). Using similar reasoning, ![]() .
.
Let ![]() and
and ![]() . Since
. Since ![]() (add up the angles),
(add up the angles), ![]() and thus
and thus ![]() . Therefore,
. Therefore, ![]() .
. ![]() as well.
as well.
Now I focus on triangle ![]() . By the Law of Cosines,
. By the Law of Cosines, ![]() , so
, so ![]() . Seeing
. Seeing ![]() and
and ![]() , we can now use the Law of Sines to get:
, we can now use the Law of Sines to get:
![]()
Now I focus on triangle ![]() .
. ![]() and
and ![]() , and we are given that
, and we are given that ![]() , so
, so
![]() We know
We know ![]() , but we need to find
, but we need to find ![]() . Using various identities, we see
. Using various identities, we see
 Returning to finding
Returning to finding ![]() , we remember
, we remember ![]() Plugging in and solving, we see
Plugging in and solving, we see ![]() . Thus, the answer is
. Thus, the answer is ![]() , which is answer choice
, which is answer choice ![]() .
.
Solution 3
Let ![]() be the desired length. One can use Parameshvara's circumradius formula, which states that for a cyclic quadrilateral with sides
be the desired length. One can use Parameshvara's circumradius formula, which states that for a cyclic quadrilateral with sides ![]() the circumradius
the circumradius ![]() satisfies
satisfies ![]() where
where ![]() is the semiperimeter. Applying this to the trapezoid with sides
is the semiperimeter. Applying this to the trapezoid with sides ![]() , we see that many terms cancel and we are left with
, we see that many terms cancel and we are left with ![]() Similar canceling occurs for the trapezoid with sides
Similar canceling occurs for the trapezoid with sides ![]() , and since the two quadrilaterals share the same circumradius, we can equate:
, and since the two quadrilaterals share the same circumradius, we can equate: ![]() Solving for
Solving for ![]() gives
gives ![]() , so the answer is
, so the answer is ![]() .
.
Solution 4
Note that minor arc ![]() is a third of the circumference, therefore,
is a third of the circumference, therefore, ![]() . minor arc
. minor arc ![]() ,
, ![]()
By the Law of Cosine, ![]()
![]() , therefore,
, therefore, 

Let ![]() be the length of the chord,
be the length of the chord, ![]()
By the triple angle formula, ![]()
![]()
Therefore, the answer is ![]() .
.
See also
| 1996 AHSME (Problems • Answer Key • Resources) | ||
| Preceded by Problem 29 |
Followed by Last Problem | |
| 1 • 2 • 3 • 4 • 5 • 6 • 7 • 8 • 9 • 10 • 11 • 12 • 13 • 14 • 15 • 16 • 17 • 18 • 19 • 20 • 21 • 22 • 23 • 24 • 25 • 26 • 27 • 28 • 29 • 30 | ||
| All AHSME Problems and Solutions | ||
The problems on this page are copyrighted by the Mathematical Association of America's American Mathematics Competitions.