Difference between revisions of "2020 AIME II Problems/Problem 15"
(→Solution 2 (Official MAA)) |
|||
| (27 intermediate revisions by 7 users not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
Let <math>\triangle ABC</math> be an acute scalene triangle with circumcircle <math>\omega</math>. The tangents to <math>\omega</math> at <math>B</math> and <math>C</math> intersect at <math>T</math>. Let <math>X</math> and <math>Y</math> be the projections of <math>T</math> onto lines <math>AB</math> and <math>AC</math>, respectively. Suppose <math>BT = CT = 16</math>, <math>BC = 22</math>, and <math>TX^2 + TY^2 + XY^2 = 1143</math>. Find <math>XY^2</math>. | Let <math>\triangle ABC</math> be an acute scalene triangle with circumcircle <math>\omega</math>. The tangents to <math>\omega</math> at <math>B</math> and <math>C</math> intersect at <math>T</math>. Let <math>X</math> and <math>Y</math> be the projections of <math>T</math> onto lines <math>AB</math> and <math>AC</math>, respectively. Suppose <math>BT = CT = 16</math>, <math>BC = 22</math>, and <math>TX^2 + TY^2 + XY^2 = 1143</math>. Find <math>XY^2</math>. | ||
| − | == | + | ==Solution 1== |
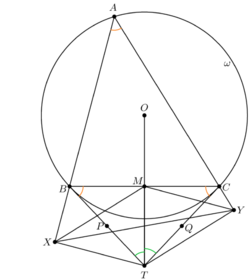
| − | + | Let <math>O</math> be the circumcenter of <math>\triangle ABC</math>; say <math>OT</math> intersects <math>BC</math> at <math>M</math>; draw segments <math>XM</math>, and <math>YM</math>. We have <math>MT=3\sqrt{15}</math>. | |
| − | == | + | [[File:Fanyuchen.png|250px|right]] |
| − | + | ||
| + | Since <math>\angle A=\angle CBT=\angle BCT</math>, we have <math>\cos A=\tfrac{11}{16}</math>. Notice that <math>AXTY</math> is cyclic, so <math>\angle XTY=180^{\circ}-A</math>, so <math>\cos XTY=-\cos A</math>, and the cosine law in <math>\triangle TXY</math> gives <cmath>1143-2XY^2=-\frac{11}{8}\cdot XT\cdot YT.</cmath> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Since <math>\triangle BMT \cong \triangle CMT</math>, we have <math>TM\perp BC</math>, and therefore quadrilaterals <math>BXTM</math> and <math>CYTM</math> are cyclic. Let <math>P</math> (resp. <math>Q</math>) be the midpoint of <math>BT</math> (resp. <math>CT</math>). So <math>P</math> (resp. <math>Q</math>) is the center of <math>(BXTM)</math> (resp. <math>CYTM</math>). Then <math>\theta=\angle ABC=\angle MTX</math> and <math>\phi=\angle ACB=\angle YTM</math>. So <math>\angle XPM=2\theta</math>, so<cmath>\frac{\frac{XM}{2}}{XP}=\sin \theta,</cmath>which yields <math>XM=2XP\sin \theta=BT(=CT)\sin \theta=TY</math>. Similarly we have <math>YM=XT</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Ptolemy's theorem in <math>BXTM</math> gives <cmath>16TY=11TX+3\sqrt{15}BX,</cmath> while Pythagoras' theorem gives <math>BX^2+XT^2=16^2</math>. Similarly, Ptolemy's theorem in <math>YTMC</math> gives<cmath>16TX=11TY+3\sqrt{15}CY</cmath> while Pythagoras' theorem in <math>\triangle CYT</math> gives <math>CY^2+YT^2=16^2</math>. Solve this for <math>XT</math> and <math>TY</math> and substitute into the equation about <math>\cos XTY</math> to obtain the result <math>XY^2=\boxed{717}</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | (Notice that <math>MXTY</math> is a parallelogram, which is an important theorem in Olympiad, and there are some other ways of computation under this observation.) | ||
| + | |||
| + | -Fanyuchen20020715 | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Solution 2 (Official MAA)== | ||
| + | Let <math>M</math> denote the midpoint of <math>\overline{BC}</math>. The critical claim is that <math>M</math> is the orthocenter of <math>\triangle AXY</math>, which has the circle with diameter <math>\overline{AT}</math> as its circumcircle. To see this, note that because <math>\angle BXT = \angle BMT = 90^\circ</math>, the quadrilateral <math>MBXT</math> is cyclic, it follows that | ||
| + | <cmath>\angle MXA = \angle MXB = \angle MTB = 90^\circ - \angle TBM = 90^\circ - \angle A,</cmath> implying that <math>\overline{MX} \perp \overline{AC}</math>. Similarly, <math>\overline{MY} \perp \overline{AB}</math>. In particular, <math>MXTY</math> is a parallelogram. | ||
| + | <asy> | ||
| + | defaultpen(fontsize(8pt)); | ||
| + | unitsize(0.8cm); | ||
| + | |||
| + | pair A = (0,0); | ||
| + | pair B = (-1.26,-4.43); | ||
| + | pair C = (-1.26+3.89, -4.43); | ||
| + | pair M = (B+C)/2; | ||
| + | pair O = circumcenter(A,B,C); | ||
| + | pair T = (0.68, -6.49); | ||
| + | pair X = foot(T,A,B); | ||
| + | pair Y = foot(T,A,C); | ||
| + | path omega = circumcircle(A,B,C); | ||
| + | real rad = circumradius(A,B,C); | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | filldraw(A--B--C--cycle, 0.2*royalblue+white); | ||
| + | label("$\omega$", O + rad*dir(45), SW); | ||
| + | //filldraw(T--Y--M--X--cycle, rgb(150, 247, 254)); | ||
| + | filldraw(T--Y--M--X--cycle, 0.2*heavygreen+white); | ||
| + | draw(M--T); | ||
| + | draw(X--Y); | ||
| + | draw(B--T--C); | ||
| + | draw(A--X--Y--cycle); | ||
| + | draw(omega); | ||
| + | dot("$X$", X, W); | ||
| + | dot("$Y$", Y, E); | ||
| + | dot("$O$", O, W); | ||
| + | dot("$T$", T, S); | ||
| + | dot("$A$", A, N); | ||
| + | dot("$B$", B, W); | ||
| + | dot("$C$", C, E); | ||
| + | dot("$M$", M, N); | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | </asy> | ||
| + | Hence, by the Parallelogram Law, | ||
| + | <cmath> TM^2 + XY^2 = 2(TX^2 + TY^2) = 2(1143-XY^2).</cmath> But <math>TM^2 = TB^2 - BM^2 = 16^2 - 11^2 = 135</math>. Therefore <cmath>XY^2 = \frac13(2 \cdot 1143-135) = \boxed{717}.</cmath> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Solution 3 (Law of Cosines)== | ||
| + | Let <math>H</math> be the orthocenter of <math>\triangle AXY</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <b>Lemma 1:</b> <math>H</math> is the midpoint of <math>BC</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <b>Proof:</b> Let <math>H'</math> be the midpoint of <math>BC</math>, and observe that <math>XBH'T</math> and <math>TH'CY</math> are cyclical. Define <math>H'Y \cap BA=E</math> and <math>H'X \cap AC=F</math>, then note that: | ||
| + | <cmath>\angle H'BT=\angle H'CT=\angle H'XT=\angle H'YT=\angle A.</cmath> | ||
| + | That implies that <math>\angle H'XB=\angle H'YC=90^\circ-\angle A</math>, <math>\angle CH'Y=\angle EH'B=90^\circ-\angle B</math>, and <math>\angle BH'Y=\angle FH'C=90^\circ-\angle C</math>. Thus <math>YH'\perp AX</math> and <math>XH' \perp AY</math>; <math>H'</math> is indeed the same as <math>H</math>, and we have proved lemma 1. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Since <math>AXTY</math> is cyclical, <math>\angle XTY=\angle XHY</math> and this implies that <math>XHYT</math> is a paralelogram. | ||
| + | By the Law of Cosines: | ||
| + | <cmath>XY^2=XT^2+TY^2+2(XT)(TY)\cdot \cos(\angle A)</cmath> | ||
| + | <cmath>XY^2=XH^2+HY^2+2(XH)(HY) \cdot \cos(\angle A)</cmath> | ||
| + | <cmath>HT^2=HX^2+XT^2-2(HX)(XT) \cdot \cos(\angle A)</cmath> | ||
| + | <cmath>HT^2=HY^2+YT^2-2(HY)(YT) \cdot \cos(\angle A).</cmath> | ||
| + | We add all these equations to get: | ||
| + | <cmath>HT^2+XY^2=2(XT^2+TY^2) \qquad (1).</cmath> | ||
| + | We have that <math>BH=HC=11</math> and <math>BT=TC=16</math> using our midpoints. Note that <math>HT \perp BC</math>, so by the Pythagorean Theorem, it follows that <math>HT^2=135</math>. We were also given that <math>XT^2+TY^2=1143-XY^2</math>, which we multiply by <math>2</math> to use equation <math>(1)</math>. <cmath>2(XT^2+TY^2)=2286-2 \cdot XY^2</cmath> Since <math>2(XT^2+TY^2)=2(HT^2+TY^2)=HT^2+XY^2</math>, we have | ||
| + | <cmath>135+XY^2=2286-2 \cdot XY^2</cmath> <cmath>3 \cdot XY^2=2151.</cmath> | ||
| + | Therefore, <math>XY^2=\boxed{717}</math>. ~ MathLuis | ||
| + | |||
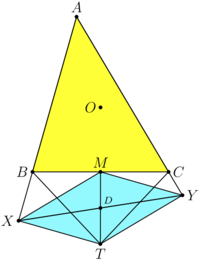
| + | ==Solution 4 (Similarity and median)== | ||
| + | [[File:AIME-II-2020-15a.png|200px|right]] | ||
| + | Using the <i><b>Claim</b></i> (below) we get <math>\triangle ABC \sim \triangle XTM \sim \triangle YMT.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Corresponding sides of similar <math>\triangle XTM \sim \triangle YMT</math> is <math>MT,</math> so | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\triangle XTM = \triangle YMT \implies MY = XT, MX = TY \implies XMYT</math> – parallelogram. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <cmath>4 TD^2 = MT^2 = \sqrt{BT^2 - BM^2} =\sqrt{153}.</cmath> | ||
| + | The formula for median <math>DT</math> of triangle <math>XYT</math> is | ||
| + | <cmath>2 DT^2 = XT^2 + TY^2 – \frac{XY^2}{2},</cmath> | ||
| + | <cmath>3 \cdot XY^2 = 2XT^2 + 2TY^2 + 2XY^2 – 4 DT^2,</cmath> | ||
| + | <cmath>3 \cdot XY^2 = 2 \cdot 1143-153 = 2151 \implies XY^2 = \boxed{717}. </cmath> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
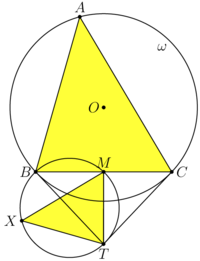
| + | [[File:AIME-II-2020-15b.png|200px|right]] | ||
| + | <i><b>Claim</b></i> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Let <math>\triangle ABC</math> be an acute scalene triangle with circumcircle <math>\omega</math>. The tangents to <math>\omega</math> at <math>B</math> and <math>C</math> intersect at <math>T</math>. Let <math>X</math> be the projections of <math>T</math> onto line <math>AB</math>. Let M be midpoint BC. Then triangle ABC is similar to triangle XTM. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <i><b>Proof</b></i> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\angle BXT = \angle BMT = 90^o \implies</math> the quadrilateral <math>MBXT</math> is cyclic. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>BM \perp MT, TX \perp AB \implies \angle MTX = \angle MBA.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\angle CBT = \angle BAC = \frac {\overset{\Large\frown} {BC}}{ 2} \implies \triangle ABC \sim \triangle XTM.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss''' | ||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
Latest revision as of 15:46, 29 January 2023
Contents
Problem
Let ![]() be an acute scalene triangle with circumcircle
be an acute scalene triangle with circumcircle ![]() . The tangents to
. The tangents to ![]() at
at ![]() and
and ![]() intersect at
intersect at ![]() . Let
. Let ![]() and
and ![]() be the projections of
be the projections of ![]() onto lines
onto lines ![]() and
and ![]() , respectively. Suppose
, respectively. Suppose ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() . Find
. Find ![]() .
.
Solution 1
Let ![]() be the circumcenter of
be the circumcenter of ![]() ; say
; say ![]() intersects
intersects ![]() at
at ![]() ; draw segments
; draw segments ![]() , and
, and ![]() . We have
. We have ![]() .
.
Since ![]() , we have
, we have ![]() . Notice that
. Notice that ![]() is cyclic, so
is cyclic, so ![]() , so
, so ![]() , and the cosine law in
, and the cosine law in ![]() gives
gives ![]()
Since ![]() , we have
, we have ![]() , and therefore quadrilaterals
, and therefore quadrilaterals ![]() and
and ![]() are cyclic. Let
are cyclic. Let ![]() (resp.
(resp. ![]() ) be the midpoint of
) be the midpoint of ![]() (resp.
(resp. ![]() ). So
). So ![]() (resp.
(resp. ![]() ) is the center of
) is the center of ![]() (resp.
(resp. ![]() ). Then
). Then ![]() and
and ![]() . So
. So ![]() , so
, so![]() which yields
which yields ![]() . Similarly we have
. Similarly we have ![]() .
.
Ptolemy's theorem in ![]() gives
gives ![]() while Pythagoras' theorem gives
while Pythagoras' theorem gives ![]() . Similarly, Ptolemy's theorem in
. Similarly, Ptolemy's theorem in ![]() gives
gives![]() while Pythagoras' theorem in
while Pythagoras' theorem in ![]() gives
gives ![]() . Solve this for
. Solve this for ![]() and
and ![]() and substitute into the equation about
and substitute into the equation about ![]() to obtain the result
to obtain the result ![]() .
.
(Notice that ![]() is a parallelogram, which is an important theorem in Olympiad, and there are some other ways of computation under this observation.)
is a parallelogram, which is an important theorem in Olympiad, and there are some other ways of computation under this observation.)
-Fanyuchen20020715
Solution 2 (Official MAA)
Let ![]() denote the midpoint of
denote the midpoint of ![]() . The critical claim is that
. The critical claim is that ![]() is the orthocenter of
is the orthocenter of ![]() , which has the circle with diameter
, which has the circle with diameter ![]() as its circumcircle. To see this, note that because
as its circumcircle. To see this, note that because ![]() , the quadrilateral
, the quadrilateral ![]() is cyclic, it follows that
is cyclic, it follows that
![]() implying that
implying that ![]() . Similarly,
. Similarly, ![]() . In particular,
. In particular, ![]() is a parallelogram.
is a parallelogram.
![[asy] defaultpen(fontsize(8pt)); unitsize(0.8cm); pair A = (0,0); pair B = (-1.26,-4.43); pair C = (-1.26+3.89, -4.43); pair M = (B+C)/2; pair O = circumcenter(A,B,C); pair T = (0.68, -6.49); pair X = foot(T,A,B); pair Y = foot(T,A,C); path omega = circumcircle(A,B,C); real rad = circumradius(A,B,C); filldraw(A--B--C--cycle, 0.2*royalblue+white); label("$\omega$", O + rad*dir(45), SW); //filldraw(T--Y--M--X--cycle, rgb(150, 247, 254)); filldraw(T--Y--M--X--cycle, 0.2*heavygreen+white); draw(M--T); draw(X--Y); draw(B--T--C); draw(A--X--Y--cycle); draw(omega); dot("$X$", X, W); dot("$Y$", Y, E); dot("$O$", O, W); dot("$T$", T, S); dot("$A$", A, N); dot("$B$", B, W); dot("$C$", C, E); dot("$M$", M, N); [/asy]](http://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/b/3/7/b37485262f643e08b4b17f0839d8e651976343d9.png) Hence, by the Parallelogram Law,
Hence, by the Parallelogram Law,
![]() But
But ![]() . Therefore
. Therefore ![]()
Solution 3 (Law of Cosines)
Let ![]() be the orthocenter of
be the orthocenter of ![]() .
.
Lemma 1: ![]() is the midpoint of
is the midpoint of ![]() .
.
Proof: Let ![]() be the midpoint of
be the midpoint of ![]() , and observe that
, and observe that ![]() and
and ![]() are cyclical. Define
are cyclical. Define ![]() and
and ![]() , then note that:
, then note that:
![]() That implies that
That implies that ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() . Thus
. Thus ![]() and
and ![]() ;
; ![]() is indeed the same as
is indeed the same as ![]() , and we have proved lemma 1.
, and we have proved lemma 1.
Since ![]() is cyclical,
is cyclical, ![]() and this implies that
and this implies that ![]() is a paralelogram.
By the Law of Cosines:
is a paralelogram.
By the Law of Cosines:
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() We add all these equations to get:
We add all these equations to get:
![]() We have that
We have that ![]() and
and ![]() using our midpoints. Note that
using our midpoints. Note that ![]() , so by the Pythagorean Theorem, it follows that
, so by the Pythagorean Theorem, it follows that ![]() . We were also given that
. We were also given that ![]() , which we multiply by
, which we multiply by ![]() to use equation
to use equation ![]() .
. ![]() Since
Since ![]() , we have
, we have
![]()
![]() Therefore,
Therefore, ![]() . ~ MathLuis
. ~ MathLuis
Solution 4 (Similarity and median)
Using the Claim (below) we get ![]()
Corresponding sides of similar ![]() is
is ![]() so
so
![]() – parallelogram.
– parallelogram.
![]() The formula for median
The formula for median ![]() of triangle
of triangle ![]() is
is
![]()
![]()
![]()
Claim
Let ![]() be an acute scalene triangle with circumcircle
be an acute scalene triangle with circumcircle ![]() . The tangents to
. The tangents to ![]() at
at ![]() and
and ![]() intersect at
intersect at ![]() . Let
. Let ![]() be the projections of
be the projections of ![]() onto line
onto line ![]() . Let M be midpoint BC. Then triangle ABC is similar to triangle XTM.
. Let M be midpoint BC. Then triangle ABC is similar to triangle XTM.
Proof
![]() the quadrilateral
the quadrilateral ![]() is cyclic.
is cyclic.
![]()
![]()
vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss
See Also
| 2020 AIME II (Problems • Answer Key • Resources) | ||
| Preceded by Problem 14 |
Followed by Last Problem | |
| 1 • 2 • 3 • 4 • 5 • 6 • 7 • 8 • 9 • 10 • 11 • 12 • 13 • 14 • 15 | ||
| All AIME Problems and Solutions | ||
The problems on this page are copyrighted by the Mathematical Association of America's American Mathematics Competitions.