Difference between revisions of "Stewart's Theorem"
m (→Statement) |
Mathsmiley (talk | contribs) m (→Statement) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Statement == | == Statement == | ||
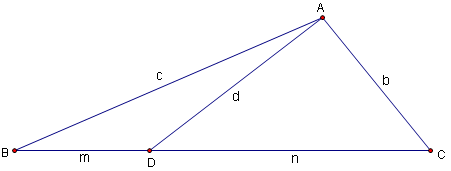
| − | Given a [[triangle]] <math>\triangle ABC</math> with sides of length <math>a, b, c</math> opposite [[vertex | vertices]] are <math>A</math>, <math>B</math>, <math>C</math>, respectively. If [[cevian]] <math>AD</math> is drawn so that <math>BD = m</math>, <math>DC = n</math> and <math>AD = d</math>, we have that <math>b^2m + c^2n = amn + d^2a</math>. (This is also often written <math>man + dad = bmb + cnc</math>, a form which invites mnemonic memorization, i.e. "A man and his dad put a bomb in the sink." | + | Given a [[triangle]] <math>\triangle ABC</math> with sides of length <math>a, b, c</math> opposite [[vertex | vertices]] are <math>A</math>, <math>B</math>, <math>C</math>, respectively. If [[cevian]] <math>AD</math> is drawn so that <math>BD = m</math>, <math>DC = n</math> and <math>AD = d</math>, we have that <math>b^2m + c^2n = amn + d^2a</math>. (This is also often written <math>man + dad = bmb + cnc</math>, a form which invites mnemonic memorization, i.e. "A man and his dad put a bomb in the sink.") |
<center>[[Image:Stewart's_theorem.png]]</center> | <center>[[Image:Stewart's_theorem.png]]</center> | ||
Revision as of 00:45, 13 July 2019
Statement
Given a triangle ![]() with sides of length
with sides of length ![]() opposite vertices are
opposite vertices are ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() , respectively. If cevian
, respectively. If cevian ![]() is drawn so that
is drawn so that ![]() ,
, ![]() and
and ![]() , we have that
, we have that ![]() . (This is also often written
. (This is also often written ![]() , a form which invites mnemonic memorization, i.e. "A man and his dad put a bomb in the sink.")
, a form which invites mnemonic memorization, i.e. "A man and his dad put a bomb in the sink.")
Proof
Applying the Law of Cosines in triangle ![]() at angle
at angle ![]() and in triangle
and in triangle ![]() at angle
at angle ![]() , we get the equations
, we get the equations
Because angles ![]() and
and ![]() are supplementary,
are supplementary, ![]() . We can therefore solve both equations for the cosine term. Using the trigonometric identity
. We can therefore solve both equations for the cosine term. Using the trigonometric identity ![]() gives us
gives us
Setting the two left-hand sides equal and clearing denominators, we arrive at the equation: ![]() .
However,
.
However, ![]() so
so ![]() .
.









