Difference between revisions of "2020 AMC 12A Problems/Problem 25"
MRENTHUSIASM (talk | contribs) (Undo revision 161840 by MRENTHUSIASM (talk)) (Tag: Undo) |
MRENTHUSIASM (talk | contribs) m (→Solution 1) |
||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
Alternatively, from <math>(3)</math> and <math>(4),</math> note that all values of <math>a</math> for which <math>0<a\leq\frac14</math> satisfy <math>1-2a>\sqrt{1-4a}.</math> We deduce that both roots in <math>(3)</math> must be positive, so <math>f\geq0</math> is always valid.<p> | Alternatively, from <math>(3)</math> and <math>(4),</math> note that all values of <math>a</math> for which <math>0<a\leq\frac14</math> satisfy <math>1-2a>\sqrt{1-4a}.</math> We deduce that both roots in <math>(3)</math> must be positive, so <math>f\geq0</math> is always valid.<p> | ||
<li><math>f<1</math></li><p> | <li><math>f<1</math></li><p> | ||
| − | We rewrite <math>(3)</math> as <cmath>f=w\Biggl(\frac{1}{2a}-1\pm\frac{\sqrt{1-4a}}{2a}\Biggr).</cmath> From <math>(4),</math> it follows that <math>\frac{1}{2a}\geq\frac{1}{1/2}=2.</math> The larger root is | + | We rewrite <math>(3)</math> as <cmath>f=w\Biggl(\frac{1}{2a}-1\pm\frac{\sqrt{1-4a}}{2a}\Biggr).</cmath> From <math>(4),</math> it follows that <math>\frac{1}{2a}\geq\frac{1}{1/2}=2.</math> The larger root is <cmath>f\geq w\left(2-1+2\sqrt{1-4a}\right)\geq 1\Biggl(2-1+2\sqrt{1-4\cdot\frac14}\Biggr)= 1,</cmath> |
| − | <cmath> | ||
| − | f | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
which contradicts <math>f<1.</math> So, we take the smaller root, from which <cmath>f=w\Biggl(\frac{1}{2a}-1-\frac{\sqrt{1-4a}}{2a}\Biggr)</cmath> for some constant <math>k=\frac{1}{2a}-1-\frac{\sqrt{1-4a}}{2a}>0.</math> We rewrite <math>f</math> as <cmath>f=wk,</cmath> in which <math>f<1</math> is valid as long as <math>k<\frac 1w.</math> Note that the solutions of <math>x</math> are generated at <cmath>w=1,2,3,\cdots,W,</cmath> up to some value <math>w=W</math> such that <math>\frac{1}{W+1}\leq k<\frac1W.</math> | which contradicts <math>f<1.</math> So, we take the smaller root, from which <cmath>f=w\Biggl(\frac{1}{2a}-1-\frac{\sqrt{1-4a}}{2a}\Biggr)</cmath> for some constant <math>k=\frac{1}{2a}-1-\frac{\sqrt{1-4a}}{2a}>0.</math> We rewrite <math>f</math> as <cmath>f=wk,</cmath> in which <math>f<1</math> is valid as long as <math>k<\frac 1w.</math> Note that the solutions of <math>x</math> are generated at <cmath>w=1,2,3,\cdots,W,</cmath> up to some value <math>w=W</math> such that <math>\frac{1}{W+1}\leq k<\frac1W.</math> | ||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
Revision as of 23:25, 7 September 2021
Contents
[hide]Problem
The number ![]() , where
, where ![]() and
and ![]() are relatively prime positive integers, has the property that the sum of all real numbers
are relatively prime positive integers, has the property that the sum of all real numbers ![]() satisfying
satisfying
![]() is
is ![]() , where
, where ![]() denotes the greatest integer less than or equal to
denotes the greatest integer less than or equal to ![]() and
and ![]() denotes the fractional part of
denotes the fractional part of ![]() . What is
. What is ![]() ?
?
![]()
Solution 1
Let ![]() and
and ![]() denote the whole part and the fractional part of
denote the whole part and the fractional part of ![]() respectively, for which
respectively, for which ![]() and
and ![]()
We rewrite the given equation as ![]() Since
Since ![]() it follows that
it follows that ![]() from which
from which ![]()
We expand and rearrange ![]() as
as ![]() which is a quadratic with either
which is a quadratic with either ![]() or
or ![]()
For simplicity purposes, we will treat ![]() as some fixed nonnegative integer so that
as some fixed nonnegative integer so that ![]() is a quadratic with
is a quadratic with ![]() By the Quadratic Formula, we have
By the Quadratic Formula, we have
 If
If ![]() then
then ![]() We get
We get ![]() which does not affect the sum of the solutions. Therefore, we consider the case for
which does not affect the sum of the solutions. Therefore, we consider the case for ![]()
Recall that ![]() so
so ![]() From the discriminant, we require that
From the discriminant, we require that ![]() or
or ![]() Combining this with the precondition
Combining this with the precondition ![]() we need
we need ![]()
We consider each part of ![]() separately:
separately:
From ![]() note that
note that ![]() and
and ![]() By Descartes' Rule of Signs, we deduce that
By Descartes' Rule of Signs, we deduce that ![]() must have two positive roots, so
must have two positive roots, so ![]() is always valid.
is always valid.
Alternatively, from ![]() and
and ![]() note that all values of
note that all values of ![]() for which
for which ![]() satisfy
satisfy ![]() We deduce that both roots in
We deduce that both roots in ![]() must be positive, so
must be positive, so ![]() is always valid.
is always valid.
We rewrite ![]() as
as ![\[f=w\Biggl(\frac{1}{2a}-1\pm\frac{\sqrt{1-4a}}{2a}\Biggr).\]](http://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/f/b/f/fbf339570471c3d8838277de42d58142e07552f2.png) From
From ![]() it follows that
it follows that ![]() The larger root is
The larger root is ![\[f\geq w\left(2-1+2\sqrt{1-4a}\right)\geq 1\Biggl(2-1+2\sqrt{1-4\cdot\frac14}\Biggr)= 1,\]](http://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/c/e/7/ce706e4c4ee3af7cddc0ab76dfd86d14b962d8eb.png) which contradicts
which contradicts ![]() So, we take the smaller root, from which
So, we take the smaller root, from which ![\[f=w\Biggl(\frac{1}{2a}-1-\frac{\sqrt{1-4a}}{2a}\Biggr)\]](http://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/0/6/b/06b15412674320c8cc986e40e743c49bd3ff1119.png) for some constant
for some constant ![]() We rewrite
We rewrite ![]() as
as ![]() in which
in which ![]() is valid as long as
is valid as long as ![]() Note that the solutions of
Note that the solutions of ![]() are generated at
are generated at ![]() up to some value
up to some value ![]() such that
such that ![]()
Now, we express ![]() in terms of
in terms of ![]() and
and ![]()
 The sum of all solutions to the original equation is
The sum of all solutions to the original equation is ![\[\sum_{w=1}^{W}w(1+k)=(1+k)\cdot\sum_{w=1}^{W}w=(1+k)\cdot\frac{W(W+1)}{2}=420. \hspace{10mm}(\bigstar)\]](http://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/0/a/7/0a7c780d69fa818ae798ba64f8d082ee11c0b9a3.png) As
As ![]() we conclude that
we conclude that ![]() is slightly above
is slightly above ![]() so that
so that ![]() is slightly below
is slightly below ![]() or
or ![]() is slightly below
is slightly below ![]() By observations, we get
By observations, we get ![]() Substituting this into
Substituting this into ![]() produces
produces ![]() which satisfies
which satisfies ![]() as required.
as required.
Finally, we solve for ![]() in
in ![]()
 Since
Since ![]() we obtain
we obtain ![]() from which
from which ![]() The answer is
The answer is ![]()
~MRENTHUSIASM (inspired by Math Jams's 2020 AMC 10/12A Discussion)
Solution 2
First note that ![]() when
when ![]() while
while ![]() . Thus we only need to look at positive solutions (
. Thus we only need to look at positive solutions (![]() doesn't affect the sum of the solutions).
Next, we break
doesn't affect the sum of the solutions).
Next, we break ![]() down for each interval
down for each interval ![]() , where
, where ![]() is a positive integer. Assume
is a positive integer. Assume ![]() , then
, then ![]() . This means that when
. This means that when ![]() ,
, ![]() . Setting this equal to
. Setting this equal to ![]() gives
gives
![]() We're looking at the solution with the positive
We're looking at the solution with the positive ![]() , which is
, which is ![]() . Note that if
. Note that if ![]() is the greatest
is the greatest ![]() such that
such that ![]() has a solution, the sum of all these solutions is slightly over
has a solution, the sum of all these solutions is slightly over ![]() , which is
, which is ![]() when
when ![]() , just under
, just under ![]() . Checking this gives
. Checking this gives
 ~ktong
~ktong
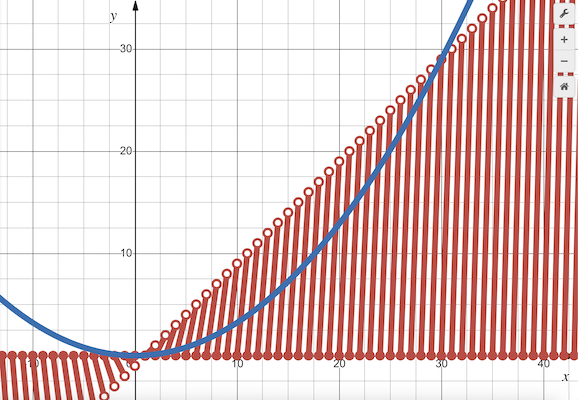
Remark
Let ![]() and
and ![]()
We make the following table of values:
![\[\begin{array}{c|c|c|clc} & & & & & \\ [-1.5ex] \boldsymbol{x} & \boldsymbol{\lfloor x \rfloor} & \boldsymbol{f(x)} & & \hspace{4mm}\textbf{Equation} & \\ [1.5ex] \hline & & & & & \\ [-1ex] [0,1) & 0 & 0 & & y=0 & \\ [1.5ex] [1,2) & 1 & [0,1) & & y=x-1 & \\ [1.5ex] [2,3) & 2 & [0,2) & & y=2x-4 & \\ [1.5ex] [3,4) & 3 & [0,3) & & y=3x-9 & \\ [1.5ex] [4,5) & 4 & [0,4) & & y=4x-16 & \\ [1.5ex] \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & & \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \cdots & \\ [1.5ex] [m,m+1) & m & [0,m) & & y=mx-m^2 & \\ [2ex] \end{array}\]](http://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/5/1/3/513eba3b9a5aaf927bf101254e86ba7d0f2006c3.png)
We graph ![]() (in red, by branches) and
(in red, by branches) and ![]() (in blue, for
(in blue, for ![]() ) as shown below.
) as shown below.
Graph in Desmos: https://www.desmos.com/calculator/ouvaiqjdzj
~MRENTHUSIASM
Video Solution 1 (Geometry)
This video shows how things like The Pythagorean Theorem and The Law of Sines work together to solve this seemingly algebraic problem: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6IJ7Jxa98zw&feature=youtu.be
Video Solution 2
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xex8TBSzKNE ~ MathEx
Video Solution 3 (by Art of Problem Solving)
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7_mdreGBPvg&t=428s&ab_channel=ArtofProblemSolving
Created by Richard Rusczyk
See Also
| 2020 AMC 12A (Problems • Answer Key • Resources) | |
| Preceded by Problem 24 |
Followed by Last Problem |
| 1 • 2 • 3 • 4 • 5 • 6 • 7 • 8 • 9 • 10 • 11 • 12 • 13 • 14 • 15 • 16 • 17 • 18 • 19 • 20 • 21 • 22 • 23 • 24 • 25 | |
| All AMC 12 Problems and Solutions | |
The problems on this page are copyrighted by the Mathematical Association of America's American Mathematics Competitions.