Difference between revisions of "2015 AMC 10A Problems/Problem 19"
Mathboy282 (talk | contribs) (→Solution 1 (No Trigonometry)) |
Erics son07 (talk | contribs) (→Solution 4 (Trigonometry)) |
||
| Line 43: | Line 43: | ||
Now, since <math>\triangle AEC\cong \triangle BDC</math> by ASA, <math>CE=CD</math>. Since, <math>DF=\frac{5\sqrt{3}-5}{2}</math>, <math>DC=2\cdot \frac{5\sqrt{3}-5}{2}=5\sqrt{3}-5</math>. By the sine area formula, <math>[CDE]=\frac{1}{2}\cdot \sin 30\cdot CD^2=\frac{1}{4}\cdot (100-50\sqrt{3})=\frac{50-25\sqrt{3}}{2}\implies \boxed{\textbf{(D)}}</math> | Now, since <math>\triangle AEC\cong \triangle BDC</math> by ASA, <math>CE=CD</math>. Since, <math>DF=\frac{5\sqrt{3}-5}{2}</math>, <math>DC=2\cdot \frac{5\sqrt{3}-5}{2}=5\sqrt{3}-5</math>. By the sine area formula, <math>[CDE]=\frac{1}{2}\cdot \sin 30\cdot CD^2=\frac{1}{4}\cdot (100-50\sqrt{3})=\frac{50-25\sqrt{3}}{2}\implies \boxed{\textbf{(D)}}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Solution 5 (Basic Trigonometry)== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Prerequisite knowledge for this solution: the side ratios of a 30-60-90, and 45-45-90 right triangle. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | We let point C be the origin. Since <math>\overline{CD}</math> and <math>\overline{CE}</math> trisect <math>\angle ACB = 90^{\circ}</math>, this means <math>m\angle CEB = 30^{\circ}</math> and the equation of <math>\overline{CE}</math> is <math>y=\frac{\sqrt{3}}{3}</math> (you can figure out that the tangent of 30 degrees gives <math>\frac{\sqrt{3}}{3}</math>). Next, we can find A to be at <math>(0, 5)</math> and B at <math>(5, 0)</math>, so the equation of <math>\overline{AB}</math> is <math>y=-x+5</math>. So we have the system: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <cmath> | ||
| + | |||
| + | By substituting values, we can arrive at <math>\frac{3+\sqrt{3}}{3}x=5</math>, or <math>x=5\cdot\frac{3}{3+\sqrt{3}}=\frac{15}{3+\sqrt{3}}</math>. We multiply <math>x=\frac{15}{3+\sqrt{3}}\cdot\frac{3-\sqrt{3}}{3-\sqrt{3}}=\frac{45-15\sqrt{3}}{6}=\frac{15-5\sqrt{3}}{2}</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Dropping an altitude from E onto <math>\overline{CB}</math>, and calling the intersection point G, we find that <math>\triangle EGB</math> is a 45-45-90 triangle with a leg of <math>\frac{15-5\sqrt{3}}{2}\cdot\frac{\sqrt{3}}{3}=\frac{15\sqrt{3}-15}{6}=\frac{5\sqrt{3}-5}{2}</math>. Thus, <math>EB=\frac{5\sqrt{3}-5}{2}\sqrt{2}=\frac{5\sqrt{6}-5\sqrt{2}}{2}</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Dropping an altitude from C onto <math>\overline{AB}</math>, and calling the intersection point H, we find that <math>CH=\frac{5\sqrt{2}}{2}=BH</math>, and by the theorem of betweenness applied to H, E, and B, we get <math>HE=HB-EB=\frac{5\sqrt{2}}{2}-\frac{5\sqrt{6}-5\sqrt{2}}{2}=\frac{10\sqrt{2}-5\sqrt{6}}{2}</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | We are almost done. By symmetry, <math>HD=HE</math>, so to find the area of the triangle CED, we only need to multiply HE by CH, <math>\frac{10\sqrt{2}-5\sqrt{6}}{2}\cdot\frac{5\sqrt{2}}{2}=\frac{100-50\sqrt{3}}{4}=\frac{50-25\sqrt{3}}{2}</math>. This is answer choice <math>\boxed{\textbf{(D) } \frac{50-25\sqrt{3}}{2}}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ~JH. L | ||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
Revision as of 21:55, 15 October 2022
Contents
[hide]Problem
The isosceles right triangle ![]() has right angle at
has right angle at ![]() and area
and area ![]() . The rays trisecting
. The rays trisecting ![]() intersect
intersect ![]() at
at ![]() and
and ![]() . What is the area of
. What is the area of ![]() ?
?
![]()
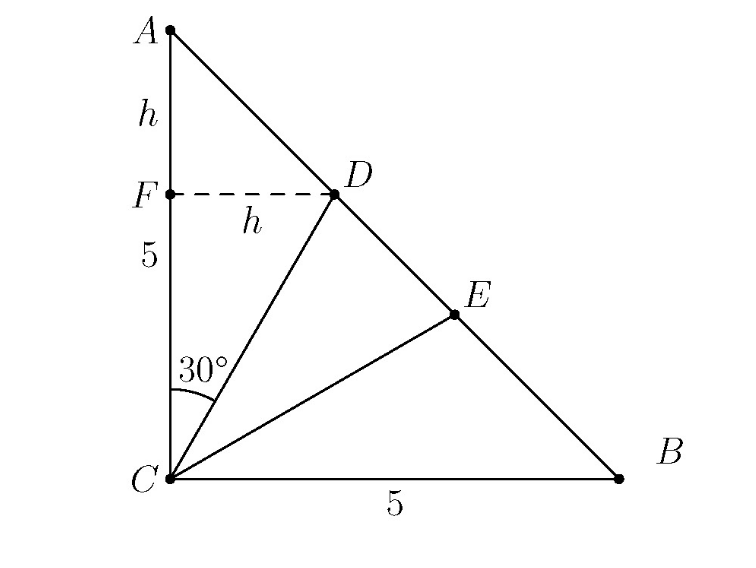
Solution 1 (No Trigonometry)
![]() can be split into a
can be split into a ![]() right triangle and a
right triangle and a ![]() right triangle by dropping a perpendicular from
right triangle by dropping a perpendicular from ![]() to side
to side ![]() . Let
. Let ![]() be where that perpendicular intersects
be where that perpendicular intersects ![]() .
.
Because the side lengths of a ![]() right triangle are in ratio
right triangle are in ratio ![]() ,
, ![]() .
.
Because the side lengths of a ![]() right triangle are in ratio
right triangle are in ratio ![]() and
and ![]() ,
, ![]() .
.
Setting the two equations for ![]() equal to each other,
equal to each other, ![]() .
.
Solving gives ![]() .
.
The area of ![]() .
.
![]() is congruent to
is congruent to ![]() , so their areas are equal.
, so their areas are equal.
A triangle's area can be written as the sum of the figures that make it up, so ![]() .
.
![]() .
.
Solving gives ![]() , so the answer is
, so the answer is 
Note
Another way to get ![]() is that you assume
is that you assume ![]() to be equal to
to be equal to ![]() , as previously mentioned, and
, as previously mentioned, and ![]() is equal to
is equal to ![]() .
. ![]()
Solution 2 (Trigonometry)
The area of ![]() is
is ![]() , and so the leg length of
, and so the leg length of ![]()
![]() is
is ![]() Thus, the altitude to hypotenuse
Thus, the altitude to hypotenuse ![]() ,
, ![]() , has length
, has length ![]() by
by ![]() right triangles. Now, it is clear that
right triangles. Now, it is clear that ![]() , and so by the Exterior Angle Theorem,
, and so by the Exterior Angle Theorem, ![]() is an isosceles
is an isosceles ![]() triangle. Thus,
triangle. Thus, ![]() by the Half-Angle formula, and so the area of
by the Half-Angle formula, and so the area of ![]() is
is ![]() . The answer is thus
. The answer is thus 
Solution 3 (Analytical Geometry)
Because the area of triangle ![]() is
is ![]() , and the triangle is right and isosceles, we can quickly see that the leg length of the triangle
, and the triangle is right and isosceles, we can quickly see that the leg length of the triangle ![]() is 5. If we put the triangle on the coordinate plane, with vertex
is 5. If we put the triangle on the coordinate plane, with vertex ![]() at the origin, and the hypotenuse in the first quadrant, we can use slope-intercept form and tangents to get three lines that intersect at the origin,
at the origin, and the hypotenuse in the first quadrant, we can use slope-intercept form and tangents to get three lines that intersect at the origin, ![]() , and
, and ![]() . Then, you can use the distance formula to get the length of
. Then, you can use the distance formula to get the length of ![]() . The height is just
. The height is just ![]() , so the area is just
, so the area is just 
Solution 4 (Trigonometry)
Just like with Solution 1, we drop a perpendicular from ![]() onto
onto ![]() , splitting it into a
, splitting it into a ![]() -
-![]() -
-![]() triangle and a
triangle and a ![]() -
-![]() -
-![]() triangle. We find that
triangle. We find that ![]() .
.
Now, since ![]() by ASA,
by ASA, ![]() . Since,
. Since, ![]() ,
, ![]() . By the sine area formula,
. By the sine area formula, ![]()
Solution 5 (Basic Trigonometry)
Prerequisite knowledge for this solution: the side ratios of a 30-60-90, and 45-45-90 right triangle.
We let point C be the origin. Since ![]() and
and ![]() trisect
trisect ![]() , this means
, this means ![]() and the equation of
and the equation of ![]() is
is ![]() (you can figure out that the tangent of 30 degrees gives
(you can figure out that the tangent of 30 degrees gives ![]() ). Next, we can find A to be at
). Next, we can find A to be at ![]() and B at
and B at ![]() , so the equation of
, so the equation of ![]() is
is ![]() . So we have the system:
. So we have the system:
![\[\begin{cases}y=\frac{\sqrt{3}}{3}x\\y=-x+5\end{cases}\]](http://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/5/5/7/557ee710ae7a14c71ea2506fac7ddd96b5e6bf84.png)
By substituting values, we can arrive at ![]() , or
, or ![]() . We multiply
. We multiply ![]() .
.
Dropping an altitude from E onto ![]() , and calling the intersection point G, we find that
, and calling the intersection point G, we find that ![]() is a 45-45-90 triangle with a leg of
is a 45-45-90 triangle with a leg of ![]() . Thus,
. Thus, ![]() .
.
Dropping an altitude from C onto ![]() , and calling the intersection point H, we find that
, and calling the intersection point H, we find that ![]() , and by the theorem of betweenness applied to H, E, and B, we get
, and by the theorem of betweenness applied to H, E, and B, we get ![]() .
.
We are almost done. By symmetry, ![]() , so to find the area of the triangle CED, we only need to multiply HE by CH,
, so to find the area of the triangle CED, we only need to multiply HE by CH, ![]() . This is answer choice
. This is answer choice 
~JH. L
See Also
Video Solution:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JWMIsCS0Ksk
| 2015 AMC 10A (Problems • Answer Key • Resources) | ||
| Preceded by Problem 18 |
Followed by Problem 20 | |
| 1 • 2 • 3 • 4 • 5 • 6 • 7 • 8 • 9 • 10 • 11 • 12 • 13 • 14 • 15 • 16 • 17 • 18 • 19 • 20 • 21 • 22 • 23 • 24 • 25 | ||
| All AMC 10 Problems and Solutions | ||
The problems on this page are copyrighted by the Mathematical Association of America's American Mathematics Competitions. ![]()