Difference between revisions of "2022 AIME I Problems/Problem 14"
(Created page with ".") |
Mathtiger6 (talk | contribs) m (→The NT Part) |
||
| (35 intermediate revisions by 11 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | . | + | ==Problem== |
| + | Given <math>\triangle ABC</math> and a point <math>P</math> on one of its sides, call line <math>\ell</math> the <math>\textit{splitting line}</math> of <math>\triangle ABC</math> through <math>P</math> if <math>\ell</math> passes through <math>P</math> and divides <math>\triangle ABC</math> into two polygons of equal perimeter. Let <math>\triangle ABC</math> be a triangle where <math>BC = 219</math> and <math>AB</math> and <math>AC</math> are positive integers. Let <math>M</math> and <math>N</math> be the midpoints of <math>\overline{AB}</math> and <math>\overline{AC},</math> respectively, and suppose that the splitting lines of <math>\triangle ABC</math> through <math>M</math> and <math>N</math> intersect at <math>30^\circ.</math> Find the perimeter of <math>\triangle ABC.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==The Geometry Part - Solution 1== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Consider the splitting line through <math>M</math>. Extend <math>D</math> on ray <math>BC</math> such that <math>CD=CA</math>. Then the splitting line bisects segment <math>BD</math>, so in particular it is the midline of triangle <math>ABD</math> and thus it is parallel to <math>AD</math>. But since triangle <math>ACD</math> is isosceles, we can easily see <math>AD</math> is parallel to the angle bisector of <math>C</math>, so the splitting line is also parallel to this bisector, and similar for the splitting line through <math>N</math>. Some simple angle chasing reveals the condition is now equivalent to <math>\angle A=120^\circ</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | - MortemEtInteritum | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==The Geometry Part - Solution 2== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Let <math>PM</math> and <math>QN</math> be the splitting lines. Reflect <math>B</math> across <math>Q</math> to be <math>B'</math> and <math>C</math> across <math>P</math> to be <math>C'</math>. Take <math>S_B</math> and <math>S_C</math>, which are spiral similarity centers on the other side of <math>BC</math> as <math>A</math> such that <math>\triangle S_BB'C \sim \triangle S_BBA</math> and <math>\triangle S_CC'B \sim \triangle S_CCA</math>. This gets that because <math>\angle S_BCB = \angle S_BCB' = \angle S_BAB</math> and <math>\angle S_CBC = \angle S_CBC' = \angle S_CAC</math>, then <math>S_B</math> and <math>S_C</math> are on <math>\triangle ABC</math>'s circumcircle. Now, we know that <math>\triangle S_BBB' \sim \triangle S_BAC</math> and <math>\triangle S_CCC' \sim \triangle S_CAB</math> so because <math>BA=B'C</math> and <math>CA=C'B</math>, then <math>S_BB=SBB'</math> and <math>S_CC=S_CC'</math> and <math>S_BQ \perp BC</math> and <math>S_CP \perp BC</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | We also notice that because <math>Q</math> and <math>N</math> correspond on <math>\triangle S_BBB'</math> and <math>\triangle S_BAC</math>, and because <math>P</math> and <math>M</math> correspond on <math>\triangle S_CCC' </math> and <math>\triangle S_CAB</math>, then the angle formed by <math>NQ</math> and <math>BA</math> is equal to the angle formed by <math>B'C</math> and <math>NQ</math> which is equal to <math>\angle BS_BQ = \angle QS_BB'</math>. Thus, <math>\angle CBA=2\angle CQN</math>. Similarly, <math>\angle BCA = 2\angle QPM</math> and so <math>\angle CBA + \angle BCA = 2\angle PQN + 2\angle QPM = 60^{\circ}</math> and <math>\angle A = 120^{\circ}</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | - kevinmathz | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==The NT Part== | ||
| + | |||
| + | We now need to solve <math>a^2+ab+b^2 = 3^2\cdot 73^2</math>. A quick <math>(\bmod 9)</math> check gives that <math>3\mid a</math> and <math>3\mid b</math>. Thus, it's equivalent to solve <math>x^2+xy+y^2 = 73^2</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Let <math>\omega</math> be one root of <math>\omega^2+\omega+1=0</math>. Then, recall that <math>\mathbb Z[\omega]</math> is the ring of integers of <math>\mathbb Q[\sqrt{-3}]</math> and is a unique factorization domain. Notice that <math>N(x-y\omega) = (x-y\omega)(x-y\omega^2) = x^2+xy+y^2</math>. Therefore, it suffices to find an element of <math>\mathbb Z[\omega]</math> with the norm <math>73^2</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | To do so, we factor <math>73</math> in <math>\mathbb Z[\omega]</math>. Since it's <math>1\pmod 3</math>, it must split. A quick inspection gives <math>73 = (8-\omega)(8-\omega^2)</math>. Thus, <math>N(8-\omega) = 73</math>, so | ||
| + | <cmath>\begin{align*} | ||
| + | 73^2 &= N((8-\omega)^2) \ | ||
| + | &= N(64 - 16\omega + \omega^2) \ | ||
| + | &= N(64 - 16\omega + (-1-\omega)) \ | ||
| + | &= N(63 - 17\omega), | ||
| + | \end{align*}</cmath> | ||
| + | giving the solution <math>x=63</math> and <math>y=17</math>, yielding <math>a=189</math> and <math>b=51</math>, so the sum is <math>\boxed{459}</math>. Since <math>8-\omega</math> and <math>8-\omega^2</math> are primes in <math>\mathbb Z[\omega]</math>, the solution must divide <math>73^2</math>. One can then easily check that this is the unique solution. | ||
| + | |||
| + | - MarkBcc168 | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Solution (Geometry + Number Theory)== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Denote <math>BC = a</math>, <math>CA = b</math>, <math>AB = c</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Let the splitting line of <math>\triangle ABC</math> through <math>M</math> (resp. <math>N</math>) crosses <math>\triangle ABC</math> at another point <math>X</math> (resp. <math>Y</math>). | ||
| + | |||
| + | WLOG, we assume <math>c \leq b</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\textbf{Case 1}</math>: <math>a \leq c \leq b</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | We extend segment <math>AB</math> to <math>D</math>, such that <math>BD = a</math>. | ||
| + | We extend segment <math>AC</math> to <math>E</math>, such that <math>CE = a</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | In this case, <math>X</math> is the midpoint of <math>AE</math>, and <math>Y</math> is the midpoint of <math>AD</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Because <math>M</math> and <math>X</math> are the midpoints of <math>AB</math> and <math>AE</math>, respectively, <math>MX \parallel BE</math>. | ||
| + | Because <math>N</math> and <math>Y</math> are the midpoints of <math>AC</math> and <math>AD</math>, respectively, <math>NY \parallel CD</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Because <math>CB = CE</math>, <math>\angle CBE =\angle CEB = \frac{\angle ACB}{2}</math>. | ||
| + | Because <math>BC = BD</math>, <math>\angle BCD = \angle BDC = \frac{\angle ABC}{2}</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Let <math>BE</math> and <math>CD</math> intersect at <math>O</math>. | ||
| + | Because <math>MX \parallel BE</math> and <math>NY \parallel CD</math>, the angle formed between lines <math>MX</math> and <math>NY</math> is congruent to <math>\angle BOD</math>. Hence, <math>\angle BOD = 30^\circ</math> or <math>150^\circ</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | We have | ||
| + | <cmath> | ||
| + | \begin{align*} | ||
| + | \angle BOD & = \angle CBE + \angle BCD \ | ||
| + | & = \frac{\angle ACB}{2} + \frac{\angle ABC}{2} \ | ||
| + | & = 90^\circ - \frac{\angle A}{2} . | ||
| + | \end{align*} | ||
| + | </cmath> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Hence, we must have <math>\angle BOD = 30^\circ</math>, not <math>150^\circ</math>. | ||
| + | Hence, <math>\angle A = 120^\circ</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | This implies <math>a > b</math> and <math>a >c</math>. This contradicts the condition specified for this case. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Therefore, this case is infeasible. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\textbf{Case 2}</math>: <math>c \leq a \leq b</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | We extend segment <math>CB</math> to <math>D</math>, such that <math>BD = c</math>. | ||
| + | We extend segment <math>AC</math> to <math>E</math>, such that <math>CE = a</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | In this case, <math>X</math> is the midpoint of <math>AE</math>, and <math>Y</math> is the midpoint of <math>CD</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Because <math>M</math> and <math>X</math> are the midpoints of <math>AB</math> and <math>AE</math>, respectively, <math>MX \parallel BE</math>. | ||
| + | Because <math>N</math> and <math>Y</math> are the midpoints of <math>AC</math> and <math>CD</math>, respectively, <math>NY \parallel AD</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Because <math>CB = CE</math>, <math>\angle CBE =\angle CEB = \frac{\angle ACB}{2}</math>. | ||
| + | Because <math>BA = BD</math>, <math>\angle BAD = \angle BDA = \frac{\angle ABC}{2}</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Let <math>O</math> be a point of <math>AC</math>, such that <math>BO \parallel AD</math>. | ||
| + | Hence, <math>\angle OBC = \angle BDA = \frac{B}{2}</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Because <math>MX \parallel BE</math> and <math>NY \parallel AD</math> and <math>AD \parallel BO</math>, the angle formed between lines <math>MX</math> and <math>NY</math> is congruent to <math>\angle OBE</math>. Hence, <math>\angle OBE = 30^\circ</math> or <math>150^\circ</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | We have | ||
| + | <cmath> | ||
| + | \begin{align*} | ||
| + | \angle OBE & = \angle OBC + \angle CBE \ | ||
| + | & = \frac{\angle ABC}{2} + \frac{\angle ACB}{2} \ | ||
| + | & = 90^\circ - \frac{\angle A}{2} . | ||
| + | \end{align*} | ||
| + | </cmath> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Hence, we must have <math>\angle OBE = 30^\circ</math>, not <math>150^\circ</math>. | ||
| + | Hence, <math>\angle A = 120^\circ</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | This implies <math>a > b</math> and <math>a >c</math>. This contradicts the condition specified for this case. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Therefore, this case is infeasible. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\textbf{Case 3}</math>: <math>c \leq b \leq a</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | We extend segment <math>CB</math> to <math>D</math>, such that <math>BD = c</math>. | ||
| + | We extend segment <math>BC</math> to <math>E</math>, such that <math>CE = b</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | In this case, <math>X</math> is the midpoint of <math>BE</math>, and <math>Y</math> is the midpoint of <math>CD</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Because <math>M</math> and <math>X</math> are the midpoints of <math>AB</math> and <math>BE</math>, respectively, <math>MX \parallel AE</math>. | ||
| + | Because <math>N</math> and <math>Y</math> are the midpoints of <math>AC</math> and <math>CD</math>, respectively, <math>NY \parallel AD</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Because <math>CA = CE</math>, <math>\angle CAE =\angle CEB = \frac{\angle ACB}{2}</math>. | ||
| + | Because <math>BA = BD</math>, <math>\angle BAD = \angle BDA = \frac{\angle ABC}{2}</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Because <math>MX \parallel AE</math> and <math>NY \parallel AD</math>, the angle formed between lines <math>MX</math> and <math>NY</math> is congruent to <math>\angle DAE</math>. Hence, <math>\angle DAE = 30^\circ</math> or <math>150^\circ</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | We have | ||
| + | <cmath> | ||
| + | \begin{align*} | ||
| + | \angle DAE & = \angle BAD + \angle CAE + \angle BAC \ | ||
| + | & = \frac{\angle ABC}{2} + \frac{\angle ACB}{2} + \angle BAC \ | ||
| + | & = 90^\circ + \frac{\angle BAC}{2} . | ||
| + | \end{align*} | ||
| + | </cmath> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Hence, we must have <math>\angle OBE = 150^\circ</math>, not <math>30^\circ</math>. | ||
| + | Hence, <math>\angle BAC = 120^\circ</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | In <math>\triangle ABC</math>, by applying the law of cosines, we have | ||
| + | <cmath> | ||
| + | \begin{align*} | ||
| + | a^2 & = b^2 + c^2 - 2bc \cos \angle BAC\ | ||
| + | & = b^2 + c^2 - 2bc \cos 120^\circ \ | ||
| + | & = b^2 + c^2 + bc . | ||
| + | \end{align*} | ||
| + | </cmath> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Because <math>a = 219</math>, we have | ||
| + | <cmath> | ||
| + | \[ | ||
| + | b^2 + c^2 + bc = 219^2 . | ||
| + | \] | ||
| + | </cmath> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Now, we find integer solution(s) of this equation with <math>c \leq b</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Multiplying this equation by 4, we get | ||
| + | <cmath> | ||
| + | \[ | ||
| + | \left( 2 c + b \right)^2 + 3 b^2 = 438^2 . \hspace{1cm} (1) | ||
| + | \] | ||
| + | </cmath> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Denote <math>d = 2 c + b</math>. Because <math>c \leq b</math>, <math>b < d \leq 3 b</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Because <math>438^2 - 3 b^2 \equiv 0 \pmod{3}</math>, <math>d^2 \equiv 0 \pmod{3}</math>. | ||
| + | Thus, <math>d \equiv 0 \pmod{3}</math>. | ||
| + | This implies <math>d^2 \equiv 0 \pmod{9}</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | We also have <math>438^2 \equiv 0 \pmod{9}</math>. | ||
| + | Hence, <math>3 b^2 \equiv 0 \pmod{9}</math>. | ||
| + | This implies <math>b \equiv 0 \pmod{3}</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Denote <math>b = 3 p</math> and <math>d = 3 q</math>. Hence, <math>p < q \leq 3 p</math>. | ||
| + | Hence, Equation (1) can be written as | ||
| + | <cmath> | ||
| + | \[ | ||
| + | q^2 + 3 p^2 = 146^2 . \hspace{1cm} (2) | ||
| + | \] | ||
| + | </cmath> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Now, we solve this equation. | ||
| + | |||
| + | First, we find an upper bound of <math>q</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | We have <math>q^2 + 3 p^2 \geq q^2 + 3 \left( \frac{q}{3} \right)^2 = \frac{4 q^2}{3}</math>. | ||
| + | Hence, <math>\frac{4 q^2}{3} \leq 146^2</math>. | ||
| + | Hence, <math>q \leq 73 \sqrt{3} < 73 \cdot 1.8 = 131.4</math>. | ||
| + | Because <math>q</math> is an integer, we must have <math>q \leq 131</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Second, we find a lower bound of <math>q</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | We have <math>q^2 + 3 p^2 < q^2 + 3 q^2 = 4 q^2</math>. | ||
| + | Hence, <math>4 q^2 > 146^2</math>. | ||
| + | Hence, <math>q > 73</math>. | ||
| + | Because <math>q</math> is an integer, we must have <math>q \geq 74</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Now, we find the integer solutions of <math>p</math> and <math>q</math> that satisfy Equation (2) with <math>74 \leq q \leq 131</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | First, modulo 9, | ||
| + | <cmath> | ||
| + | \begin{align*} | ||
| + | q^2 & \equiv 146^2 - 3 p^2 \ | ||
| + | & \equiv 4 - 3 \cdot ( 0 \mbox{ or } 1 ) \ | ||
| + | & \equiv 4 \mbox{ or } 1 . | ||
| + | \end{align*} | ||
| + | </cmath> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Hence <math>q \equiv \pm 1, \pm 2 \pmod{9}</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Second, modulo 5, | ||
| + | <cmath> | ||
| + | \begin{align*} | ||
| + | q^2 & \equiv 146^2 - 3 p^2 \ | ||
| + | & \equiv 1 + 2 p^2 \ | ||
| + | & \equiv 1 + 2 \cdot ( 0 \mbox{ or } 1 \mbox{ or } -1 ) \ | ||
| + | & \equiv 1 \mbox{ or } 3 \mbox{ or } - 1 . | ||
| + | \end{align*} | ||
| + | </cmath> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Because <math>q^2 \equiv 0 \mbox{ or } 1 \mbox{ or } - 1</math>, we must have <math>q^2 \equiv 1 \mbox{ or } - 1</math>. | ||
| + | Hence, <math>5 \nmid q</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Third, modulo 7, | ||
| + | <cmath> | ||
| + | \begin{align*} | ||
| + | q^2 & \equiv 146^2 - 3 p^2 \ | ||
| + | & \equiv 1 - 3 \cdot ( 0 \mbox{ or } 1 \mbox{ or } 5 \mbox{ or } 2 ) \ | ||
| + | & \equiv 1 \mbox{ or } 2 \mbox{ or } 3 \mbox{ or } 5 . | ||
| + | \end{align*} | ||
| + | </cmath> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Because <math>q^2 \equiv 0 \mbox{ or } 1 \mbox{ or } 2 \mbox{ or } 4 \pmod{ 7 }</math>, we must have <math>q^2 \equiv 1 \mbox{ or } 2 \pmod{7}</math>. | ||
| + | Hence, <math>q \equiv 1, 3, 4, 6 \pmod{7}</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Given all conditions above, the possible <math>q</math> are 74, 83, 88, 92, 97, 101, 106, 109, 116, 118, 127. | ||
| + | |||
| + | By testing all these numbers, we find that the only solution is <math>q = 97</math>. | ||
| + | This implies <math>p = 63</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Hence, <math>b = 3p = 189</math> and <math>d = 3q = 291</math>. | ||
| + | Hence, <math>c = \frac{d - b}{2} = 51</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Therefore, the perimeter of <math>\triangle ABC</math> is <math>b + c + a = 189 + 51 + 219 = \boxed{\textbf{(459) }}</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ~Steven Chen (www.professorchenedu.com) | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==Solution (Number Theory Part)== | ||
| + | We wish to solve the Diophantine equation <math>a^2+ab+b^2=3^2 \cdot 73^2</math>. It can be shown that <math>3|a</math> and <math>3|b</math>, so we make the substitution <math>a=3x</math> and <math>b=3y</math> to obtain <math>x^2+xy+y^2=73^2</math> as our new equation to solve for. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Notice that <math>r^2+r+1=(r-\omega)(r-{\omega}^2)</math>, where <math>\omega=e^{i\frac{2\pi}{3}}</math>. Thus, | ||
| + | <cmath>x^2+xy+y^2 = y^2((x/y)^2+(x/y)+1) = y^2 (\frac{x}{y}-\omega)(\frac{x}{y}-{\omega}^2) = (x-y\omega)(x-y{\omega}^2).</cmath> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Note that <math>8^2+1^2+8 \cdot 1=73</math>. Thus, <math>(8-\omega)(8-{\omega}^2)=73</math>. Squaring both sides yields | ||
| + | <cmath>\begin{align} | ||
| + | (8-\omega)^2(8-{\omega}^2)^2&=73^2\ | ||
| + | (63-17\omega)(63-17{\omega}^2)&=73^2. | ||
| + | \end{align}</cmath> | ||
| + | Thus, by <math>(2)</math>, <math>(63, 17)</math> is a solution to <math>x^2+xy+y^2=73^2</math>. This implies that <math>a=189</math> and <math>b=51</math>, so our final answer is <math>189+51+219=\boxed{459}</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ~ Leo.Euler | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Solution(Visual geometry)== | ||
| + | [[File:AIME-I-2022-14a.png|400px|right]] | ||
| + | [[File:AIME-I-2022-14b.png|400px|right]] | ||
| + | [[File:AIME-I-2022-14c.png|400px|right]] | ||
| + | We look at upper and middle diagrams and get <math>\angle BAC = 120^\circ</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Next we use only the lower Diagram. Let <math>I</math> be incenter <math>\triangle ABC</math>, E be midpoint of biggest arc <math>\overset{\Large\frown} {BC}.</math> | ||
| + | Then bisector <math>AI</math> cross circumcircle <math>\triangle ABC</math> at point <math>E</math>. Quadrilateral <math>ABEC</math> is cyclic, so | ||
| + | <cmath> \angle BEC = 180^\circ - \angle ABC = 60^\circ \implies BE = CE = IE = BC.</cmath> | ||
| + | <cmath>AE \cdot BC = AB \cdot CE + AC \cdot BE \implies AE = AB + AC</cmath> | ||
| + | <math>\implies AI +EI = AB + AC, \hspace{10mm} AI = AB+ AC – BC</math> is integer. | ||
| + | <cmath>AI = \frac {2AB \cdot AC \cdot cos \angle CAI}{AB+AC + BC} = \frac {AB \cdot AC}{AB+AC + BC} =</cmath> | ||
| + | <cmath>= AB + AC – BC \implies AC^2 + AB^2 + AB \cdot AC = BC^2.</cmath> | ||
| + | A quick <math>(\mod9)</math> check gives that <math>3\mid AC</math> and <math>3\mid AB</math>. | ||
| + | <cmath>AI \le A_0I_0 = EA_0 – EI_0 = \frac{2 BC}{\sqrt{3}} – BC = \frac {2 - \sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{3}} BC = 33.88.</cmath> | ||
| + | Denote <math>a= \frac {BC}{3}= 73, b = \frac {AC}{3}, c = \frac {AB}{3}, l = \frac {AI}{3} \le 11.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | We have equations in integers | ||
| + | <math>\frac{bc}{a+b+c} = b + c – a = l \le 11.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | The solution <math>(b > c)</math> is | ||
| + | <cmath>b = \frac{a + l +\sqrt{a^2 – 6al – 3l^2}}{2}, | ||
| + | c = \frac{a + l -\sqrt{a^2 – 6al – 3l^2}}{2}.</cmath> | ||
| + | Suppose, <math>a^2 – 6al – 3l^2 = (a – 3l – t)^2 \implies \frac {12l^2}{t} + t + 6l= 2a = 146.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Now we check all possible <math>t = {2,3,4,6,12, ml}.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Case <math>t = 2 \implies 6l^2 + 6l = 146 – 2 \implies l^2 + l = 24 \implies \O </math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Case <math>t = 3 \implies 4l^2 + 6l = 146 – 3 = 143\implies \O.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Case <math>t = 4 \implies 3l^2 + 6l = 146 – 4 =142 \implies \O.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Case <math>t = 6 \implies 2l^2 + 6l = 146 – 6 = 140 \implies l = 7, b = 63, c = 17.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Case <math>t = 12 \implies l^2 + 6l = 146 – 12 = 134 \implies \O.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Case <math>t = ml \implies \frac{12l}{m} + 6l + ml = 146 \implies \frac{12}{m} + 6 + m = \frac{73 \cdot 2}{l}\implies \O.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Video Solution== | ||
| + | https://youtu.be/T6zq1e1RZdg | ||
| + | |||
| + | ~MathProblemSolvingSkills.com | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==Video Solution== | ||
| + | |||
| + | https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kkous52vPps&t=3023s | ||
| + | |||
| + | ~Steven Chen (wwww.professorchenedu.com) | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Animated Video Solution== | ||
| + | https://youtu.be/o-aDdxdnTWY | ||
| + | |||
| + | ~Star League (https://starleague.us) | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==See Also== | ||
| + | {{AIME box|year=2022|n=I|num-b=13|num-a=15}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Intermediate Geometry Problems]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Intermediate Number Theory Problems]] | ||
| + | {{MAA Notice}} | ||
Latest revision as of 01:56, 4 January 2023
Contents
[hide]Problem
Given ![]() and a point
and a point ![]() on one of its sides, call line
on one of its sides, call line ![]() the
the ![]() of
of ![]() through
through ![]() if
if ![]() passes through
passes through ![]() and divides
and divides ![]() into two polygons of equal perimeter. Let
into two polygons of equal perimeter. Let ![]() be a triangle where
be a triangle where ![]() and
and ![]() and
and ![]() are positive integers. Let
are positive integers. Let ![]() and
and ![]() be the midpoints of
be the midpoints of ![]() and
and ![]() respectively, and suppose that the splitting lines of
respectively, and suppose that the splitting lines of ![]() through
through ![]() and
and ![]() intersect at
intersect at ![]() Find the perimeter of
Find the perimeter of ![]()
The Geometry Part - Solution 1
Consider the splitting line through ![]() . Extend
. Extend ![]() on ray
on ray ![]() such that
such that ![]() . Then the splitting line bisects segment
. Then the splitting line bisects segment ![]() , so in particular it is the midline of triangle
, so in particular it is the midline of triangle ![]() and thus it is parallel to
and thus it is parallel to ![]() . But since triangle
. But since triangle ![]() is isosceles, we can easily see
is isosceles, we can easily see ![]() is parallel to the angle bisector of
is parallel to the angle bisector of ![]() , so the splitting line is also parallel to this bisector, and similar for the splitting line through
, so the splitting line is also parallel to this bisector, and similar for the splitting line through ![]() . Some simple angle chasing reveals the condition is now equivalent to
. Some simple angle chasing reveals the condition is now equivalent to ![]() .
.
- MortemEtInteritum
The Geometry Part - Solution 2
Let ![]() and
and ![]() be the splitting lines. Reflect
be the splitting lines. Reflect ![]() across
across ![]() to be
to be ![]() and
and ![]() across
across ![]() to be
to be ![]() . Take
. Take ![]() and
and ![]() , which are spiral similarity centers on the other side of
, which are spiral similarity centers on the other side of ![]() as
as ![]() such that
such that ![]() and
and ![]() . This gets that because
. This gets that because ![]() and
and ![]() , then
, then ![]() and
and ![]() are on
are on ![]() 's circumcircle. Now, we know that
's circumcircle. Now, we know that ![]() and
and ![]() so because
so because ![]() and
and ![]() , then
, then ![]() and
and ![]() and
and ![]() and
and ![]() .
.
We also notice that because ![]() and
and ![]() correspond on
correspond on ![]() and
and ![]() , and because
, and because ![]() and
and ![]() correspond on
correspond on ![]() and
and ![]() , then the angle formed by
, then the angle formed by ![]() and
and ![]() is equal to the angle formed by
is equal to the angle formed by ![]() and
and ![]() which is equal to
which is equal to ![]() . Thus,
. Thus, ![]() . Similarly,
. Similarly, ![]() and so
and so ![]() and
and ![]() .
.
- kevinmathz
The NT Part
We now need to solve ![]() . A quick
. A quick ![]() check gives that
check gives that ![]() and
and ![]() . Thus, it's equivalent to solve
. Thus, it's equivalent to solve ![]() .
.
Let ![]() be one root of
be one root of ![]() . Then, recall that
. Then, recall that ![]() is the ring of integers of
is the ring of integers of ![]() and is a unique factorization domain. Notice that
and is a unique factorization domain. Notice that ![]() . Therefore, it suffices to find an element of
. Therefore, it suffices to find an element of ![]() with the norm
with the norm ![]() .
.
To do so, we factor ![]() in
in ![]() . Since it's
. Since it's ![]() , it must split. A quick inspection gives
, it must split. A quick inspection gives ![]() . Thus,
. Thus, ![]() , so
, so
 giving the solution
giving the solution ![]() and
and ![]() , yielding
, yielding ![]() and
and ![]() , so the sum is
, so the sum is ![]() . Since
. Since ![]() and
and ![]() are primes in
are primes in ![]() , the solution must divide
, the solution must divide ![]() . One can then easily check that this is the unique solution.
. One can then easily check that this is the unique solution.
- MarkBcc168
Solution (Geometry + Number Theory)
Denote ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() .
.
Let the splitting line of ![]() through
through ![]() (resp.
(resp. ![]() ) crosses
) crosses ![]() at another point
at another point ![]() (resp.
(resp. ![]() ).
).
WLOG, we assume ![]() .
.
![]() :
: ![]() .
.
We extend segment ![]() to
to ![]() , such that
, such that ![]() .
We extend segment
.
We extend segment ![]() to
to ![]() , such that
, such that ![]() .
.
In this case, ![]() is the midpoint of
is the midpoint of ![]() , and
, and ![]() is the midpoint of
is the midpoint of ![]() .
.
Because ![]() and
and ![]() are the midpoints of
are the midpoints of ![]() and
and ![]() , respectively,
, respectively, ![]() .
Because
.
Because ![]() and
and ![]() are the midpoints of
are the midpoints of ![]() and
and ![]() , respectively,
, respectively, ![]() .
.
Because ![]() ,
, ![]() .
Because
.
Because ![]() ,
, ![]() .
.
Let ![]() and
and ![]() intersect at
intersect at ![]() .
Because
.
Because ![]() and
and ![]() , the angle formed between lines
, the angle formed between lines ![]() and
and ![]() is congruent to
is congruent to ![]() . Hence,
. Hence, ![]() or
or ![]() .
.
We have

Hence, we must have ![]() , not
, not ![]() .
Hence,
.
Hence, ![]() .
.
This implies ![]() and
and ![]() . This contradicts the condition specified for this case.
. This contradicts the condition specified for this case.
Therefore, this case is infeasible.
![]() :
: ![]() .
.
We extend segment ![]() to
to ![]() , such that
, such that ![]() .
We extend segment
.
We extend segment ![]() to
to ![]() , such that
, such that ![]() .
.
In this case, ![]() is the midpoint of
is the midpoint of ![]() , and
, and ![]() is the midpoint of
is the midpoint of ![]() .
.
Because ![]() and
and ![]() are the midpoints of
are the midpoints of ![]() and
and ![]() , respectively,
, respectively, ![]() .
Because
.
Because ![]() and
and ![]() are the midpoints of
are the midpoints of ![]() and
and ![]() , respectively,
, respectively, ![]() .
.
Because ![]() ,
, ![]() .
Because
.
Because ![]() ,
, ![]() .
.
Let ![]() be a point of
be a point of ![]() , such that
, such that ![]() .
Hence,
.
Hence, ![]() .
.
Because ![]() and
and ![]() and
and ![]() , the angle formed between lines
, the angle formed between lines ![]() and
and ![]() is congruent to
is congruent to ![]() . Hence,
. Hence, ![]() or
or ![]() .
.
We have

Hence, we must have ![]() , not
, not ![]() .
Hence,
.
Hence, ![]() .
.
This implies ![]() and
and ![]() . This contradicts the condition specified for this case.
. This contradicts the condition specified for this case.
Therefore, this case is infeasible.
![]() :
: ![]() .
.
We extend segment ![]() to
to ![]() , such that
, such that ![]() .
We extend segment
.
We extend segment ![]() to
to ![]() , such that
, such that ![]() .
.
In this case, ![]() is the midpoint of
is the midpoint of ![]() , and
, and ![]() is the midpoint of
is the midpoint of ![]() .
.
Because ![]() and
and ![]() are the midpoints of
are the midpoints of ![]() and
and ![]() , respectively,
, respectively, ![]() .
Because
.
Because ![]() and
and ![]() are the midpoints of
are the midpoints of ![]() and
and ![]() , respectively,
, respectively, ![]() .
.
Because ![]() ,
, ![]() .
Because
.
Because ![]() ,
, ![]() .
.
Because ![]() and
and ![]() , the angle formed between lines
, the angle formed between lines ![]() and
and ![]() is congruent to
is congruent to ![]() . Hence,
. Hence, ![]() or
or ![]() .
.
We have

Hence, we must have ![]() , not
, not ![]() .
Hence,
.
Hence, ![]() .
.
In ![]() , by applying the law of cosines, we have
, by applying the law of cosines, we have

Because ![]() , we have
, we have
![]()
Now, we find integer solution(s) of this equation with ![]() .
.
Multiplying this equation by 4, we get
![]()
Denote ![]() . Because
. Because ![]() ,
, ![]() .
.
Because ![]() ,
, ![]() .
Thus,
.
Thus, ![]() .
This implies
.
This implies ![]() .
.
We also have ![]() .
Hence,
.
Hence, ![]() .
This implies
.
This implies ![]() .
.
Denote ![]() and
and ![]() . Hence,
. Hence, ![]() .
Hence, Equation (1) can be written as
.
Hence, Equation (1) can be written as
![]()
Now, we solve this equation.
First, we find an upper bound of ![]() .
.
We have ![]() .
Hence,
.
Hence, ![]() .
Hence,
.
Hence, ![]() .
Because
.
Because ![]() is an integer, we must have
is an integer, we must have ![]() .
.
Second, we find a lower bound of ![]() .
.
We have ![]() .
Hence,
.
Hence, ![]() .
Hence,
.
Hence, ![]() .
Because
.
Because ![]() is an integer, we must have
is an integer, we must have ![]() .
.
Now, we find the integer solutions of ![]() and
and ![]() that satisfy Equation (2) with
that satisfy Equation (2) with ![]() .
.
First, modulo 9,

Hence ![]() .
.
Second, modulo 5,

Because ![]() , we must have
, we must have ![]() .
Hence,
.
Hence, ![]() .
.
Third, modulo 7,

Because ![]() , we must have
, we must have ![]() .
Hence,
.
Hence, ![]() .
.
Given all conditions above, the possible ![]() are 74, 83, 88, 92, 97, 101, 106, 109, 116, 118, 127.
are 74, 83, 88, 92, 97, 101, 106, 109, 116, 118, 127.
By testing all these numbers, we find that the only solution is ![]() .
This implies
.
This implies ![]() .
.
Hence, ![]() and
and ![]() .
Hence,
.
Hence, ![]() .
.
Therefore, the perimeter of ![]() is
is ![]() .
.
~Steven Chen (www.professorchenedu.com)
Solution (Number Theory Part)
We wish to solve the Diophantine equation ![]() . It can be shown that
. It can be shown that ![]() and
and ![]() , so we make the substitution
, so we make the substitution ![]() and
and ![]() to obtain
to obtain ![]() as our new equation to solve for.
as our new equation to solve for.
Notice that ![]() , where
, where ![]() . Thus,
. Thus,
![]()
Note that ![]() . Thus,
. Thus, ![]() . Squaring both sides yields
. Squaring both sides yields
![]() Thus, by
Thus, by ![]() ,
, ![]() is a solution to
is a solution to ![]() . This implies that
. This implies that ![]() and
and ![]() , so our final answer is
, so our final answer is ![]() .
.
~ Leo.Euler
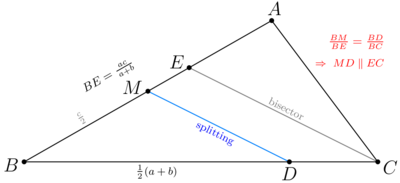
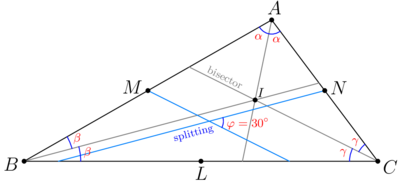
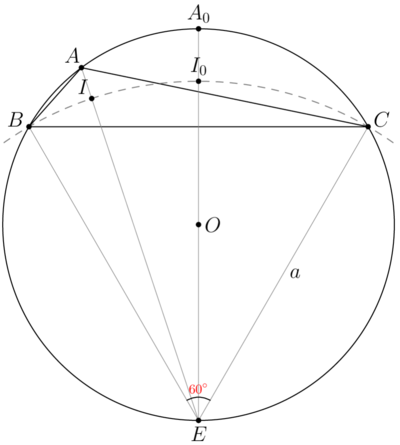
Solution(Visual geometry)
We look at upper and middle diagrams and get ![]() .
.
Next we use only the lower Diagram. Let ![]() be incenter
be incenter ![]() , E be midpoint of biggest arc
, E be midpoint of biggest arc ![]() Then bisector
Then bisector ![]() cross circumcircle
cross circumcircle ![]() at point
at point ![]() . Quadrilateral
. Quadrilateral ![]() is cyclic, so
is cyclic, so
![]()
![]()
![]() is integer.
is integer.
![]()
![]() A quick
A quick ![]() check gives that
check gives that ![]() and
and ![]() .
.
![]() Denote
Denote ![]()
We have equations in integers
![]()
The solution ![]() is
is
![]() Suppose,
Suppose, ![]()
Now we check all possible ![]()
Case ![]()
Case ![]()
Case ![]()
Case ![]()
Case ![]()
Case ![]()
vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss
Video Solution
~MathProblemSolvingSkills.com
Video Solution
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kkous52vPps&t=3023s
~Steven Chen (wwww.professorchenedu.com)
Animated Video Solution
~Star League (https://starleague.us)
See Also
| 2022 AIME I (Problems • Answer Key • Resources) | ||
| Preceded by Problem 13 |
Followed by Problem 15 | |
| 1 • 2 • 3 • 4 • 5 • 6 • 7 • 8 • 9 • 10 • 11 • 12 • 13 • 14 • 15 | ||
| All AIME Problems and Solutions | ||
The problems on this page are copyrighted by the Mathematical Association of America's American Mathematics Competitions. ![]()