Difference between revisions of "1998 AHSME Problems/Problem 16"
m (→Solution) |
|||
| (4 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
| − | The area of the whole circle is <math>A_{big} = \pi\cdot (a + b)^2</math> | + | The area of the whole circle is <math>A_{\mathrm{big}} = \pi\cdot (a + b)^2</math> |
The area of the white area is about <math>\frac{A_{big}}{2}</math>, which is the bottom half of the circle. However, you need to subtract the little shaded semicircle on the bottom, and add the area of the big unshaded semicircle on top. Thus, it is actually <math>A_{white} = \frac{1}{2}\pi\cdot (a+b)^2 - \frac{1}{2}\pi a^2 + \frac{1}{2}\pi b^2</math> | The area of the white area is about <math>\frac{A_{big}}{2}</math>, which is the bottom half of the circle. However, you need to subtract the little shaded semicircle on the bottom, and add the area of the big unshaded semicircle on top. Thus, it is actually <math>A_{white} = \frac{1}{2}\pi\cdot (a+b)^2 - \frac{1}{2}\pi a^2 + \frac{1}{2}\pi b^2</math> | ||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
Factoring gives <math>A_{white} = \frac{\pi}{2}\cdot (a^2 + 2ab + b^2 - a^2 + b^2)</math> | Factoring gives <math>A_{white} = \frac{\pi}{2}\cdot (a^2 + 2ab + b^2 - a^2 + b^2)</math> | ||
| − | Simplfying the inside gives <math>A_{white} = \frac{\pi}{2}\cdot (2ab + | + | Simplfying the inside gives <math>A_{white} = \frac{\pi}{2}\cdot (2ab + 2b^2)</math> |
<math>A_{white} = \pi(ab + b^2)</math> | <math>A_{white} = \pi(ab + b^2)</math> | ||
Latest revision as of 00:56, 8 January 2025
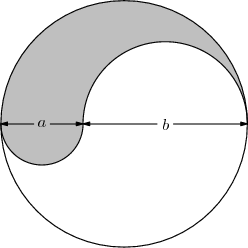
Problem
The figure shown is the union of a circle and two semicircles of diameters ![]() and
and ![]() , all of whose centers are collinear. The ratio of the area, of the shaded region to that of the unshaded region is
, all of whose centers are collinear. The ratio of the area, of the shaded region to that of the unshaded region is
![]()
Solution
To simplify calculations, double the radius of the large circle from ![]() to
to ![]() . Each region is similar to the old region, so this should not change the ratio of any areas.
. Each region is similar to the old region, so this should not change the ratio of any areas.
In other words, relabel ![]() and
and ![]() to
to ![]() and
and ![]() .
.
The area of the whole circle is ![]()
The area of the white area is about ![]() , which is the bottom half of the circle. However, you need to subtract the little shaded semicircle on the bottom, and add the area of the big unshaded semicircle on top. Thus, it is actually
, which is the bottom half of the circle. However, you need to subtract the little shaded semicircle on the bottom, and add the area of the big unshaded semicircle on top. Thus, it is actually ![]()
Factoring gives ![]()
Simplfying the inside gives ![]()
![]()
With similar calculations, or noting the symmetry of the situation, ![]()
The desired ratio is thus ![]() , which is option
, which is option ![]() .
.
See also
| 1998 AHSME (Problems • Answer Key • Resources) | ||
| Preceded by Problem 15 |
Followed by Problem 17 | |
| 1 • 2 • 3 • 4 • 5 • 6 • 7 • 8 • 9 • 10 • 11 • 12 • 13 • 14 • 15 • 16 • 17 • 18 • 19 • 20 • 21 • 22 • 23 • 24 • 25 • 26 • 27 • 28 • 29 • 30 | ||
| All AHSME Problems and Solutions | ||
The problems on this page are copyrighted by the Mathematical Association of America's American Mathematics Competitions. ![]()