Difference between revisions of "2004 AMC 12A Problems/Problem 18"
Aops12142015 (talk | contribs) (→Solution 3) |
Aops12142015 (talk | contribs) (→Solution 3) |
||
| Line 61: | Line 61: | ||
Clearly, <math>EA = EF = BG</math>. Thus, the sides of [[right triangle]] <math>CDE</math> are in arithmetic progression. Thus it is [[similar triangles|similar]] to the triangle <math>3 - 4 - 5</math> and since <math>DC = 2</math>, <math>CE = 5/2</math>. | Clearly, <math>EA = EF = BG</math>. Thus, the sides of [[right triangle]] <math>CDE</math> are in arithmetic progression. Thus it is [[similar triangles|similar]] to the triangle <math>3 - 4 - 5</math> and since <math>DC = 2</math>, <math>CE = 5/2</math>. | ||
| − | == Solution | + | == Solution 4 == |
<asy> | <asy> | ||
size(150); | size(150); | ||
| Line 82: | Line 82: | ||
</asy> | </asy> | ||
| − | Let us call the midpoint of side <math>AB</math>, point <math>G</math>. Since the semicircle has radius 1, we can do the Pythagorean theorem on sides <math>GB, BC, GC</math>. We get <math>GC=\sqrt{5}</math>. We then know that <math>CF=2</math> by Pythagorean theorem. Then by connecting <math>EG</math>, we get similar triangles <math>EFG</math> and <math>GFC</math>. Solving the ratios, we get | + | Let us call the midpoint of side <math>AB</math>, point <math>G</math>. Since the semicircle has radius 1, we can do the Pythagorean theorem on sides <math>GB, BC, GC</math>. We get <math>GC=\sqrt{5}</math>. We then know that <math>CF=2</math> by Pythagorean theorem. Then by connecting <math>EG</math>, we get similar triangles <math>EFG</math> and <math>GFC</math>. Solving the ratios, we get <math>x=\frac{1}{2}</math>, so the answer is <math> \frac{5}{2} \Rightarrow\boxed{\mathrm{(D)}\ \frac{5}{2}}</math>. |
== See also == | == See also == | ||
Revision as of 23:00, 13 July 2016
- The following problem is from both the 2004 AMC 12A #18 and 2004 AMC 10A #22, so both problems redirect to this page.
Problem
Square ![]() has side length
has side length ![]() . A semicircle with diameter
. A semicircle with diameter ![]() is constructed inside the square, and the tangent to the semicircle from
is constructed inside the square, and the tangent to the semicircle from ![]() intersects side
intersects side ![]() at
at ![]() . What is the length of
. What is the length of ![]() ?
?
![[asy] size(100); defaultpen(fontsize(10)); pair A=(0,0), B=(2,0), C=(2,2), D=(0,2), E=(0,1/2); draw(A--B--C--D--cycle);draw(C--E); draw(Arc((1,0),1,0,180)); label("$A$",A,(-1,-1)); label("$B$",B,( 1,-1)); label("$C$",C,( 1, 1)); label("$D$",D,(-1, 1)); label("$E$",E,(-1, 0)); [/asy]](http://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/d/a/e/daef6f3ebe3e1fc6cfacd8611db1d6d449c8d2d4.png)
![]()
Solution 1
![[asy] size(150); defaultpen(fontsize(10)); pair A=(0,0), B=(2,0), C=(2,2), D=(0,2), E=(0,1/2), F=E+(C-E)/abs(C-E)/2; draw(A--B--C--D--cycle);draw(C--E); draw(Arc((1,0),1,0,180));draw((A+B)/2--F); label("$A$",A,(-1,-1)); label("$B$",B,( 1,-1)); label("$C$",C,( 1, 1)); label("$D$",D,(-1, 1)); label("$E$",E,(-1, 0)); label("$F$",F,( 0, 1)); label("$x$",(A+E)/2,(-1, 0)); label("$x$",(E+F)/2,( 0, 1)); label("$2$",(F+C)/2,( 0, 1)); label("$2$",(D+C)/2,( 0, 1)); label("$2$",(B+C)/2,( 1, 0)); label("$2-x$",(D+E)/2,(-1, 0)); [/asy]](http://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/4/8/2/4820e9c378ef42e0fe36c7d37d2bb816d542a300.png) Let the point of tangency be
Let the point of tangency be ![]() . By the Two Tangent Theorem
. By the Two Tangent Theorem ![]() and
and ![]() . Thus
. Thus ![]() . The Pythagorean Theorem on
. The Pythagorean Theorem on ![]() yields
yields

Hence ![]() .
.
Solution 2
Call the point of tangency point ![]() and the midpoint of
and the midpoint of ![]() as
as ![]() .
. ![]() by the pythagorean theorem. Notice that
by the pythagorean theorem. Notice that ![]() . Thus,
. Thus, ![]() . Adding, the answer is
. Adding, the answer is ![]() .
.
Solution 3
Clearly, ![]() . Thus, the sides of right triangle
. Thus, the sides of right triangle ![]() are in arithmetic progression. Thus it is similar to the triangle
are in arithmetic progression. Thus it is similar to the triangle ![]() and since
and since ![]() ,
, ![]() .
.
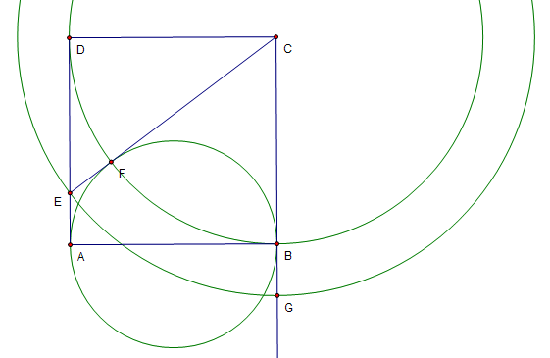
Solution 4
![[asy] size(150); defaultpen(fontsize(10)); pair A=(0,0), B=(2,0), C=(2,2), D=(0,2), E=(0,1/2), F=E+(C-E)/abs(C-E)/2; draw(A--B--C--D--cycle);draw(C--E); draw(Arc((1,0),1,0,180));draw((A+B)/2--F); label("$A$",A,(-1,-1)); label("$B$",B,( 1,-1)); label("$C$",C,( 1, 1)); label("$D$",D,(-1, 1)); label("$E$",E,(-1, 0)); label("$F$",F,( 0, 1)); label("$x$",(A+E)/2,(-1, 0)); label("$x$",(E+F)/2,( 0, 1)); label("$2$",(F+C)/2,( 0, 1)); label("$2$",(D+C)/2,( 0, 1)); label("$2$",(B+C)/2,( 1, 0)); label("$2-x$",(D+E)/2,(-1, 0)); [/asy]](http://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/4/8/2/4820e9c378ef42e0fe36c7d37d2bb816d542a300.png)
Let us call the midpoint of side ![]() , point
, point ![]() . Since the semicircle has radius 1, we can do the Pythagorean theorem on sides
. Since the semicircle has radius 1, we can do the Pythagorean theorem on sides ![]() . We get
. We get ![]() . We then know that
. We then know that ![]() by Pythagorean theorem. Then by connecting
by Pythagorean theorem. Then by connecting ![]() , we get similar triangles
, we get similar triangles ![]() and
and ![]() . Solving the ratios, we get
. Solving the ratios, we get ![]() , so the answer is
, so the answer is ![]() .
.
See also
| 2004 AMC 12A (Problems • Answer Key • Resources) | |
| Preceded by Problem 17 |
Followed by Problem 19 |
| 1 • 2 • 3 • 4 • 5 • 6 • 7 • 8 • 9 • 10 • 11 • 12 • 13 • 14 • 15 • 16 • 17 • 18 • 19 • 20 • 21 • 22 • 23 • 24 • 25 | |
| All AMC 12 Problems and Solutions | |
| 2004 AMC 10A (Problems • Answer Key • Resources) | ||
| Preceded by Problem 21 |
Followed by Problem 23 | |
| 1 • 2 • 3 • 4 • 5 • 6 • 7 • 8 • 9 • 10 • 11 • 12 • 13 • 14 • 15 • 16 • 17 • 18 • 19 • 20 • 21 • 22 • 23 • 24 • 25 | ||
| All AMC 10 Problems and Solutions | ||
The problems on this page are copyrighted by the Mathematical Association of America's American Mathematics Competitions.