2021 Fall AMC 12B Problems/Problem 17
Contents
[hide]Problem
A bug starts at a vertex of a grid made of equilateral triangles of side length ![]() . At each step the bug moves in one of the
. At each step the bug moves in one of the ![]() possible directions along the grid lines randomly and independently with equal probability. What is the probability that after
possible directions along the grid lines randomly and independently with equal probability. What is the probability that after ![]() moves the bug never will have been more than
moves the bug never will have been more than ![]() unit away from the starting position?
unit away from the starting position?
![]()
Solution 1 (Recursion)
Let ![]() be the number of paths of
be the number of paths of ![]() moves such that the bug never will have been more than
moves such that the bug never will have been more than ![]() unit away from the starting position. Clearly, by symmetry, there are two possible states here, the bug being on the center and the bug being on one of the vertices of the unit hexagon around the center. Let
unit away from the starting position. Clearly, by symmetry, there are two possible states here, the bug being on the center and the bug being on one of the vertices of the unit hexagon around the center. Let ![]() be the number of paths with the aforementioned restriction that end on the center. Let
be the number of paths with the aforementioned restriction that end on the center. Let ![]() be the number of paths with the aforementioned restriction that end on a vertex of the surrounding unit hexagon. We have
be the number of paths with the aforementioned restriction that end on a vertex of the surrounding unit hexagon. We have ![]() since from the center, there are
since from the center, there are ![]() possible points to land to and from a vertex there are
possible points to land to and from a vertex there are ![]() possible points to land to (the two adjacent vertices and the center). We also have
possible points to land to (the two adjacent vertices and the center). We also have ![]() , since to get to the center the bug must have come from a vertex, and
, since to get to the center the bug must have come from a vertex, and ![]() since from a vertex there are two vertices to move to, and from the center there are
since from a vertex there are two vertices to move to, and from the center there are ![]() vertices to move to. We can construct a recursion table using the base cases
vertices to move to. We can construct a recursion table using the base cases ![]() and
and ![]() and our recursive rules for
and our recursive rules for ![]() and
and ![]() as follows:
as follows:
![\[\begin{array}{c|c|c} n & V(n) & C(n) \\ \hline & & \\ [-2ex] 1 & 6 & 0 \\ 2 & 12 & 6 \\ 3 & 60 & 12 \\ 4 & 192 & 60 \\ \end{array}\]](http://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/f/7/b/f7bae7d074e53940976cad59a49b95aa41371c30.png) Then,
Then, ![]() and the desired probability is thus
and the desired probability is thus ![]()
~fidgetboss_4000
Solution 2 (Recursion)
Let ![]() be such probability after
be such probability after ![]() moves.
moves. ![]() ,
, ![]() . Then,
. Then, ![]() . Then, we can prove the recursive formula
. Then, we can prove the recursive formula ![]() Now, we evaluate
Now, we evaluate ![]() .
.
Solution 3 (Recursion)
We use ![]() to denote the bug's current state. We wish to find
to denote the bug's current state. We wish to find ![]() .
.
The first argument ![]() denotes the bug's current position.
We use
denotes the bug's current position.
We use ![]() to denote the bug's starting point.
We use
to denote the bug's starting point.
We use ![]() to denote any point whose distance to the bug's starting point is
to denote any point whose distance to the bug's starting point is ![]() .
.
The second argument ![]() denotes the remaining number of moves the bug has.
denotes the remaining number of moves the bug has.
For ![]() and
and ![]() , we have
, we have ![]() For
For ![]() and
and ![]() , we have
, we have ![]() For
For ![]() and
and ![]() , we have
, we have ![]() We solve this recursive equation by using backward induction:
We solve this recursive equation by using backward induction:
![\[\begin{array}{ll} P(0,1) = 1, & P(1,1) = \frac{1}{2}, \\ [1ex] P(0,2) = \frac{1}{2}, & P(1,2) = \frac{1}{3}, \\ [1ex] P(0,3) = \frac{1}{3}, & P(1,3) = \frac{7}{36}, \\ [1ex] P(0,4) = \frac{7}{36}, & P(1,4) = \frac{13}{108}. \end{array}\]](http://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/5/7/6/57636a3a3fe73ee85612e6ed327fe37951322b68.png) Therefore, the answer is
Therefore, the answer is ![]() .
.
~Steven Chen (www.professorchenedu.com)
Solution 4 (Generating Function)
Use a generating function, define ![]() be
be ![]() ways for the destination be
ways for the destination be ![]() units away from the origin.
units away from the origin.
We conclude that:
- If the current point is origin, then we need to multiply by
 .
.
- If the current point on vertex of the unit hexagon, then we need to multiply by
 , where there is
, where there is  way to return to the origin and there are two ways to keep distance
way to return to the origin and there are two ways to keep distance  .
.
Now let's start with ![]() .
.
![]() st step:
st step: ![]()
![]() nd step:
nd step: ![]()
![]() rd step:
rd step: ![]()
![]() th step:
th step: ![]()
![]() th step:
th step: ![]()
So, there are ![]() ways for the bug never moves more than
ways for the bug never moves more than ![]() unit away from origin. The answer is
unit away from origin. The answer is ![]() .
.
~wwei.yu
Solution 5 (Casework)
In the following diagram, let ![]() denote the vertex where the bug starts (shown in red) and
denote the vertex where the bug starts (shown in red) and ![]() denote one of the
denote one of the ![]() adjacent vertices (shown in green).
adjacent vertices (shown in green).
![[asy] /* Made by MRENTHUSIASM */ size(150); pair[] A, B, C; for (int i = 0; i <= 5; ++i) { A[i] = dir(60*i); B[i] = 2 * dir(60*i); C[i] = sqrt(3) * dir(30+60i); } draw(B[2]--B[3]^^C[1]--C[3]^^B[1]--B[4]^^C[0]--C[4]^^B[0]--B[5]^^B[3]--B[4]^^C[2]--C[4]^^B[2]--B[5]^^C[1]--C[5]^^B[1]--B[0]^^B[2]--B[1]^^C[2]--C[0]^^B[3]--B[0]^^C[3]--C[5]^^B[4]--B[5]); dot(origin,red+linewidth(5)); for (int i = 0; i <= 5; ++i) { dot(A[i],green+linewidth(5)); dot(B[i],linewidth(5)); dot(C[i],linewidth(5)); } [/asy]](http://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/8/d/f/8dfe010cca3c81abf8904e5b7b88e36b16a233a2.png) Note that:
Note that:
- If the bug is at
 then the probability that it moves to
then the probability that it moves to  next is
next is 
- If the bug is at
 then the probability that it moves to
then the probability that it moves to  next is
next is 
- If the bug is at
 then the probability that it moves to
then the probability that it moves to  next is
next is 
We apply casework to the possible paths of the bug:

The probability for this case is


The probability for this case is


The probability for this case is


The probability for this case is


The probability for this case is


The probability for this case is


The probability for this case is


The probability for this case is

Together, the answer is ![]() ~MRENTHUSIASM
~MRENTHUSIASM
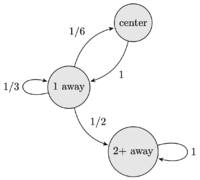
Solution 6 (Markov Chain)
We can use a Markov chain to represent the different states of the bug.
Let "center" (C) represent the starting point, "1 away" (O) represent a point on the grid 1 move and 1 unit away from the starting point, and "2+ away" (T) represent the case where the bug has ventured more than 1 unit away from its starting point.
Notice that the bug must move to the 1 away state from the center. From there, it moves back to the center with a ![]() probability, to a point 2 units away from the center with
probability, to a point 2 units away from the center with ![]() probability, and to another point 1 unit away with
probability, and to another point 1 unit away with ![]() probability.
probability.
We are trying to find the probability that the bug does not reach the 2+ away state in 5 moves. To accomplish this, we can find the complement by listing out the cases that the bug does reach the 2+ away state in a specified number of moves.
Clearly, the bug cannot reach the 2+ away (T) state in 0 moves.
In 1 move, the bug can only reach the 1 away (O) state, so it cannot reach the T state in 1 move either.
In 2 moves, the bug can move to the O state followed by the T state with probability ![]() .
.
In 3 moves, the bug can follow the pattern OOT with probability ![]() .
.
In 4 moves, the bug can follow the paths of OOOT or OCOT, with probabilities ![]() and
and ![]() respectively.
respectively.
In 5 moves, the bug can follow the paths of OOOOT, OCOOT, or OOCOT, with probabilities ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() .
.
Adding up these probabilities, we obtain ![]() . Finding the complement of this, we subtract from 1 to get the answer of
. Finding the complement of this, we subtract from 1 to get the answer of ![]() .
.
![]() ~diyarv
~diyarv
See Also
| 2021 Fall AMC 12B (Problems • Answer Key • Resources) | |
| Preceded by Problem 16 |
Followed by Problem 18 |
| 1 • 2 • 3 • 4 • 5 • 6 • 7 • 8 • 9 • 10 • 11 • 12 • 13 • 14 • 15 • 16 • 17 • 18 • 19 • 20 • 21 • 22 • 23 • 24 • 25 | |
| All AMC 12 Problems and Solutions | |
The problems on this page are copyrighted by the Mathematical Association of America's American Mathematics Competitions. ![]()