Difference between revisions of "2012 AIME II Problems/Problem 15"
(→Solution 1) |
(→Solution 6:) |
||
| (78 intermediate revisions by 22 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Problem 15 == | == Problem 15 == | ||
Triangle <math>ABC</math> is inscribed in circle <math>\omega</math> with <math>AB=5</math>, <math>BC=7</math>, and <math>AC=3</math>. The bisector of angle <math>A</math> meets side <math>\overline{BC}</math> at <math>D</math> and circle <math>\omega</math> at a second point <math>E</math>. Let <math>\gamma</math> be the circle with diameter <math>\overline{DE}</math>. Circles <math>\omega</math> and <math>\gamma</math> meet at <math>E</math> and a second point <math>F</math>. Then <math>AF^2 = \frac mn</math>, where <math>m</math> and <math>n</math> are relatively prime positive integers. Find <math>m+n</math>. | Triangle <math>ABC</math> is inscribed in circle <math>\omega</math> with <math>AB=5</math>, <math>BC=7</math>, and <math>AC=3</math>. The bisector of angle <math>A</math> meets side <math>\overline{BC}</math> at <math>D</math> and circle <math>\omega</math> at a second point <math>E</math>. Let <math>\gamma</math> be the circle with diameter <math>\overline{DE}</math>. Circles <math>\omega</math> and <math>\gamma</math> meet at <math>E</math> and a second point <math>F</math>. Then <math>AF^2 = \frac mn</math>, where <math>m</math> and <math>n</math> are relatively prime positive integers. Find <math>m+n</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Quick Solution using Olympiad Terms == | ||
| + | |||
| + | Take a force-overlaid inversion about <math>A</math> and note <math>D</math> and <math>E</math> map to each other. As <math>DE</math> was originally the diameter of <math>\gamma</math>, <math>DE</math> is still the diameter of <math>\gamma</math>. Thus <math>\gamma</math> is preserved. Note that the midpoint <math>M</math> of <math>BC</math> lies on <math>\gamma</math>, and <math>BC</math> and <math>\omega</math> are swapped. Thus points <math>F</math> and <math>M</math> map to each other, and are isogonal. It follows that <math>AF</math> is a symmedian of <math>\triangle{ABC}</math>, or that <math>ABFC</math> is harmonic. Then <math>(AB)(FC)=(BF)(CA)</math>, and thus we can let <math>BF=5x, CF=3x</math> for some <math>x</math>. By the LoC, it is easy to see <math>\angle{BAC}=120^\circ</math> so <math>(5x)^2+(3x)^2-2\cos{60^\circ}(5x)(3x)=49</math>. Solving gives <math>x^2=\frac{49}{19}</math>, from which by Ptolemy's we see <math>AF=\frac{30}{\sqrt{19}}</math>. We conclude the answer is <math>900+19=\boxed{919}</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''- Emathmaster''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Side Note: You might be wondering what the motivation for this solution is. Most of the people who've done EGMO Chapter 8 should recognize this as problem 8.32 (2009 Russian Olympiad) with the computational finish afterwards. | ||
| + | Now if you haven't done this, but still know what inversion is, here's the motivation. We'd see that it's kinda hard to angle chase, and if we could, it would still be a bit hard to apply (you could use trig, but it won't be so clean most likely). If you give up after realizing that angle chasing won't work, you'd likely go in a similar approach to Solution 1 (below) or maybe be a bit more insightful and go with the elementary solution above. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Finally, we notice there's circles! Classic setup for inversion! Since we're involving an angle-bisector, the first thing that comes to mind is a force overlaid inversion described in Lemma 8.16 of EGMO (where we invert with radius <math>\sqrt{AB \cdot AC}</math> and center <math>A</math>, then reflect over the <math>A</math>-angle bisector, which fixes <math>B, C</math>). We try applying this to the problem, and it's fruitful - we end up with this solution. | ||
| + | -MSC | ||
== Solution 1== | == Solution 1== | ||
| − | Use the angle bisector theorem to find <math>CD=21 | + | Use the angle bisector theorem to find <math>CD=\tfrac{21}{8}</math>, <math>BD=\tfrac{35}{8}</math>, and use Stewart's Theorem to find <math>AD=\tfrac{15}{8}</math>. Use Power of Point <math>D</math> to find <math>DE=\tfrac{49}{8}</math>, and so <math>AE=8</math>. Use law of cosines to find <math>\angle CAD = \tfrac{\pi} {3}</math>, hence <math>\angle BAD = \tfrac{\pi}{3}</math> as well, and <math>\triangle BCE</math> is equilateral, so <math>BC=CE=BE=7</math>. |
| + | <asy> | ||
| + | size(150); | ||
| + | defaultpen(fontsize(9pt)); | ||
| + | picture pic; | ||
| + | pair A,B,C,D,E,F,W; | ||
| + | B=MP("B",origin,dir(180)); C=MP("C",(7,0),dir(0)); A=MP("A",IP(CR(B,5),CR(C,3)),N); D=MP("D",extension(B,C,A,bisectorpoint(C,A,B)),dir(220)); path omega=circumcircle(A,B,C); E=MP("E",OP(omega,A--(A+20*(D-A))),S); path gamma=CR(midpoint(D--E),length(D-E)/2); F=MP("F",OP(omega,gamma),SE); | ||
| + | draw(omega^^A--B--C--cycle^^gamma); draw(pic, A--E--F--cycle, gray); add(pic); | ||
| + | dot("$W$",circumcenter(A,B,C),dir(180)); label("$\gamma$",gamma,dir(180)); | ||
| + | </asy> | ||
| + | In triangle <math>AEF</math>, let <math>X</math> be the foot of the altitude from <math>A</math>; then <math>EF=EX+XF</math>, where we use signed lengths. Writing <math>EX=AE \cdot \cos \angle AEF</math> and <math>XF=AF \cdot \cos \angle AFE</math>, we get | ||
| + | <cmath>\begin{align}\tag{1} | ||
| + | EF = AE \cdot \cos \angle AEF + AF \cdot \cos \angle AFE. | ||
| + | \end{align}</cmath> | ||
| + | Note <math>\angle AFE = \angle ACE</math>, and the Law of Cosines in <math>\triangle ACE</math> gives <math>\cos \angle ACE = -\tfrac 17</math>. | ||
| + | Also, <math>\angle AEF = \angle DEF</math>, and <math>\angle DFE = \tfrac{\pi}{2}</math> (<math>DE</math> is a diameter), so <math>\cos \angle AEF = \tfrac{EF}{DE} = \tfrac{8}{49}\cdot EF</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Plugging in all our values into equation <math>(1)</math>, we get: | ||
| + | <cmath>EF = \tfrac{64}{49} EF -\tfrac{1}{7} AF \quad \Longrightarrow \quad EF = \tfrac{7}{15} AF.</cmath> | ||
| + | The Law of Cosines in <math>\triangle AEF</math>, with <math>EF=\tfrac 7{15}AF</math> and <math>\cos\angle AFE = -\tfrac 17</math> gives | ||
| + | <cmath>8^2 = AF^2 + \tfrac{49}{225} AF^2 + \tfrac 2{15} AF^2 = \tfrac{225+49+30}{225}\cdot AF^2</cmath> | ||
| + | Thus <math>AF^2 = \frac{900}{19}</math>. The answer is <math>\boxed{919}</math>. | ||
| + | ~Shen Kislay Kai | ||
| − | + | == Solution 2== | |
| − | <math> | + | Let <math>a = BC</math>, <math>b = CA</math>, <math>c = AB</math> for convenience. Let <math>M</math> be the midpoint of segment <math>BC</math>. We claim that <math>\angle MAD=\angle DAF</math>. |
| − | <math> | + | <math>\textit{Proof}</math>. Since <math>AE</math> is the angle bisector, it follows that <math>EB = EC</math> and consequently <math>EM\perp BC</math>. Therefore, <math>M\in \gamma</math>. Now let <math>X = FD\cap \omega</math>. Since <math>\angle EFX=90^\circ</math>, <math>EX</math> is a diameter, so <math>X</math> lies on the perpendicular bisector of <math>BC</math>; hence <math>E</math>, <math>M</math>, <math>X</math> are collinear. From <math>\angle DAG = \angle DMX = 90^\circ</math>, quadrilateral <math>ADMX</math> is cyclic. Therefore, <math>\angle MAD = \angle MXD</math>. But <math>\angle MXD</math> and <math>\angle EAF</math> are both subtended by arc <math>EF</math> in <math>\omega</math>, so they are equal. Thus <math>\angle MAD=\angle DAF</math>, as claimed. |
| + | <asy> | ||
| + | size(175); | ||
| + | defaultpen(fontsize(10pt)); | ||
| + | picture pic; | ||
| + | pair A,B,C,D,E,F,W; | ||
| + | B=MP("B",origin,dir(180)); C=MP("C",(7,0),dir(0)); A=MP("A",IP(CR(B,5),CR(C,3)),N); D=MP("D",extension(B,C,A,bisectorpoint(C,A,B)),dir(220)); path omega=circumcircle(A,B,C); E=MP("E",OP(omega,A--(A+20*(D-A))),S); path gamma=CR(midpoint(D--E),length(D-E)/2); F=MP("F",OP(omega,gamma),SE); pair X=MP("X",IP(omega,F--(F+2*(D-F))),N); pair M=MP("M",midpoint(B--C),dir(220)); | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | draw(omega^^A--B--C--cycle^^gamma); draw(A--E--F--cycle, gray); draw(E--X--F, gray); draw(pic, A--M--C--cycle^^A--B--F--cycle); draw(A--M, royalblue); | |
| − | + | dot("$W$",circumcenter(A,B,C),dir(180)); dot(circumcenter(D,E,F)); label("$\gamma$",gamma,dir(180)); | |
| + | draw(A--B--F--cycle, black+1); | ||
| + | </asy> | ||
| + | As a result, <math>\angle CAM = \angle FAB</math>. Combined with <math>\angle BFA=\angle MCA</math>, we get <math>\triangle ABF\sim\triangle AMC</math> and therefore<cmath>\frac c{AM}=\frac {AF}b\qquad \Longrightarrow \qquad AF^2=\frac{b^2c^2}{AM^2} = \frac{15^2}{AM^2}</cmath> | ||
| + | By Stewart's Theorem on <math>\triangle ABC</math> (with cevian <math>AM</math>), we get <cmath>AM^2 = \tfrac 12 (b^2+c^2)-\tfrac 14 a^2 = \tfrac{19}{4},</cmath> so <math>AF^2 = \tfrac{900}{19}</math>, so the answer is <math>900+19=\boxed{919}</math>. | ||
| − | + | '''-Solution by thecmd999''' | |
| − | <math> | + | ==Solution 3== |
| + | Use the angle bisector theorem to find <math>CD=\tfrac{21}{8}</math>, <math>BD=\tfrac{35}{8}</math>, and use Stewart's Theorem to find <math>AD=\tfrac{15}{8}</math>. Use Power of Point <math>D</math> to find <math>DE=\tfrac{49}{8}</math>, and so <math>AE=8</math>. Then use the Extended Law of Sine to find that the length of the circumradius of <math>\triangle ABC</math> is <math>\tfrac{7\sqrt{3}}{3}</math>. | ||
| + | <asy> | ||
| + | size(175); | ||
| + | defaultpen(fontsize(9pt)); | ||
| + | pair A,B,C,D,E,F,W; | ||
| + | B=MP("B",origin,dir(180)); C=MP("C",(7,0),dir(0)); A=MP("A",IP(CR(B,5),CR(C,3)),N); D=MP("D",extension(B,C,A,bisectorpoint(C,A,B)),dir(220)); path omega=circumcircle(A,B,C); E=MP("E",OP(omega,A--(A+20*(D-A))),S); path gamma=CR(midpoint(D--E),length(D-E)/2); F=MP("F",OP(omega,gamma),SE); pair X=MP("X",IP(omega,F--(F+2*(D-F))),N); | ||
| − | + | draw(omega^^A--B--C--cycle^^gamma); draw(A--E--F--cycle, gray); draw(E--X--F, royalblue); | |
| − | <math> | + | dot("$W$",circumcenter(A,B,C),dir(180)); dot(circumcenter(D,E,F)); label("$\gamma$",gamma,dir(180)); label("$u$",X--D,dir(60)); label("$v$",D--F,dir(70)); |
| + | </asy> | ||
| + | Since <math>DE</math> is the diameter of circle <math>\gamma</math>, <math>\angle DFE</math> is <math>90^\circ</math>. Extending <math>DF</math> to intersect circle <math>\omega</math> at <math>X</math>, we find that <math>XE</math> is the diameter of <math>\omega</math> (since <math>\angle DFE</math> is <math>90^\circ</math>). Therefore, <math>XE=\tfrac{14\sqrt{3}}{3}</math>. | ||
| − | <math> | + | Let <math>EF=x</math>, <math>XD=u</math>, and <math>DF=v</math>. Then <math>XE^2-XF^2=EF^2=DE^2-DF^2</math>, so we get |
| + | <cmath>(u+v)^2-v^2=\frac{196}{3}-\frac{2401}{64}</cmath> | ||
| + | which simplifies to | ||
| + | <cmath>u^2+2uv = \frac{5341}{192}.</cmath> | ||
| + | By Power of Point <math>D</math>, <math>uv=BD \cdot DC=735/64</math>. Combining with above, we get | ||
| + | <cmath>XD^2=u^2=\frac{931}{192}.</cmath> | ||
| + | Note that <math>\triangle XDE\sim \triangle ADF</math> and the ratio of similarity is <math>\rho = AD : XD = \tfrac{15}{8}:u</math>. Then <math>AF=\rho\cdot XE = \tfrac{15}{8u}\cdot R</math> and <cmath>AF^2 = \frac{225}{64}\cdot \frac{R^2}{u^2} = \frac{900}{19}.</cmath> | ||
| + | The answer is <math>900+19=\boxed{919}</math>. | ||
| − | == Solution 2== | + | '''-Solution by TheBoomBox77''' |
| + | |||
| + | ==Solution 4== | ||
| + | Use Law of Cosines in <math>\triangle ABC</math> to get <math>\angle BAC=120^\circ</math>. Because <math>AE</math> bisects <math>\angle A</math>, <math>E</math> is the midpoint of major arc <math>BC</math> so <math>BE=CE,</math> and <math>\angle BEC=60^\circ.</math> Thus <math>\triangle BEC</math> is equilateral. Notice now that <math>\angle BFC=\angle BFE= 60^\circ.</math> But <math>\angle DFE=90^\circ</math> so <math>FD</math> bisects <math>\angle BFC.</math> Thus, <cmath>\frac{BF}{CF}=\frac{BD}{CD}=\frac{BA}{CA}=\frac{5}{3}.</cmath> | ||
| + | Let <math>BF=5k, CF=3k.</math> Use Law of Cosines on <math>\triangle BFC</math> to get<cmath>25k^2+9k^2-15k^2 = 49 \qquad \Longrightarrow\qquad k=\frac 7{\sqrt{19}}</cmath> Use Ptolemy's Theorem on <math>BFCA</math>, to get <cmath>15k+15k=7\cdot AF, \qquad \Longrightarrow\qquad AF= \frac{30}{\sqrt{19}},</cmath> so <math>AF^2=\frac{900}{19}</math> and the answer is <math>900+19=919</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ~Shen Kislay Kai | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Solution 5== | ||
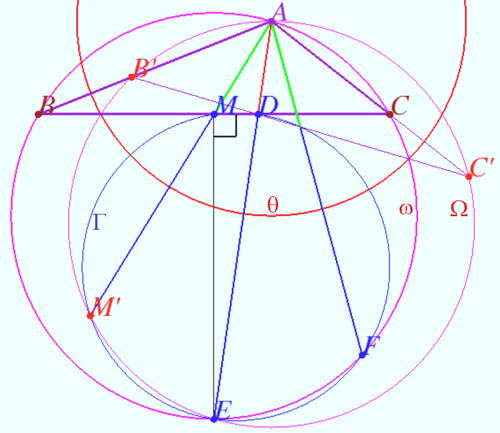
| + | [[File:2012 AIME II 15a.png|500px|right]] | ||
| + | Denote <math>AB = c, BC = a, AC = b, \angle A = 2 \alpha.</math> | ||
| + | Let M be midpoint BC. Let <math>\theta</math> be the circle centered at <math>A</math> with radius <math>\sqrt{AB \cdot AC} =\sqrt{bc}.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | We calculate the length of some segments. | ||
| + | The median <math>AM = \sqrt{\frac {b^2}{2} + \frac {c^2}{2} - \frac {a^2}{4}}.</math> | ||
| + | The bisector <math>AD = \frac {2 b c \cos \alpha}{b+c}.</math> One can use Stewart's Theorem in both cases. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>AD</math> is bisector of <math>\angle A \implies BD = \frac {a c}{b + c}, CD = \frac {a b}{b + c} \implies</math> | ||
| + | <cmath>BD \cdot CD = \frac {a^2 bc }{(b+c)^2}.</cmath> | ||
| + | We use Power of Point <math>D</math> and get <math>AD \cdot DE = BD \cdot CD. </math> | ||
| + | <cmath>AE = AD + DE = AD + \frac {BD \cdot CD}{AD},</cmath> | ||
| + | <cmath>AE =\frac {2 b c \cos \alpha}{b+c} + \frac {a^2 bc \cdot (b+c) }{(b+c)^2 \cdot 2 b c \cos \alpha} =</cmath> | ||
| + | <cmath>= \frac {b c \cos^2 \alpha + a^2}{2(b+c)\cos \alpha} =\frac {4bc \cos^2 \alpha + b^2 +c^2 -2 b c \cos 2\alpha}{2(b+c) \cos \alpha} = \frac {b+c}{2} \implies AD \cdot AE = 2 bc \cos \alpha.</cmath> | ||
| + | We consider the inversion with respect <math>\theta.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>B</math> swap <math>B' \implies AB' = AC, B' \in AB \implies B'</math> is symmetric to <math>C</math> with respect to <math>AE.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>C</math> swap <math>C' \implies AC' = AB, C'</math> lies on line <math>AC \implies C'</math> is symmetric to <math>B</math> with respect to <math>AE.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>BC^2 = AB^2 + AC^2 + AB \cdot BC \implies \alpha = 60^\circ \implies AD \cdot AE = bc \implies D</math> swap <math>E.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Points <math>D</math> and <math>E</math> lies on <math>\Gamma \implies \Gamma </math> swap <math>\Gamma.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>DE</math> is diameter <math>\Gamma, \angle DME = 90^\circ \implies M \in \Gamma.</math> Therefore <math>M</math> is crosspoint of <math>BC</math> and <math>\Gamma.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Let <math>\Omega</math> be circumcircle <math>AB'C'. \Omega</math> is image of line <math>BC.</math> | ||
| + | Point <math>M</math> maps into <math>M' \implies M' = \Gamma \cap \Omega.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Points <math>A, B',</math> and <math>C'</math> are symmetric to <math>A, C,</math> and <math>B,</math> respectively. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Point <math>M'</math> lies on <math>\Gamma</math> which is symmetric with respect to <math>AE</math> and on <math>\Omega</math> which is symmetric to <math>\omega</math> with respect to <math>AE \implies</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <i><b><math>M'</math> is symmetric <math>F</math> with respect to <math>AE \implies AM' = AF.</math></b></i> | ||
| + | |||
| + | We use Power of Point <math>A</math> and get | ||
| + | <cmath>AF = AM' = \frac {AD \cdot AE}{AM} = \frac {4b c}{\sqrt{2 b^2 + 2 c^2 – a^2}} = \frac {4 \cdot 3 \cdot 5}{\sqrt{ 50 + 18 – 49}} | ||
| + | = \frac {30}{\sqrt{19}} \implies \boxed{\textbf{919}}.</cmath> | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss''' | ||
| + | == Solution 6: == | ||
| + | To do this, we first define the intersection of <math>EF</math> and <math>BC</math> to be <math>K</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <b>Lemma 1:</b> <math>(K, C, D, B)</math> are harmonic. First of all, define the midpoint of <math>BC</math> to be <math>M</math>. Then, we have that angle FMD is <math>90</math> degrees, and as a result, <math>M</math> lies on this circle. By [[Power of a Point]], <math>(KD)(KM) = (KE)(KF) = (KB)(KC)</math>. As a result, <math>(K, C, D, B)</math> are harmonic from another famous harmonic lemma. | ||
| + | |||
| + | As a result, since <math>\angle EFD = 90^{\circ}</math>, by another Harmonic Lemma, <math>FD</math> is the angle bisector of <math>BFC</math>. Since <math>\frac{BD}{CD} = \frac{5}{3}</math> by [[angle bisector theorem]], <math>\frac{BF}{CF} = \frac{5}{3}</math>. Since <math>\angle BAC</math> is <math>120^{\circ}</math> by [[Law of Cosines]] (LOC), we can use LOC to finish off. Call <math>BF = 5a</math>, and <math>CF = 3a</math>, <math>(5a)^2+(3a)^2-15a^2 = 49</math>, so <math>a = \frac{7}{\sqrt{19}}</math>. We do [[Ptolemy's Theorem]] on <math>ABFC</math>. Our answer is: | ||
| + | <cmath>\frac{(3)(35)+(5)(21)}{7\sqrt{19}} = \frac{30}{\sqrt{19}}.</cmath> | ||
| + | As a result, the final answer is <math>\boxed{919}</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | -sepehr2010 | ||
| − | + | Minor edits ~[[Zhenghua]] | |
| − | + | ==Video Solution by mop 2024== | |
| + | https://youtu.be/mIFUuY4ybeg | ||
| − | + | ~r00tsOfUnity | |
== See Also == | == See Also == | ||
{{AIME box|year=2012|n=II|num-b=14|after=Last Problem}} | {{AIME box|year=2012|n=II|num-b=14|after=Last Problem}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Intermediate Geometry Problems]] | ||
{{MAA Notice}} | {{MAA Notice}} | ||
Latest revision as of 16:28, 17 September 2024
Contents
Problem 15
Triangle ![]() is inscribed in circle
is inscribed in circle ![]() with
with ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() . The bisector of angle
. The bisector of angle ![]() meets side
meets side ![]() at
at ![]() and circle
and circle ![]() at a second point
at a second point ![]() . Let
. Let ![]() be the circle with diameter
be the circle with diameter ![]() . Circles
. Circles ![]() and
and ![]() meet at
meet at ![]() and a second point
and a second point ![]() . Then
. Then ![]() , where
, where ![]() and
and ![]() are relatively prime positive integers. Find
are relatively prime positive integers. Find ![]() .
.
Quick Solution using Olympiad Terms
Take a force-overlaid inversion about ![]() and note
and note ![]() and
and ![]() map to each other. As
map to each other. As ![]() was originally the diameter of
was originally the diameter of ![]() ,
, ![]() is still the diameter of
is still the diameter of ![]() . Thus
. Thus ![]() is preserved. Note that the midpoint
is preserved. Note that the midpoint ![]() of
of ![]() lies on
lies on ![]() , and
, and ![]() and
and ![]() are swapped. Thus points
are swapped. Thus points ![]() and
and ![]() map to each other, and are isogonal. It follows that
map to each other, and are isogonal. It follows that ![]() is a symmedian of
is a symmedian of ![]() , or that
, or that ![]() is harmonic. Then
is harmonic. Then ![]() , and thus we can let
, and thus we can let ![]() for some
for some ![]() . By the LoC, it is easy to see
. By the LoC, it is easy to see ![]() so
so ![]() . Solving gives
. Solving gives ![]() , from which by Ptolemy's we see
, from which by Ptolemy's we see ![]() . We conclude the answer is
. We conclude the answer is ![]() .
.
- Emathmaster
Side Note: You might be wondering what the motivation for this solution is. Most of the people who've done EGMO Chapter 8 should recognize this as problem 8.32 (2009 Russian Olympiad) with the computational finish afterwards. Now if you haven't done this, but still know what inversion is, here's the motivation. We'd see that it's kinda hard to angle chase, and if we could, it would still be a bit hard to apply (you could use trig, but it won't be so clean most likely). If you give up after realizing that angle chasing won't work, you'd likely go in a similar approach to Solution 1 (below) or maybe be a bit more insightful and go with the elementary solution above.
Finally, we notice there's circles! Classic setup for inversion! Since we're involving an angle-bisector, the first thing that comes to mind is a force overlaid inversion described in Lemma 8.16 of EGMO (where we invert with radius ![]() and center
and center ![]() , then reflect over the
, then reflect over the ![]() -angle bisector, which fixes
-angle bisector, which fixes ![]() ). We try applying this to the problem, and it's fruitful - we end up with this solution.
-MSC
). We try applying this to the problem, and it's fruitful - we end up with this solution.
-MSC
Solution 1
Use the angle bisector theorem to find ![]() ,
, ![]() , and use Stewart's Theorem to find
, and use Stewart's Theorem to find ![]() . Use Power of Point
. Use Power of Point ![]() to find
to find ![]() , and so
, and so ![]() . Use law of cosines to find
. Use law of cosines to find ![]() , hence
, hence ![]() as well, and
as well, and ![]() is equilateral, so
is equilateral, so ![]() .
.
![[asy] size(150); defaultpen(fontsize(9pt)); picture pic; pair A,B,C,D,E,F,W; B=MP("B",origin,dir(180)); C=MP("C",(7,0),dir(0)); A=MP("A",IP(CR(B,5),CR(C,3)),N); D=MP("D",extension(B,C,A,bisectorpoint(C,A,B)),dir(220)); path omega=circumcircle(A,B,C); E=MP("E",OP(omega,A--(A+20*(D-A))),S); path gamma=CR(midpoint(D--E),length(D-E)/2); F=MP("F",OP(omega,gamma),SE); draw(omega^^A--B--C--cycle^^gamma); draw(pic, A--E--F--cycle, gray); add(pic); dot("$W$",circumcenter(A,B,C),dir(180)); label("$\gamma$",gamma,dir(180)); [/asy]](http://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/e/f/9/ef948e37e744fe519e4f88abc5dd4a4d8ff9f957.png) In triangle
In triangle ![]() , let
, let ![]() be the foot of the altitude from
be the foot of the altitude from ![]() ; then
; then ![]() , where we use signed lengths. Writing
, where we use signed lengths. Writing ![]() and
and ![]() , we get
, we get
![]() Note
Note ![]() , and the Law of Cosines in
, and the Law of Cosines in ![]() gives
gives ![]() .
Also,
.
Also, ![]() , and
, and ![]() (
(![]() is a diameter), so
is a diameter), so ![]() .
.
Plugging in all our values into equation ![]() , we get:
, we get:
![]() The Law of Cosines in
The Law of Cosines in ![]() , with
, with ![]() and
and ![]() gives
gives
![]() Thus
Thus ![]() . The answer is
. The answer is ![]() .
~Shen Kislay Kai
.
~Shen Kislay Kai
Solution 2
Let ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() for convenience. Let
for convenience. Let ![]() be the midpoint of segment
be the midpoint of segment ![]() . We claim that
. We claim that ![]() .
.
![]() . Since
. Since ![]() is the angle bisector, it follows that
is the angle bisector, it follows that ![]() and consequently
and consequently ![]() . Therefore,
. Therefore, ![]() . Now let
. Now let ![]() . Since
. Since ![]() ,
, ![]() is a diameter, so
is a diameter, so ![]() lies on the perpendicular bisector of
lies on the perpendicular bisector of ![]() ; hence
; hence ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() are collinear. From
are collinear. From ![]() , quadrilateral
, quadrilateral ![]() is cyclic. Therefore,
is cyclic. Therefore, ![]() . But
. But ![]() and
and ![]() are both subtended by arc
are both subtended by arc ![]() in
in ![]() , so they are equal. Thus
, so they are equal. Thus ![]() , as claimed.
, as claimed.
![[asy] size(175); defaultpen(fontsize(10pt)); picture pic; pair A,B,C,D,E,F,W; B=MP("B",origin,dir(180)); C=MP("C",(7,0),dir(0)); A=MP("A",IP(CR(B,5),CR(C,3)),N); D=MP("D",extension(B,C,A,bisectorpoint(C,A,B)),dir(220)); path omega=circumcircle(A,B,C); E=MP("E",OP(omega,A--(A+20*(D-A))),S); path gamma=CR(midpoint(D--E),length(D-E)/2); F=MP("F",OP(omega,gamma),SE); pair X=MP("X",IP(omega,F--(F+2*(D-F))),N); pair M=MP("M",midpoint(B--C),dir(220)); draw(omega^^A--B--C--cycle^^gamma); draw(A--E--F--cycle, gray); draw(E--X--F, gray); draw(pic, A--M--C--cycle^^A--B--F--cycle); draw(A--M, royalblue); dot("$W$",circumcenter(A,B,C),dir(180)); dot(circumcenter(D,E,F)); label("$\gamma$",gamma,dir(180)); draw(A--B--F--cycle, black+1); [/asy]](http://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/1/c/3/1c39c1cc48bbc0924afd6a695e6df968a3000320.png) As a result,
As a result, ![]() . Combined with
. Combined with ![]() , we get
, we get ![]() and therefore
and therefore![]() By Stewart's Theorem on
By Stewart's Theorem on ![]() (with cevian
(with cevian ![]() ), we get
), we get ![]() so
so ![]() , so the answer is
, so the answer is ![]() .
.
-Solution by thecmd999
Solution 3
Use the angle bisector theorem to find ![]() ,
, ![]() , and use Stewart's Theorem to find
, and use Stewart's Theorem to find ![]() . Use Power of Point
. Use Power of Point ![]() to find
to find ![]() , and so
, and so ![]() . Then use the Extended Law of Sine to find that the length of the circumradius of
. Then use the Extended Law of Sine to find that the length of the circumradius of ![]() is
is ![]() .
.
![[asy] size(175); defaultpen(fontsize(9pt)); pair A,B,C,D,E,F,W; B=MP("B",origin,dir(180)); C=MP("C",(7,0),dir(0)); A=MP("A",IP(CR(B,5),CR(C,3)),N); D=MP("D",extension(B,C,A,bisectorpoint(C,A,B)),dir(220)); path omega=circumcircle(A,B,C); E=MP("E",OP(omega,A--(A+20*(D-A))),S); path gamma=CR(midpoint(D--E),length(D-E)/2); F=MP("F",OP(omega,gamma),SE); pair X=MP("X",IP(omega,F--(F+2*(D-F))),N); draw(omega^^A--B--C--cycle^^gamma); draw(A--E--F--cycle, gray); draw(E--X--F, royalblue); dot("$W$",circumcenter(A,B,C),dir(180)); dot(circumcenter(D,E,F)); label("$\gamma$",gamma,dir(180)); label("$u$",X--D,dir(60)); label("$v$",D--F,dir(70)); [/asy]](http://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/9/1/3/9138b42f66ef6363e93d57d59a66c546dea1c214.png) Since
Since ![]() is the diameter of circle
is the diameter of circle ![]() ,
, ![]() is
is ![]() . Extending
. Extending ![]() to intersect circle
to intersect circle ![]() at
at ![]() , we find that
, we find that ![]() is the diameter of
is the diameter of ![]() (since
(since ![]() is
is ![]() ). Therefore,
). Therefore, ![]() .
.
Let ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() . Then
. Then ![]() , so we get
, so we get
![]() which simplifies to
which simplifies to
![]() By Power of Point
By Power of Point ![]() ,
, ![]() . Combining with above, we get
. Combining with above, we get
![]() Note that
Note that ![]() and the ratio of similarity is
and the ratio of similarity is ![]() . Then
. Then ![]() and
and ![]() The answer is
The answer is ![]() .
.
-Solution by TheBoomBox77
Solution 4
Use Law of Cosines in ![]() to get
to get ![]() . Because
. Because ![]() bisects
bisects ![]() ,
, ![]() is the midpoint of major arc
is the midpoint of major arc ![]() so
so ![]() and
and ![]() Thus
Thus ![]() is equilateral. Notice now that
is equilateral. Notice now that ![]() But
But ![]() so
so ![]() bisects
bisects ![]() Thus,
Thus, ![]() Let
Let ![]() Use Law of Cosines on
Use Law of Cosines on ![]() to get
to get![]() Use Ptolemy's Theorem on
Use Ptolemy's Theorem on ![]() , to get
, to get ![]() so
so ![]() and the answer is
and the answer is ![]()
~Shen Kislay Kai
Solution 5
Denote ![]() Let M be midpoint BC. Let
Let M be midpoint BC. Let ![]() be the circle centered at
be the circle centered at ![]() with radius
with radius ![]()
We calculate the length of some segments.
The median ![]() The bisector
The bisector ![]() One can use Stewart's Theorem in both cases.
One can use Stewart's Theorem in both cases.
![]() is bisector of
is bisector of ![]()
![]() We use Power of Point
We use Power of Point ![]() and get
and get ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() We consider the inversion with respect
We consider the inversion with respect ![]()
![]() swap
swap ![]() is symmetric to
is symmetric to ![]() with respect to
with respect to ![]()
![]() swap
swap ![]() lies on line
lies on line ![]() is symmetric to
is symmetric to ![]() with respect to
with respect to ![]()
![]() swap
swap ![]()
Points ![]() and
and ![]() lies on
lies on ![]() swap
swap ![]()
![]() is diameter
is diameter ![]() Therefore
Therefore ![]() is crosspoint of
is crosspoint of ![]() and
and ![]()
Let ![]() be circumcircle
be circumcircle ![]() is image of line
is image of line ![]() Point
Point ![]() maps into
maps into ![]()
Points ![]() and
and ![]() are symmetric to
are symmetric to ![]() and
and ![]() respectively.
respectively.
Point ![]() lies on
lies on ![]() which is symmetric with respect to
which is symmetric with respect to ![]() and on
and on ![]() which is symmetric to
which is symmetric to ![]() with respect to
with respect to ![]()
![]() is symmetric
is symmetric ![]() with respect to
with respect to ![]()
We use Power of Point ![]() and get
and get
![]()
vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss
Solution 6:
To do this, we first define the intersection of ![]() and
and ![]() to be
to be ![]() .
.
Lemma 1: ![]() are harmonic. First of all, define the midpoint of
are harmonic. First of all, define the midpoint of ![]() to be
to be ![]() . Then, we have that angle FMD is
. Then, we have that angle FMD is ![]() degrees, and as a result,
degrees, and as a result, ![]() lies on this circle. By Power of a Point,
lies on this circle. By Power of a Point, ![]() . As a result,
. As a result, ![]() are harmonic from another famous harmonic lemma.
are harmonic from another famous harmonic lemma.
As a result, since ![]() , by another Harmonic Lemma,
, by another Harmonic Lemma, ![]() is the angle bisector of
is the angle bisector of ![]() . Since
. Since ![]() by angle bisector theorem,
by angle bisector theorem, ![]() . Since
. Since ![]() is
is ![]() by Law of Cosines (LOC), we can use LOC to finish off. Call
by Law of Cosines (LOC), we can use LOC to finish off. Call ![]() , and
, and ![]() ,
, ![]() , so
, so ![]() . We do Ptolemy's Theorem on
. We do Ptolemy's Theorem on ![]() . Our answer is:
. Our answer is:
![]() As a result, the final answer is
As a result, the final answer is ![]() .
.
-sepehr2010
Minor edits ~Zhenghua
Video Solution by mop 2024
~r00tsOfUnity
See Also
| 2012 AIME II (Problems • Answer Key • Resources) | ||
| Preceded by Problem 14 |
Followed by Last Problem | |
| 1 • 2 • 3 • 4 • 5 • 6 • 7 • 8 • 9 • 10 • 11 • 12 • 13 • 14 • 15 | ||
| All AIME Problems and Solutions | ||
The problems on this page are copyrighted by the Mathematical Association of America's American Mathematics Competitions.