Difference between revisions of "2005 AMC 10A Problems/Problem 17"
Rachanamadhu (talk | contribs) (→See Also) |
(→See Also) |
||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
| − | {{AMC10 box|year=2005|ab=A|num-b= | + | {{AMC10 box|year=2005|ab=A|num-b=16|num-a=18}} |
[[Category:Introductory Geometry Problems]] | [[Category:Introductory Geometry Problems]] | ||
[[Category:Area Ratio Problems]] | [[Category:Area Ratio Problems]] | ||
{{MAA Notice}} | {{MAA Notice}} | ||
Revision as of 11:50, 26 November 2015
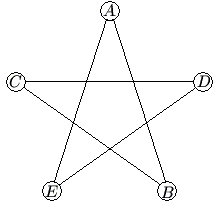
Problem
In the five-sided star shown, the letters ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() are replaced by the numbers
are replaced by the numbers ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() , although not necessarily in this order. The sums of the numbers at the ends of the line segments
, although not necessarily in this order. The sums of the numbers at the ends of the line segments ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() form an arithmetic sequence, although not necessarily in this order. What is the middle term of the sequence?
form an arithmetic sequence, although not necessarily in this order. What is the middle term of the sequence?
![]()
Solution
Each corner (a,b,c,d,e) goes to two sides/numbers. (A goes to AE and AB, D goes to DC and DE). The sum of every term is equal to ![]()
Since the middle term in an arithmetic sequence is the average of all the terms in the sequence, the middle number is ![]()
See Also
| 2005 AMC 10A (Problems • Answer Key • Resources) | ||
| Preceded by Problem 16 |
Followed by Problem 18 | |
| 1 • 2 • 3 • 4 • 5 • 6 • 7 • 8 • 9 • 10 • 11 • 12 • 13 • 14 • 15 • 16 • 17 • 18 • 19 • 20 • 21 • 22 • 23 • 24 • 25 | ||
| All AMC 10 Problems and Solutions | ||
The problems on this page are copyrighted by the Mathematical Association of America's American Mathematics Competitions. ![]()