Difference between revisions of "2022 AIME II Problems/Problem 11"
(→Solution 2) |
(→Solution 3 (Visual)) |
||
| Line 88: | Line 88: | ||
==Solution 3 (Visual)== | ==Solution 3 (Visual)== | ||
| − | + | [[File:AIME 2022 11a.png|300px|right]] | |
<b><i>Lemma</b></i> | <b><i>Lemma</b></i> | ||
| Line 94: | Line 94: | ||
<b><i> Proof</b></i> | <b><i> Proof</b></i> | ||
| + | |||
Let <math>A = 2\alpha.</math> Then <math>\angle DBC = \angle DCB = \alpha.</math> | Let <math>A = 2\alpha.</math> Then <math>\angle DBC = \angle DCB = \alpha.</math> | ||
| − | Let <math>E</math> be the intersection point of the perpendicular dropped from <math>D</math> to <math>AB</ | + | Let <math>E</math> be the intersection point of the perpendicular dropped from <math>D</math> to <math>AB</math> with the circle. |
| − | Then the sum of arcs < | + | |
| − | Let < | + | Then the sum of arcs <math>\overset{\Large\frown} {BE} + \overset{\Large\frown}{AC} + \overset{\Large\frown}{CD} = \pi.</math> |
| + | <cmath>\overset{\Large\frown} {BE} = \pi – 2\alpha – \overset{\Large\frown}{AC}.</cmath> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Let <math>E'</math> be the point of intersection of the line <math>CM</math> with the circle. | ||
| + | <math>CM</math> is perpendicular to <math>AD, \angle AMC = \frac {\pi}{2} – \alpha,</math> the sum of arcs <math>\overset{\Large\frown}{A}C + \overset{\Large\frown}{BE'} = \pi – 2\alpha,</math> hence <math>E'</math> coincides with <math>E.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | The inscribed angles <math>\angle DEM = \angle DEB, M</math> is symmetric to <math>B</math> with respect to <math>DE, DM = DB.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <b><i> Solution</b></i> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Let <math>AB' = AB, DC' = DC, B'</math> and <math>C'</math> on <math>AD.</math> | ||
| + | Then <math>AB' = 2, DC' = 3, B'C' = 2 = AB'.</math> | ||
| + | Quadrilateral <math>ABMC'</math> is inscribed. | ||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
{{AIME box|year=2022|n=II|num-b=10|num-a=12}} | {{AIME box|year=2022|n=II|num-b=10|num-a=12}} | ||
{{MAA Notice}} | {{MAA Notice}} | ||
Revision as of 14:34, 1 June 2022
Problem
Let ![]() be a convex quadrilateral with
be a convex quadrilateral with ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() such that the bisectors of acute angles
such that the bisectors of acute angles ![]() and
and ![]() intersect at the midpoint of
intersect at the midpoint of ![]() . Find the square of the area of
. Find the square of the area of ![]() .
.
Solution 1
According to the problem, we have ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]()
Because ![]() is the midpoint of
is the midpoint of ![]() , we have
, we have ![]() , so:
, so: ![]()
Then, we can see that ![]() is an isosceles triangle with
is an isosceles triangle with ![]()
Therefore, we could start our angle chasing: ![]() .
.
This is when we found that points ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() are on a circle. Thus,
are on a circle. Thus, ![]() . This is the time we found that
. This is the time we found that ![]() .
.
Thus, ![]()
Point ![]() is the midpoint of
is the midpoint of ![]() , and
, and ![]() .
. ![]() .
.
The area of this quadrilateral is the sum of areas of triangles: ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Finally, the square of the area is ![]()
~DSAERF-CALMIT (https://binaryphi.site)
Solution 2
Denote by ![]() the midpoint of segment
the midpoint of segment ![]() .
Let points
.
Let points ![]() and
and ![]() be on segment
be on segment ![]() , such that
, such that ![]() and
and ![]() .
.
Denote ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() .
.
Denote ![]() . Because
. Because ![]() is the midpoint of
is the midpoint of ![]() ,
, ![]() .
.
Because ![]() is the angle bisector of
is the angle bisector of ![]() and
and ![]() ,
, ![]() .
Hence,
.
Hence, ![]() and
and ![]() .
Hence,
.
Hence, ![]() .
.
Because ![]() is the angle bisector of
is the angle bisector of ![]() and
and ![]() ,
, ![]() .
Hence,
.
Hence, ![]() and
and ![]() .
Hence,
.
Hence, ![]() .
.
Because ![]() is the midpoint of segment
is the midpoint of segment ![]() ,
, ![]() .
Because
.
Because ![]() and
and ![]() ,
, ![]() .
.
Thus, ![]() .
.
Thus,
![]()
In ![]() ,
, ![]() .
In addition,
.
In addition, ![]() .
Thus,
.
Thus,
![]()
Taking ![]() , we get
, we get ![]() .
Taking
.
Taking ![]() , we get
, we get ![]() .
.
Therefore, ![]() .
.
Hence, ![]() and
and ![]() .
Thus,
.
Thus, ![]() and
and ![]() .
.
In ![]() , by applying the law of cosines,
, by applying the law of cosines, ![]() .
Hence,
.
Hence, ![]() .
Hence,
.
Hence, ![]() .
.
Therefore,

Therefore, the square of ![]() is
is ![]() .
.
~Steven Chen (www.professorchenedu.com)
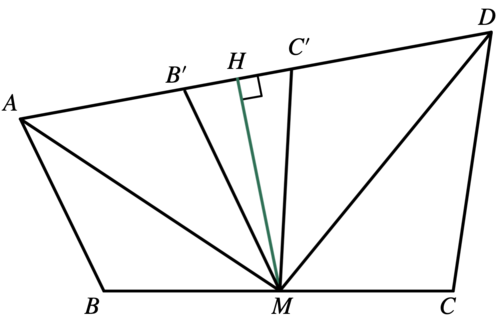
Solution 3 (Visual)
Lemma
In the triangle ![]() is the midpoint of
is the midpoint of ![]() is the point of intersection of the circumscribed circle and the bisector of angle
is the point of intersection of the circumscribed circle and the bisector of angle ![]() Then
Then ![]()
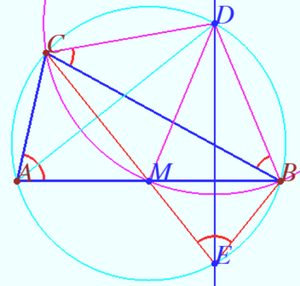
Proof
Let ![]() Then
Then ![]()
Let ![]() be the intersection point of the perpendicular dropped from
be the intersection point of the perpendicular dropped from ![]() to
to ![]() with the circle.
with the circle.
Then the sum of arcs ![]()
![]()
Let ![]() be the point of intersection of the line
be the point of intersection of the line ![]() with the circle.
with the circle.
![]() is perpendicular to
is perpendicular to ![]() the sum of arcs
the sum of arcs ![]() hence
hence ![]() coincides with
coincides with ![]()
The inscribed angles ![]() is symmetric to
is symmetric to ![]() with respect to
with respect to ![]()
Solution
Let ![]() and
and ![]() on
on ![]() Then
Then ![]()
Quadrilateral ![]() is inscribed.
is inscribed.
See Also
| 2022 AIME II (Problems • Answer Key • Resources) | ||
| Preceded by Problem 10 |
Followed by Problem 12 | |
| 1 • 2 • 3 • 4 • 5 • 6 • 7 • 8 • 9 • 10 • 11 • 12 • 13 • 14 • 15 | ||
| All AIME Problems and Solutions | ||
The problems on this page are copyrighted by the Mathematical Association of America's American Mathematics Competitions.