Difference between revisions of "2012 AMC 8 Problems/Problem 5"
Adithyau89 (talk | contribs) (→Solution) |
|||
| Line 43: | Line 43: | ||
<math> \textbf{(A)}\hspace{.05in}1\qquad\textbf{(B)}\hspace{.05in}2\qquad\textbf{(C)}\hspace{.05in}3\qquad\textbf{(D)}\hspace{.05in}4\qquad\textbf{(E)}\hspace{.05in}5 </math> | <math> \textbf{(A)}\hspace{.05in}1\qquad\textbf{(B)}\hspace{.05in}2\qquad\textbf{(C)}\hspace{.05in}3\qquad\textbf{(D)}\hspace{.05in}4\qquad\textbf{(E)}\hspace{.05in}5 </math> | ||
| − | ==Solution== | + | ==Solution 1== |
[[File:2012amc85.png]] | [[File:2012amc85.png]] | ||
| Line 52: | Line 52: | ||
Thus, the answer is <math> \boxed{\textbf{(E)}\ 5} </math>. | Thus, the answer is <math> \boxed{\textbf{(E)}\ 5} </math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Solution 2== | ||
| + | [[File:bcd57a9d78159bce4d3873f81f5d879beaed1d5a.png|300px|center]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Note that we only need to consider the value below the marked red line, so we have equation: | ||
| + | <cmath> X + 2 = 6 + 1 </cmath> | ||
| + | <cmath> X = </cmath> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Hence, the answer is <math> \boxed{\textbf{(E)}\ 5} </math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ~[[User:Bloggish|Bloggish]] | ||
==Video Solution== | ==Video Solution== | ||
Revision as of 20:10, 29 January 2023
Contents
[hide]Problem
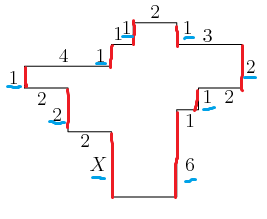
In the diagram, all angles are right angles and the lengths of the sides are given in centimeters. Note the diagram is not drawn to scale. What is , ![]() in centimeters?
in centimeters?
![[asy] pair A,B,C,D,E,F,G,H,I,J,K,L,M,N,O,P,Q,R; A=(4,0); B=(7,0); C=(7,4); D=(8,4); E=(8,5); F=(10,5); G=(10,7); H=(7,7); I=(7,8); J=(5,8); K=(5,7); L=(4,7); M=(4,6); N=(0,6); O=(0,5); P=(2,5); Q=(2,3); R=(4,3); draw(A--B--C--D--E--F--G--H--I--J--K--L--M--N--O--P--Q--R--cycle); label("$X$",(3.4,1.5)); label("6",(7.6,1.5)); label("1",(7.6,3.5)); label("1",(8.4,4.6)); label("2",(9.4,4.6)); label("2",(10.4,6)); label("3",(8.4,7.4)); label("1",(7.5,7.8)); label("2",(6,8.5)); label("1",(4.7,7.8)); label("1",(4.3,7.5)); label("1",(3.5,6.5)); label("4",(1.8,6.5)); label("1",(-0.5,5.5)); label("2",(0.8,4.5)); label("2",(1.5,3.8)); label("2",(2.8,2.6));[/asy]](http://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/b/c/d/bcd57a9d78159bce4d3873f81f5d879beaed1d5a.png)
![]()
Solution 1

Thus, the answer is ![]() .
.
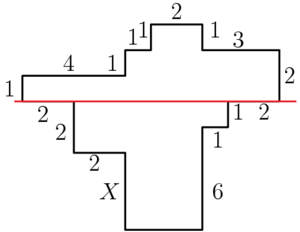
Solution 2
Note that we only need to consider the value below the marked red line, so we have equation:
![]()
![]()
Hence, the answer is ![]() .
.
Video Solution
https://youtu.be/m4g-Nmot-c8 ~savannahsolver
See Also
| 2012 AMC 8 (Problems • Answer Key • Resources) | ||
| Preceded by Problem 4 |
Followed by Problem 6 | |
| 1 • 2 • 3 • 4 • 5 • 6 • 7 • 8 • 9 • 10 • 11 • 12 • 13 • 14 • 15 • 16 • 17 • 18 • 19 • 20 • 21 • 22 • 23 • 24 • 25 | ||
| All AJHSME/AMC 8 Problems and Solutions | ||
The problems on this page are copyrighted by the Mathematical Association of America's American Mathematics Competitions. ![]()