Difference between revisions of "2024 AMC 10A Problems"
(→Problem 24) |
MRENTHUSIASM (talk | contribs) (→Problem 20) |
||
| (132 intermediate revisions by 39 users not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
==Problem 1== | ==Problem 1== | ||
| − | + | What is the value of <math>9901\cdot101-99\cdot10101?</math> | |
| − | <math> \textbf{(A)} | + | <math>\textbf{(A)}~2\qquad\textbf{(B)}~20\qquad\textbf{(C)}~200\qquad\textbf{(D)}~202\qquad\textbf{(E)}~2020</math> |
| + | |||
| + | [[2024 AMC 10A Problems/Problem 1|Solution]] | ||
==Problem 2== | ==Problem 2== | ||
| − | + | A model used to estimate the time it will take to hike to the top of the mountain on a trail is of the form <math>T=aL+bG,</math> where <math>a</math> and <math>b</math> are constants, <math>T</math> is the time in minutes, <math>L</math> is the length of the trail in miles, and <math>G</math> is the altitude gain in feet. The model estimates that it will take <math>69</math> minutes to hike to the top if a trail is <math>1.5</math> miles long and ascends <math>800</math> feet, as well as if a trail is <math>1.2</math> miles long and ascends <math>1100</math> feet. How many minutes does the model estimates it will take to hike to the top if the trail is <math>4.2</math> miles long and ascends <math>4000</math> feet? | |
| + | |||
| + | <math>\textbf{(A) }240\qquad\textbf{(B) }246\qquad\textbf{(C) }252\qquad\textbf{(D) }258\qquad\textbf{(E) }264</math> | ||
| − | + | [[2024 AMC 10A Problems/Problem 2|Solution]] | |
==Problem 3== | ==Problem 3== | ||
| − | |||
| − | <math>\textbf{(A)} | + | What is the sum of the digits of the smallest prime that can be written as a sum of <math>5</math> distinct primes? |
| + | |||
| + | <math>\textbf{(A) }5\qquad\textbf{(B) }7\qquad\textbf{(C) }8\qquad\textbf{(D) }10\qquad\textbf{(E) }13</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[2024 AMC 10A Problems/Problem 3|Solution]] | ||
==Problem 4== | ==Problem 4== | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | The number <math>2024</math> is written as the sum of not necessarily distinct two-digit numbers. What is the least number of two-digit numbers needed to write this sum? | |
| − | <math>\textbf{(A)} | + | |
| − | \textbf{(B)} | + | <math>\textbf{(A) }20\qquad\textbf{(B) }21\qquad\textbf{(C) }22\qquad\textbf{(D) }23\qquad\textbf{(E) }24</math> |
| − | \textbf{(C)} | + | |
| − | \textbf{(D)} | + | [[2024 AMC 10A Problems/Problem 4|Solution]] |
| − | \textbf{(E)} | ||
==Problem 5== | ==Problem 5== | ||
| − | |||
| − | <math>\textbf{(A) } | + | What is the least value of <math>n</math> such that <math>n!</math> is a multiple of <math>2024</math>? |
| − | \textbf{(B) } | + | |
| − | \textbf{(C) } | + | <math>\textbf{(A) } 11\qquad\textbf{(B) } 21\qquad\textbf{(C) } 22\qquad\textbf{(D) } 23\qquad\textbf{(E) } 253</math> |
| − | \textbf{(D) } | + | |
| − | \textbf{(E) } | + | [[2024 AMC 10A Problems/Problem 5|Solution]] |
==Problem 6== | ==Problem 6== | ||
| − | + | What is the minimum number of successive swaps of adjacent letters in the string <math>ABCDEF</math> that are needed to change the string to <math>FEDCBA?</math> (For example, <math>3</math> swaps are required to change <math>ABC</math> to <math>CBA;</math> one such sequence of swaps is | |
| + | <math>ABC\to BAC\to BCA\to CBA.</math>) | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\textbf{(A)}~6\qquad\textbf{(B)}~10\qquad\textbf{(C)}~12\qquad\textbf{(D)}~15\qquad\textbf{(E)}~24</math> | ||
| − | + | [[2024 AMC 10A Problems/Problem 6|Solution]] | |
==Problem 7== | ==Problem 7== | ||
| − | + | The product of three integers is <math>60</math>. What is the least possible positive sum of the | |
| + | three integers? | ||
| − | <math> | + | <math>\textbf{(A) }2\qquad\textbf{(B) }3\qquad\textbf{(C) }5\qquad\textbf{(D) }6\qquad\textbf{(E) }13</math> |
| − | \textbf{(A) } | + | |
| − | \textbf{(B) } | + | [[2024 AMC 10A Problems/Problem 7|Solution]] |
| − | \textbf{(C) } | ||
| − | \textbf{(D) } | ||
| − | \textbf{(E) } | ||
| − | </math> | ||
==Problem 8== | ==Problem 8== | ||
| − | On | + | Amy, Bomani, Charlie, and Daria work in a chocolate factory. On Monday Amy, Bomani, and Charlie started working at <math>1:00 PM</math> and were able to pack <math>4</math>, <math>3</math>, and <math>3</math> packages, respectively, every <math>3</math> minutes. At some later time, Daria joined the group, and Daria was able to pack <math>5</math> packages every <math>4</math> minutes. Together, they finished packing <math>450</math> packages at exactly <math>2:45 PM</math>. At what time did Daria join the group? |
| − | <math> \textbf{(A)}\ | + | <math>\textbf{(A) }1:25\text{ PM}\qquad\textbf{(B) }1:35\text{ PM}\qquad\textbf{(C) }1:45\text{ PM}\qquad\textbf{(D) }1:55\text{ PM}\qquad\textbf{(E) }2:05\text{ PM}</math> |
| + | |||
| + | [[2024 AMC 10A Problems/Problem 8|Solution]] | ||
==Problem 9== | ==Problem 9== | ||
| − | In | + | In how many ways can <math>6</math> juniors and <math>6</math> seniors form <math>3</math> disjoint teams of <math>4</math> people so |
| + | that each team has <math>2</math> juniors and <math>2</math> seniors? | ||
| − | < | + | <math>\textbf{(A) }720\qquad\textbf{(B) }1350\qquad\textbf{(C) }2700\qquad\textbf{(D) }3280\qquad\textbf{(E) }8100</math> |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | } | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | } | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | } | ||
| − | </ | ||
| − | + | [[2024 AMC 10A Problems/Problem 9|Solution]] | |
==Problem 10== | ==Problem 10== | ||
| − | |||
| − | <math>\ | + | Consider the following operation. Given a positive integer <math>n</math>, if <math>n</math> is a multiple of <math>3</math>, then you replace <math>n</math> by <math>\frac{n}{3}</math>. If <math>n</math> is not a multiple of <math>3</math>, then you replace <math>n</math> by <math>n+10</math>. For example, beginning with <math>n=4</math>, this procedure gives <math>4\to14\to24\to8\to18\to6\to2\to12\to\cdots</math>. Suppose you start with <math>n=100</math>. What value results if you perform this operation exactly <math>100</math> times? |
| + | |||
| + | <math>\textbf{(A) }10\qquad\textbf{(B) }20\qquad\textbf{(C) }30\qquad\textbf{(D) }40\qquad\textbf{(E) }50</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[2024 AMC 10A Problems/Problem 10|Solution]] | ||
==Problem 11== | ==Problem 11== | ||
| − | |||
| − | <math>\textbf{(A)} | + | How many ordered pairs of integers <math>(m, n)</math> satisfy <math>\sqrt{n^2 - 49} = m</math>? |
| + | |||
| + | <math>\textbf{(A)}~1\qquad\textbf{(B)}~2\qquad\textbf{(C)}~3\qquad\textbf{(D)}~4\qquad\textbf{(E)}</math> Infinitely many | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[2024 AMC 10A Problems/Problem 11|Solution]] | ||
==Problem 12== | ==Problem 12== | ||
| − | + | Zelda played the ''Adventures of Math'' game on August 1 and scored <math>1,700</math> points. She continued to play daily over the next <math>5</math> days. The bar chart below shows the daily change in her score compared to the day before. (For example, Zelda's score on August 2 was <math>1,700 + 80 = 1,780</math> points.) What was Zelda's average score in points over the <math>6</math> days?[[File:Screenshot_2024-11-08_1.51.51_PM.png]] | |
| − | <math>\textbf{(A)} | + | <math>\textbf{(A)}~1700\qquad\textbf{(B)}~1702\qquad\textbf{(C)}~1703\qquad\textbf{(D)}~1713\qquad\textbf{(E)}~1715</math> |
| + | |||
| + | [[2024 AMC 10A Problems/Problem 12|Solution]] | ||
==Problem 13== | ==Problem 13== | ||
| + | Two transformations are said to commute if applying the first followed by the second | ||
| + | gives the same result as applying the second followed by the first. Consider these | ||
| + | four transformations of the coordinate plane: | ||
| + | |||
| + | * a translation <math>2</math> units to the right, | ||
| + | |||
| + | * a <math>90^{\circ}</math>-rotation counterclockwise about the origin, | ||
| + | |||
| + | * a reflection across the <math>x</math>-axis, and | ||
| + | |||
| + | * a dilation centered at the origin with scale factor <math>2.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Of the <math>6</math> pairs of distinct transformations from this list, how many commute? | ||
| − | + | <math>\textbf{(A)}~1\qquad\textbf{(B)}~2\qquad\textbf{(C)}~3\qquad\textbf{(D)}~4\qquad\textbf{(E)}~5</math> | |
| − | + | [[2024 AMC 10A Problems/Problem 13|Solution]] | |
==Problem 14== | ==Problem 14== | ||
| − | The | + | One side of an equilateral triangle of height <math>24</math> lies on line <math>\ell</math>. A circle of radius <math>12</math> is tangent to line <math>\ell</math> and is externally tangent to the triangle. The area of the region exterior to the triangle and the circle and bounded by the triangle, the circle, and line <math>\ell</math> can be written as <math>a \sqrt{b} - c \pi</math>, where <math>a</math>, <math>b</math>, and <math>c</math> are positive integers and <math>b</math> is not divisible by the square of any prime. What is <math>a + b + c</math>? |
| + | |||
| + | <math>\textbf{(A)}~72\qquad\textbf{(B)}~73\qquad\textbf{(C)}~74\qquad\textbf{(D)}~75\qquad\textbf{(E)}~76</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[2024 AMC 10A Problems/Problem 14|Solution]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Problem 15== | ||
| − | <math> | + | Let <math>M</math> be the greatest integer such that both <math>M+1213</math> and <math>M+3773</math> are perfect squares. What is the units digit of <math>M</math>? |
| − | + | <math>\textbf{(A) }1\qquad\textbf{(B) }2\qquad\textbf{(C) }3\qquad\textbf{(D) }6\qquad\textbf{(E) }8</math> | |
| − | + | [[2024 AMC 10A Problems/Problem 15|Solution]] | |
==Problem 16== | ==Problem 16== | ||
| − | All the | + | All of the rectangles in the figure below, which is drawn to scale, are similar to the enclosing rectangle. Each number represents the area of the rectangle. What is length <math>AB</math>? <math>\newline</math> |
| + | [[File:Screenshot 2024-11-08 2.08.49 PM.png]] | ||
| + | <math>\textbf{(A) }4+4\sqrt5\qquad\textbf{(B) }10\sqrt2\qquad\textbf{(C) }5+5\sqrt5\qquad\textbf{(D) }10\sqrt[4]{8}\qquad\textbf{(E) }20</math> | ||
| − | + | [[2024 AMC 10A Problems/Problem 16|Solution]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Problem 17== | ==Problem 17== | ||
| − | |||
| − | <math>\ | + | Two teams are in a best-two-out-of-three playoff: the teams will play at most <math>3</math> games, and the winner of the playoff is the first team to win <math>2</math> games. The first game is played on Team A's home field, and the remaining games are played on Team B's home field. Team A has a <math>\frac{2}{3}</math> chance of winning at home, and its probability of winning when playing away from home is <math>p</math>. Outcomes of the games are independent. The probability that Team A wins the playoff is <math>\frac{1}{2}</math>. Then <math>p</math> can be written in the form <math>\frac{1}{2}(m - \sqrt{n})</math>, where <math>m</math> and <math>n</math> are positive integers. What is <math>m+n</math>? |
| + | |||
| + | <math>\textbf{(A)}~10\qquad\textbf{(B)}~11\qquad\textbf{(C)}~12\qquad\textbf{(D)}~13\qquad\textbf{(E)}~14</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[2024 AMC 10A Problems/Problem 17|Solution]] | ||
==Problem 18== | ==Problem 18== | ||
| − | + | There are exactly <math>K</math> positive integers <math>5 \leq b \leq 2024</math> such that the base-<math>b</math> integer <math>2024_{b}</math> is divisible by <math>16</math>(where <math>16</math> is in base ten). What is the sum of the digits of <math>K</math>? | |
| + | |||
| + | <math>\textbf{(A)}~16\qquad\textbf{(B)}~17\qquad\textbf{(C)}~18\qquad\textbf{(D)}~20\qquad\textbf{(E)}~21</math> | ||
| − | + | [[2024 AMC 10A Problems/Problem 18|Solution]] | |
| − | [[ | ||
==Problem 19== | ==Problem 19== | ||
| − | + | The first three terms of a geometric sequence are the integers <math>a, 720</math> and <math>b</math>, where <math>a < 720 < b</math>. What is the sum of the digits of the least possible value of <math>b</math>? | |
| + | |||
| + | <math>\textbf{(A) } 9\qquad\textbf{(B) } 12\qquad\textbf{(C) } 16\qquad\textbf{(D) } 18\qquad\textbf{(E) } 21</math> | ||
| − | + | [[2024 AMC 10A Problems/Problem 19|Solution]] | |
==Problem 20== | ==Problem 20== | ||
| − | |||
| − | <math>\textbf{(A) } | + | Let <math>S</math> be a subset of <math>\{1, 2, 3, \dots, 2024\}</math> such that the following two conditions hold: |
| + | |||
| + | *If <math>x</math> and <math>y</math> are distinct elements of <math>S</math>, then <math>|x-y| > 2.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | *If <math>x</math> and <math>y</math> are distinct odd elements of <math>S</math>, then <math>|x-y| > 6.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | What is the maximum possible number of elements in <math>S</math>? | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\textbf{(A) }436 \qquad \textbf{(B) }506 \qquad \textbf{(C) }608 \qquad \textbf{(D) }654 \qquad \textbf{(E) }675</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[2024 AMC 10A Problems/Problem 20|Solution]] | ||
==Problem 21== | ==Problem 21== | ||
| − | + | The numbers, in order, of each row and the numbers, in order, of each column of a <math>5 \times 5</math> array of integers form an arithmetic progression of length <math>5</math>. The numbers in positions <math>(5, 5)</math>, <math>(2, 4)</math>, <math>(4, 3)</math> and <math>(3, 1)</math> are <math>0</math>, <math>48</math>, <math>16</math>, and <math>12</math>, respectively. What number is in position <math>(1, 2)</math>? | |
| + | <cmath> \begin{bmatrix} . & ? &.&.&. \ .&.&.&48&.\ 12&.&.&.&.\ .&.&16&.&.\ .&.&.&.&0\end{bmatrix}</cmath> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\textbf{(A)}~19\qquad\textbf{(B)}~24\qquad\textbf{(C)}~29\qquad\textbf{(D)}~34\qquad\textbf{(E)}~39</math> | ||
| − | + | [[2024 AMC 10A Problems/Problem 21|Solution]] | |
==Problem 22== | ==Problem 22== | ||
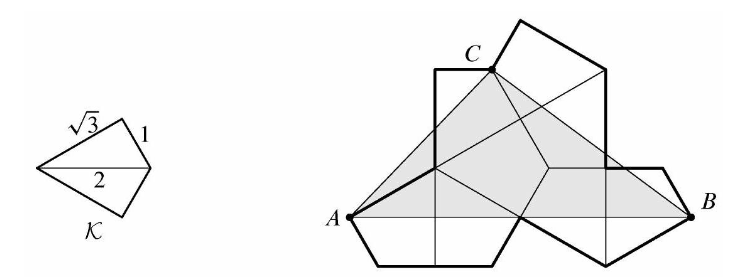
| − | |||
| − | <math>\textbf{(A) } | + | Let <math>\mathcal K</math> be the kite formed by joining two right triangles with legs <math>1</math> and <math>\sqrt3</math> along a common hypotenuse. Eight copies of <math>\mathcal K</math> are used to form the polygon shown below. What is the area of triangle <math>\Delta ABC</math>? [[File:Screenshot_2024-11-08_3.23.29_PM.png]] |
| + | |||
| + | <math>\textbf{(A) }2+3\sqrt3\qquad\textbf{(B) }\dfrac92\sqrt3\qquad\textbf{(C) }\dfrac{10+8\sqrt3}{3}\qquad\textbf{(D) }8\qquad\textbf{(E) }5\sqrt3</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[2024 AMC 10A Problems/Problem 22|Solution]] | ||
==Problem 23== | ==Problem 23== | ||
| − | |||
| − | <math>\textbf{(A)} | + | Integers <math>a</math>, <math>b</math>, and <math>c</math> satisfy <math>ab + c = 100</math>, <math>bc + a = 87</math>, and <math>ca + b = 60</math>. What is <math>ab + bc + ca?</math> |
| + | |||
| + | <math> | ||
| + | \textbf{(A) }212 \qquad | ||
| + | \textbf{(B) }247 \qquad | ||
| + | \textbf{(C) }258 \qquad | ||
| + | \textbf{(D) }276 \qquad | ||
| + | \textbf{(E) }284 \qquad | ||
| + | </math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[2024 AMC 10A Problems/Problem 23|Solution]] | ||
==Problem 24== | ==Problem 24== | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | A bee is moving in three-dimensional space. A fair six-sided die with faces labeled <math>A^+, A^-, B^+, B^-, C^+,</math> and <math>C^-</math> is rolled. Suppose the bee occupies the point <math>(a,b,c).</math> If the die shows <math>A^+</math>, then the bee moves to the point <math>(a+1,b,c)</math> and if the die shows <math>A^-,</math> then the bee moves to the point <math>(a-1,b,c).</math> Analogous moves are made with the other four outcomes. Suppose the bee starts at the point <math>(0,0,0)</math> and the die is rolled four times. What is the probability that the bee traverses four distinct edges of some unit cube? | |
| + | |||
| + | <math>\textbf{(A) }\frac{1}{54}\qquad\textbf{(B) }\frac{7}{54}\qquad\textbf{(C) }\frac{1}{6}\qquad\textbf{(D) }\frac{5}{18}\qquad\textbf{(E) }\frac{2}{5}</math> | ||
| − | + | [[2024 AMC 10A Problems/Problem 24|Solution]] | |
==Problem 25== | ==Problem 25== | ||
| − | + | The figure below shows a dotted grid <math>8</math> cells wide and <math>3</math> cells tall consisting of <math>1''\times1''</math> squares. Carl places <math>1</math>-inch toothpicks along some of the sides of the squares to create a closed loop that does not intersect itself. The numbers in the cells indicate the number of sides of that square that are to be covered by toothpicks, and any number of toothpicks are allowed if no number is written. In how many ways can Carl place the toothpicks? | |
| + | <asy> | ||
| + | size(6cm); | ||
| + | for (int i=0; i<9; ++i) { | ||
| + | draw((i,0)--(i,3),dotted); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | for (int i=0; i<4; ++i){ | ||
| + | draw((0,i)--(8,i),dotted); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | for (int i=0; i<8; ++i) { | ||
| + | for (int j=0; j<3; ++j) { | ||
| + | if (j==1) { | ||
| + | label("1",(i+0.5,1.5)); | ||
| + | }}} | ||
| + | </asy> | ||
| + | <math>\textbf{(A) }130\qquad\textbf{(B) }144\qquad\textbf{(C) }146\qquad\textbf{(D) }162\qquad\textbf{(E) }196</math> | ||
| − | + | [[2024 AMC 10A Problems/Problem 25|Solution]] | |
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
| Line 190: | Line 247: | ||
* [[Mathematics competitions]] | * [[Mathematics competitions]] | ||
* [[Mathematics competition resources]] | * [[Mathematics competition resources]] | ||
| − | |||
Revision as of 05:53, 14 December 2024
| 2024 AMC 10A (Answer Key) Printable versions: • AoPS Resources • PDF | ||
|
Instructions
| ||
| 1 • 2 • 3 • 4 • 5 • 6 • 7 • 8 • 9 • 10 • 11 • 12 • 13 • 14 • 15 • 16 • 17 • 18 • 19 • 20 • 21 • 22 • 23 • 24 • 25 | ||
Contents
[hide]- 1 Problem 1
- 2 Problem 2
- 3 Problem 3
- 4 Problem 4
- 5 Problem 5
- 6 Problem 6
- 7 Problem 7
- 8 Problem 8
- 9 Problem 9
- 10 Problem 10
- 11 Problem 11
- 12 Problem 12
- 13 Problem 13
- 14 Problem 14
- 15 Problem 15
- 16 Problem 16
- 17 Problem 17
- 18 Problem 18
- 19 Problem 19
- 20 Problem 20
- 21 Problem 21
- 22 Problem 22
- 23 Problem 23
- 24 Problem 24
- 25 Problem 25
- 26 See also
Problem 1
What is the value of ![]()
![]()
Problem 2
A model used to estimate the time it will take to hike to the top of the mountain on a trail is of the form ![]() where
where ![]() and
and ![]() are constants,
are constants, ![]() is the time in minutes,
is the time in minutes, ![]() is the length of the trail in miles, and
is the length of the trail in miles, and ![]() is the altitude gain in feet. The model estimates that it will take
is the altitude gain in feet. The model estimates that it will take ![]() minutes to hike to the top if a trail is
minutes to hike to the top if a trail is ![]() miles long and ascends
miles long and ascends ![]() feet, as well as if a trail is
feet, as well as if a trail is ![]() miles long and ascends
miles long and ascends ![]() feet. How many minutes does the model estimates it will take to hike to the top if the trail is
feet. How many minutes does the model estimates it will take to hike to the top if the trail is ![]() miles long and ascends
miles long and ascends ![]() feet?
feet?
![]()
Problem 3
What is the sum of the digits of the smallest prime that can be written as a sum of ![]() distinct primes?
distinct primes?
![]()
Problem 4
The number ![]() is written as the sum of not necessarily distinct two-digit numbers. What is the least number of two-digit numbers needed to write this sum?
is written as the sum of not necessarily distinct two-digit numbers. What is the least number of two-digit numbers needed to write this sum?
![]()
Problem 5
What is the least value of ![]() such that
such that ![]() is a multiple of
is a multiple of ![]() ?
?
![]()
Problem 6
What is the minimum number of successive swaps of adjacent letters in the string ![]() that are needed to change the string to
that are needed to change the string to ![]() (For example,
(For example, ![]() swaps are required to change
swaps are required to change ![]() to
to ![]() one such sequence of swaps is
one such sequence of swaps is
![]() )
)
![]()
Problem 7
The product of three integers is ![]() . What is the least possible positive sum of the
three integers?
. What is the least possible positive sum of the
three integers?
![]()
Problem 8
Amy, Bomani, Charlie, and Daria work in a chocolate factory. On Monday Amy, Bomani, and Charlie started working at ![]() and were able to pack
and were able to pack ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() packages, respectively, every
packages, respectively, every ![]() minutes. At some later time, Daria joined the group, and Daria was able to pack
minutes. At some later time, Daria joined the group, and Daria was able to pack ![]() packages every
packages every ![]() minutes. Together, they finished packing
minutes. Together, they finished packing ![]() packages at exactly
packages at exactly ![]() . At what time did Daria join the group?
. At what time did Daria join the group?
![]()
Problem 9
In how many ways can ![]() juniors and
juniors and ![]() seniors form
seniors form ![]() disjoint teams of
disjoint teams of ![]() people so
that each team has
people so
that each team has ![]() juniors and
juniors and ![]() seniors?
seniors?
![]()
Problem 10
Consider the following operation. Given a positive integer ![]() , if
, if ![]() is a multiple of
is a multiple of ![]() , then you replace
, then you replace ![]() by
by ![]() . If
. If ![]() is not a multiple of
is not a multiple of ![]() , then you replace
, then you replace ![]() by
by ![]() . For example, beginning with
. For example, beginning with ![]() , this procedure gives
, this procedure gives ![]() . Suppose you start with
. Suppose you start with ![]() . What value results if you perform this operation exactly
. What value results if you perform this operation exactly ![]() times?
times?
![]()
Problem 11
How many ordered pairs of integers ![]() satisfy
satisfy ![]() ?
?
![]() Infinitely many
Infinitely many
Problem 12
Zelda played the Adventures of Math game on August 1 and scored ![]() points. She continued to play daily over the next
points. She continued to play daily over the next ![]() days. The bar chart below shows the daily change in her score compared to the day before. (For example, Zelda's score on August 2 was
days. The bar chart below shows the daily change in her score compared to the day before. (For example, Zelda's score on August 2 was ![]() points.) What was Zelda's average score in points over the
points.) What was Zelda's average score in points over the ![]() days?
days?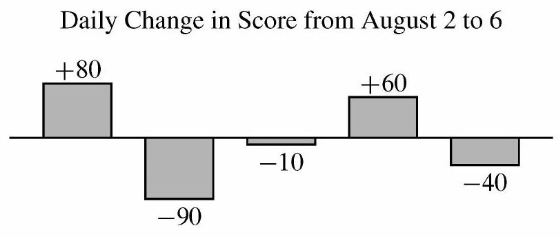
![]()
Problem 13
Two transformations are said to commute if applying the first followed by the second gives the same result as applying the second followed by the first. Consider these four transformations of the coordinate plane:
- a translation
 units to the right,
units to the right,
- a
 -rotation counterclockwise about the origin,
-rotation counterclockwise about the origin,
- a reflection across the
 -axis, and
-axis, and
- a dilation centered at the origin with scale factor

Of the ![]() pairs of distinct transformations from this list, how many commute?
pairs of distinct transformations from this list, how many commute?
![]()
Problem 14
One side of an equilateral triangle of height ![]() lies on line
lies on line ![]() . A circle of radius
. A circle of radius ![]() is tangent to line
is tangent to line ![]() and is externally tangent to the triangle. The area of the region exterior to the triangle and the circle and bounded by the triangle, the circle, and line
and is externally tangent to the triangle. The area of the region exterior to the triangle and the circle and bounded by the triangle, the circle, and line ![]() can be written as
can be written as ![]() , where
, where ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() are positive integers and
are positive integers and ![]() is not divisible by the square of any prime. What is
is not divisible by the square of any prime. What is ![]() ?
?
![]()
Problem 15
Let ![]() be the greatest integer such that both
be the greatest integer such that both ![]() and
and ![]() are perfect squares. What is the units digit of
are perfect squares. What is the units digit of ![]() ?
?
![]()
Problem 16
All of the rectangles in the figure below, which is drawn to scale, are similar to the enclosing rectangle. Each number represents the area of the rectangle. What is length ![]() ?
? ![]()

![]()
Problem 17
Two teams are in a best-two-out-of-three playoff: the teams will play at most ![]() games, and the winner of the playoff is the first team to win
games, and the winner of the playoff is the first team to win ![]() games. The first game is played on Team A's home field, and the remaining games are played on Team B's home field. Team A has a
games. The first game is played on Team A's home field, and the remaining games are played on Team B's home field. Team A has a ![]() chance of winning at home, and its probability of winning when playing away from home is
chance of winning at home, and its probability of winning when playing away from home is ![]() . Outcomes of the games are independent. The probability that Team A wins the playoff is
. Outcomes of the games are independent. The probability that Team A wins the playoff is ![]() . Then
. Then ![]() can be written in the form
can be written in the form ![]() , where
, where ![]() and
and ![]() are positive integers. What is
are positive integers. What is ![]() ?
?
![]()
Problem 18
There are exactly ![]() positive integers
positive integers ![]() such that the base-
such that the base-![]() integer
integer ![]() is divisible by
is divisible by ![]() (where
(where ![]() is in base ten). What is the sum of the digits of
is in base ten). What is the sum of the digits of ![]() ?
?
![]()
Problem 19
The first three terms of a geometric sequence are the integers ![]() and
and ![]() , where
, where ![]() . What is the sum of the digits of the least possible value of
. What is the sum of the digits of the least possible value of ![]() ?
?
![]()
Problem 20
Let ![]() be a subset of
be a subset of ![]() such that the following two conditions hold:
such that the following two conditions hold:
- If
 and
and  are distinct elements of
are distinct elements of  , then
, then 
- If
 and
and  are distinct odd elements of
are distinct odd elements of  , then
, then 
What is the maximum possible number of elements in ![]() ?
?
![]()
Problem 21
The numbers, in order, of each row and the numbers, in order, of each column of a ![]() array of integers form an arithmetic progression of length
array of integers form an arithmetic progression of length ![]() . The numbers in positions
. The numbers in positions ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() and
and ![]() are
are ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() , respectively. What number is in position
, respectively. What number is in position ![]() ?
?
![\[\begin{bmatrix} . & ? &.&.&. \\ .&.&.&48&.\\ 12&.&.&.&.\\ .&.&16&.&.\\ .&.&.&.&0\end{bmatrix}\]](http://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/2/c/a/2caa51c2881f478a1e28bf45df93c383dff268f6.png)
![]()
Problem 22
Let ![]() be the kite formed by joining two right triangles with legs
be the kite formed by joining two right triangles with legs ![]() and
and ![]() along a common hypotenuse. Eight copies of
along a common hypotenuse. Eight copies of ![]() are used to form the polygon shown below. What is the area of triangle
are used to form the polygon shown below. What is the area of triangle ![]() ?
? 
![]()
Problem 23
Integers ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() satisfy
satisfy ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() . What is
. What is ![]()
![]()
Problem 24
A bee is moving in three-dimensional space. A fair six-sided die with faces labeled ![]() and
and ![]() is rolled. Suppose the bee occupies the point
is rolled. Suppose the bee occupies the point ![]() If the die shows
If the die shows ![]() , then the bee moves to the point
, then the bee moves to the point ![]() and if the die shows
and if the die shows ![]() then the bee moves to the point
then the bee moves to the point ![]() Analogous moves are made with the other four outcomes. Suppose the bee starts at the point
Analogous moves are made with the other four outcomes. Suppose the bee starts at the point ![]() and the die is rolled four times. What is the probability that the bee traverses four distinct edges of some unit cube?
and the die is rolled four times. What is the probability that the bee traverses four distinct edges of some unit cube?
![]()
Problem 25
The figure below shows a dotted grid ![]() cells wide and
cells wide and ![]() cells tall consisting of
cells tall consisting of ![]() squares. Carl places
squares. Carl places ![]() -inch toothpicks along some of the sides of the squares to create a closed loop that does not intersect itself. The numbers in the cells indicate the number of sides of that square that are to be covered by toothpicks, and any number of toothpicks are allowed if no number is written. In how many ways can Carl place the toothpicks?
-inch toothpicks along some of the sides of the squares to create a closed loop that does not intersect itself. The numbers in the cells indicate the number of sides of that square that are to be covered by toothpicks, and any number of toothpicks are allowed if no number is written. In how many ways can Carl place the toothpicks?
![[asy] size(6cm); for (int i=0; i<9; ++i) { draw((i,0)--(i,3),dotted); } for (int i=0; i<4; ++i){ draw((0,i)--(8,i),dotted); } for (int i=0; i<8; ++i) { for (int j=0; j<3; ++j) { if (j==1) { label("1",(i+0.5,1.5)); }}} [/asy]](http://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/9/d/1/9d176dfd41e3e8e875c6b5d84fdb4f5e4f7d43a6.png)
![]()
See also
| 2024 AMC 10A (Problems • Answer Key • Resources) | ||
| Preceded by 2023 AMC 10B Problems |
Followed by 2024 AMC 10B Problems | |
| 1 • 2 • 3 • 4 • 5 • 6 • 7 • 8 • 9 • 10 • 11 • 12 • 13 • 14 • 15 • 16 • 17 • 18 • 19 • 20 • 21 • 22 • 23 • 24 • 25 | ||
| All AMC 10 Problems and Solutions | ||









