Difference between revisions of "2007 AMC 12A Problems/Problem 10"
(→Solution 2) |
(→Solution 3 (dimensional analysis)) |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
~mobius247 | ~mobius247 | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Solution 3 (dimensional analysis)== | ||
| + | Using the theorem that the hypotenuse of a right triangle inscribed in a circle is the diameter, one can determine that the diameter of the triangle is 6. As a result the ratio between the triangular ratios and their real values is (6/5). Using dimensional analysis, one can see that because the ratio between lengths is (6/5), the ratio between areas is (6/5)^2. This gives ((3 * 4)(6/5)^2)/2 as the area of the triangle or answer choice (A). | ||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
Latest revision as of 03:49, 1 July 2024
- The following problem is from both the 2007 AMC 12A #10 and 2007 AMC 10A #14, so both problems redirect to this page.
Problem
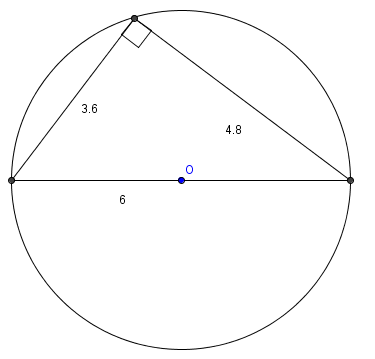
A triangle with side lengths in the ratio ![]() is inscribed in a circle with radius 3. What is the area of the triangle?
is inscribed in a circle with radius 3. What is the area of the triangle?
![]()
Solution
Since 3-4-5 is a Pythagorean triple, the triangle is a right triangle. Since the hypotenuse is a diameter of the circumcircle, the hypotenuse is ![]() . Then the other legs are
. Then the other legs are ![]() and
and ![]() . The area is
. The area is ![]()
Solution 2
The hypotenuse of the triangle is a diameter of the circumcircle, so it has length ![]() . The triangle is similar to a 3-4-5 triangle with the ratio of their side lengths equal to
. The triangle is similar to a 3-4-5 triangle with the ratio of their side lengths equal to ![]() . The area of a 3-4-5 triangle is
. The area of a 3-4-5 triangle is ![]() .
The square of the ratio of their side lengths is equal to the ratio of their areas. Call the area of the triangle
.
The square of the ratio of their side lengths is equal to the ratio of their areas. Call the area of the triangle ![]() . Therefore,
. Therefore, ![]()
~mobius247
Solution 3 (dimensional analysis)
Using the theorem that the hypotenuse of a right triangle inscribed in a circle is the diameter, one can determine that the diameter of the triangle is 6. As a result the ratio between the triangular ratios and their real values is (6/5). Using dimensional analysis, one can see that because the ratio between lengths is (6/5), the ratio between areas is (6/5)^2. This gives ((3 * 4)(6/5)^2)/2 as the area of the triangle or answer choice (A).
See also
| 2007 AMC 12A (Problems • Answer Key • Resources) | |
| Preceded by Problem 9 |
Followed by Problem 11 |
| 1 • 2 • 3 • 4 • 5 • 6 • 7 • 8 • 9 • 10 • 11 • 12 • 13 • 14 • 15 • 16 • 17 • 18 • 19 • 20 • 21 • 22 • 23 • 24 • 25 | |
| All AMC 12 Problems and Solutions | |
| 2007 AMC 10A (Problems • Answer Key • Resources) | ||
| Preceded by Problem 13 |
Followed by Problem 15 | |
| 1 • 2 • 3 • 4 • 5 • 6 • 7 • 8 • 9 • 10 • 11 • 12 • 13 • 14 • 15 • 16 • 17 • 18 • 19 • 20 • 21 • 22 • 23 • 24 • 25 | ||
| All AMC 10 Problems and Solutions | ||
The problems on this page are copyrighted by the Mathematical Association of America's American Mathematics Competitions.