Difference between revisions of "2010 AMC 12A Problems/Problem 8"
(→Solution 2) |
(Tag: Undo) |
||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
Since <math>\frac{AC}{AB} = \frac{1}{2}</math>, triangle <math>ABC</math> is a <math>30-60-90</math> triangle, so <math>\angle BCA = \boxed{90^\circ\,\textbf{(C)}}</math>. | Since <math>\frac{AC}{AB} = \frac{1}{2}</math>, triangle <math>ABC</math> is a <math>30-60-90</math> triangle, so <math>\angle BCA = \boxed{90^\circ\,\textbf{(C)}}</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Solution 2 == | ||
| + | |||
| + | Applying the Law of Sines on <math>\bigtriangleup ABC</math>, we have | ||
| + | <cmath>\frac{\sin{\angle ABC}}{AC}=\frac{\sin{\angle ACB}}{AB}</cmath> | ||
| + | Since | ||
== See also == | == See also == | ||
Revision as of 13:20, 17 November 2019
Contents
Problem
Triangle ![]() has
has ![]() . Let
. Let ![]() and
and ![]() be on
be on ![]() and
and ![]() , respectively, such that
, respectively, such that ![]() . Let
. Let ![]() be the intersection of segments
be the intersection of segments ![]() and
and ![]() , and suppose that
, and suppose that ![]() is equilateral. What is
is equilateral. What is ![]() ?
?
![]()
Solution
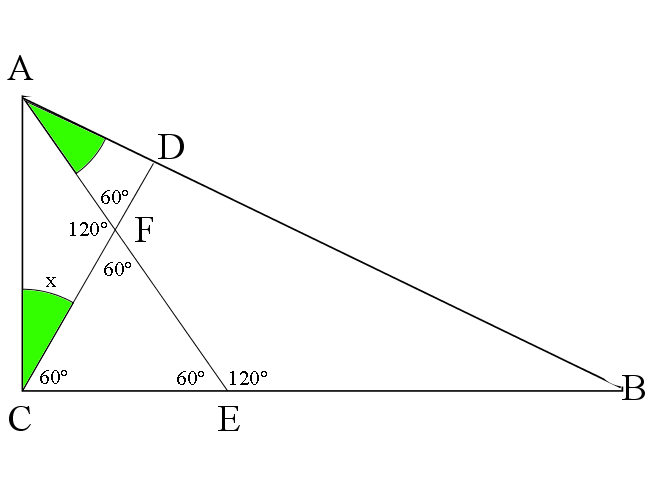
Let ![]() .
.

Since ![]() , triangle
, triangle ![]() is a
is a ![]() triangle, so
triangle, so ![]() .
.
Solution 2
Applying the Law of Sines on ![]() , we have
, we have
![]() Since
Since
See also
| 2010 AMC 12A (Problems • Answer Key • Resources) | |
| Preceded by Problem 7 |
Followed by Problem 9 |
| 1 • 2 • 3 • 4 • 5 • 6 • 7 • 8 • 9 • 10 • 11 • 12 • 13 • 14 • 15 • 16 • 17 • 18 • 19 • 20 • 21 • 22 • 23 • 24 • 25 | |
| All AMC 12 Problems and Solutions | |
The problems on this page are copyrighted by the Mathematical Association of America's American Mathematics Competitions. 









