Difference between revisions of "1999 AIME Problems/Problem 6"
Danielguo94 (talk | contribs) (→Solution) |
Danielguo94 (talk | contribs) (→Solution) |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
== Solution == | == Solution == | ||
| − | <cmath>\begin{eqnarray*}A' = | + | <cmath>\begin{eqnarray*}A' = & (\sqrt {900}, \sqrt {300})\ |
| − | B' = | + | B' = & (\sqrt {1800}, \sqrt {600})\ |
| − | C' = | + | C' = & (\sqrt {600}, \sqrt {1800})\ |
| − | D' = | + | D' = & (\sqrt {300}, \sqrt {900}) \end{eqnarray*}</cmath> |
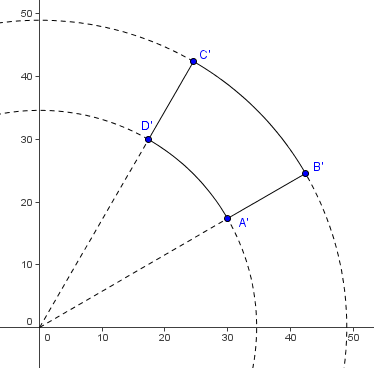
First we see that lines passing through <math>AB</math> and <math>CD</math> have [[equation]]s <math>y = \frac {1}{3}x</math> and <math>y = 3x</math>, respectively. Looking at the points above, we see the equations for <math>A'B'</math> and <math>C'D'</math> are <math>y^2 = \frac {1}{3}x^2</math> and <math>y^2 = 3x^2</math>, or, after manipulation <math>y = \frac {x}{\sqrt {3}}</math> and <math>y = \sqrt {3}x</math>, respectively, which are still linear functions. Basically the square of the image points gives back the original points and we could plug them back into the original equation to get the equation of the image lines. | First we see that lines passing through <math>AB</math> and <math>CD</math> have [[equation]]s <math>y = \frac {1}{3}x</math> and <math>y = 3x</math>, respectively. Looking at the points above, we see the equations for <math>A'B'</math> and <math>C'D'</math> are <math>y^2 = \frac {1}{3}x^2</math> and <math>y^2 = 3x^2</math>, or, after manipulation <math>y = \frac {x}{\sqrt {3}}</math> and <math>y = \sqrt {3}x</math>, respectively, which are still linear functions. Basically the square of the image points gives back the original points and we could plug them back into the original equation to get the equation of the image lines. | ||
Revision as of 22:32, 24 March 2011
Problem
A transformation of the first quadrant of the coordinate plane maps each point ![]() to the point
to the point ![]() The vertices of quadrilateral
The vertices of quadrilateral ![]() are
are ![]() and
and ![]() Let
Let ![]() be the area of the region enclosed by the image of quadrilateral
be the area of the region enclosed by the image of quadrilateral ![]() Find the greatest integer that does not exceed
Find the greatest integer that does not exceed ![]()
Solution

First we see that lines passing through ![]() and
and ![]() have equations
have equations ![]() and
and ![]() , respectively. Looking at the points above, we see the equations for
, respectively. Looking at the points above, we see the equations for ![]() and
and ![]() are
are ![]() and
and ![]() , or, after manipulation
, or, after manipulation ![]() and
and ![]() , respectively, which are still linear functions. Basically the square of the image points gives back the original points and we could plug them back into the original equation to get the equation of the image lines.
, respectively, which are still linear functions. Basically the square of the image points gives back the original points and we could plug them back into the original equation to get the equation of the image lines.
Now take a look at ![]() and
and ![]() , which have the equations
, which have the equations ![]() and
and ![]() . The image equations hence are
. The image equations hence are ![]() and
and ![]() , respectively, which are the equations for circles.
, respectively, which are the equations for circles.
To find the area between the circles (actually, parts of the circles), we need to figure out the angle of the arc. This could be done by ![]() . So the requested areas are the area of the enclosed part of the smaller circle subtracted from the area enclosed by the part of the larger circle =
. So the requested areas are the area of the enclosed part of the smaller circle subtracted from the area enclosed by the part of the larger circle = ![]() . Hence the answer is
. Hence the answer is ![]() .
.
See also
| 1999 AIME (Problems • Answer Key • Resources) | ||
| Preceded by Problem 5 |
Followed by Problem 7 | |
| 1 • 2 • 3 • 4 • 5 • 6 • 7 • 8 • 9 • 10 • 11 • 12 • 13 • 14 • 15 | ||
| All AIME Problems and Solutions | ||